Capturing the diversity of multilingual societies
Paper and Code
May 12, 2021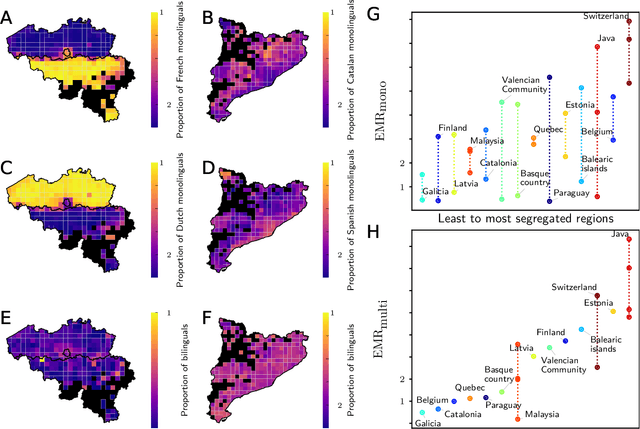
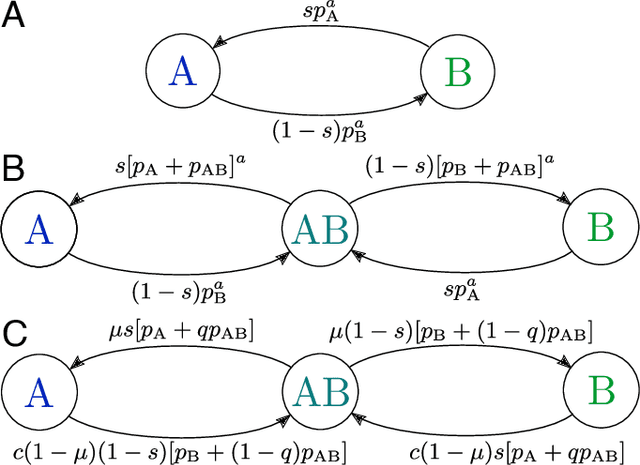
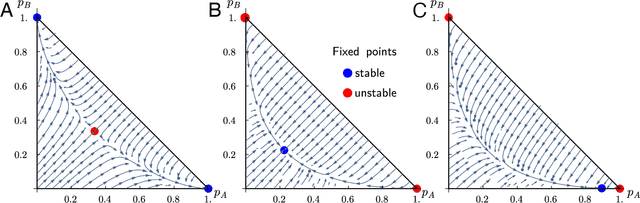
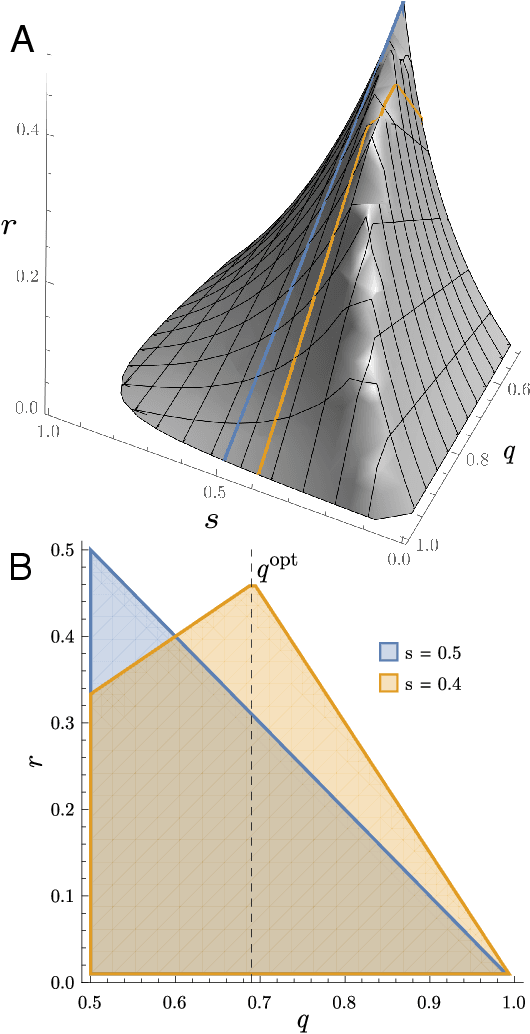
Cultural diversity encoded within languages of the world is at risk, as many languages have become endangered in the last decades in a context of growing globalization. To preserve this diversity, it is first necessary to understand what drives language extinction, and which mechanisms might enable coexistence. Here, we consider the processes at work in language shift through a conjunction of theoretical and data-driven perspectives. A large-scale empirical study of spatial patterns of languages in multilingual societies using Twitter and census data yields a wide diversity. It ranges from an almost complete mixing of language speakers, including multilinguals, to segregation with a neat separation of the linguistic domains and with multilinguals mainly at their boundaries. To understand how these different states can emerge and, especially, become stable, we propose a model in which coexistence of languages may be reached when learning the other language is facilitated and when bilinguals favor the use of the endangered language. Simulations carried out in a metapopulation framework highlight the importance of spatial interactions arising from people mobility to explain the stability of a mixed state or the presence of a boundary between two linguistic regions. Changes in the parameters regulating the relation between the languages can destabilize a system, which undergoes global transitions. According to our model, the evolution of the system once it undergoes a transition is highly history-dependent. It is easy to change the status quo but going back to a previous state may not be simple or even possible.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge