Behnam Bahrak
University of Tehran
MasalBench: A Benchmark for Contextual and Cross-Cultural Understanding of Persian Proverbs in LLMs
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:In recent years, multilingual Large Language Models (LLMs) have become an inseparable part of daily life, making it crucial for them to master the rules of conversational language in order to communicate effectively with users. While previous work has evaluated LLMs' understanding of figurative language in high-resource languages, their performance in low-resource languages remains underexplored. In this paper, we introduce MasalBench, a comprehensive benchmark for assessing LLMs' contextual and cross-cultural understanding of Persian proverbs, which are a key component of conversation in this low-resource language. We evaluate eight state-of-the-art LLMs on MasalBench and find that they perform well in identifying Persian proverbs in context, achieving accuracies above 0.90. However, their performance drops considerably when tasked with identifying equivalent English proverbs, with the best model achieving 0.79 accuracy. Our findings highlight the limitations of current LLMs in cultural knowledge and analogical reasoning, and they provide a framework for assessing cross-cultural understanding in other low-resource languages. MasalBench is available at https://github.com/kalhorghazal/MasalBench.
ArtCognition: A Multimodal AI Framework for Affective State Sensing from Visual and Kinematic Drawing Cues
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:The objective assessment of human affective and psychological states presents a significant challenge, particularly through non-verbal channels. This paper introduces digital drawing as a rich and underexplored modality for affective sensing. We present a novel multimodal framework, named ArtCognition, for the automated analysis of the House-Tree-Person (HTP) test, a widely used psychological instrument. ArtCognition uniquely fuses two distinct data streams: static visual features from the final artwork, captured by computer vision models, and dynamic behavioral kinematic cues derived from the drawing process itself, such as stroke speed, pauses, and smoothness. To bridge the gap between low-level features and high-level psychological interpretation, we employ a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) architecture. This grounds the analysis in established psychological knowledge, enhancing explainability and reducing the potential for model hallucination. Our results demonstrate that the fusion of visual and behavioral kinematic cues provides a more nuanced assessment than either modality alone. We show significant correlations between the extracted multimodal features and standardized psychological metrics, validating the framework's potential as a scalable tool to support clinicians. This work contributes a new methodology for non-intrusive affective state assessment and opens new avenues for technology-assisted mental healthcare.
A Large-Scale Analysis of Persian Tweets Regarding Covid-19 Vaccination
Feb 09, 2023Abstract:The Covid-19 pandemic had an enormous effect on our lives, especially on people's interactions. By introducing Covid-19 vaccines, both positive and negative opinions were raised over the subject of taking vaccines or not. In this paper, using data gathered from Twitter, including tweets and user profiles, we offer a comprehensive analysis of public opinion in Iran about the Coronavirus vaccines. For this purpose, we applied a search query technique combined with a topic modeling approach to extract vaccine-related tweets. We utilized transformer-based models to classify the content of the tweets and extract themes revolving around vaccination. We also conducted an emotion analysis to evaluate the public happiness and anger around this topic. Our results demonstrate that Covid-19 vaccination has attracted considerable attention from different angles, such as governmental issues, safety or hesitancy, and side effects. Moreover, Coronavirus-relevant phenomena like public vaccination and the rate of infection deeply impacted public emotional status and users' interactions.
Persian Emotion Detection using ParsBERT and Imbalanced Data Handling Approaches
Nov 17, 2022



Abstract:Emotion recognition is one of the machine learning applications which can be done using text, speech, or image data gathered from social media spaces. Detecting emotion can help us in different fields, including opinion mining. With the spread of social media, different platforms like Twitter have become data sources, and the language used in these platforms is informal, making the emotion detection task difficult. EmoPars and ArmanEmo are two new human-labeled emotion datasets for the Persian language. These datasets, especially EmoPars, are suffering from inequality between several samples between two classes. In this paper, we evaluate EmoPars and compare them with ArmanEmo. Throughout this analysis, we use data augmentation techniques, data re-sampling, and class-weights with Transformer-based Pretrained Language Models(PLMs) to handle the imbalance problem of these datasets. Moreover, feature selection is used to enhance the models' performance by emphasizing the text's specific features. In addition, we provide a new policy for selecting data from EmoPars, which selects the high-confidence samples; as a result, the model does not see samples that do not have specific emotion during training. Our model reaches a Macro-averaged F1-score of 0.81 and 0.76 on ArmanEmo and EmoPars, respectively, which are new state-of-the-art results in these benchmarks.
* 14 pages, 5 figures, 9 tables
UTNLP at SemEval-2022 Task 6: A Comparative Analysis of Sarcasm Detection using generative-based and mutation-based data augmentation
Apr 18, 2022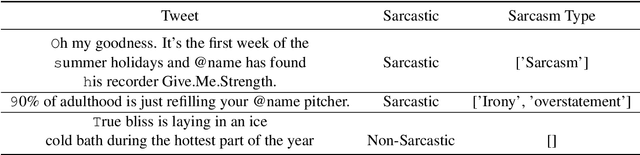
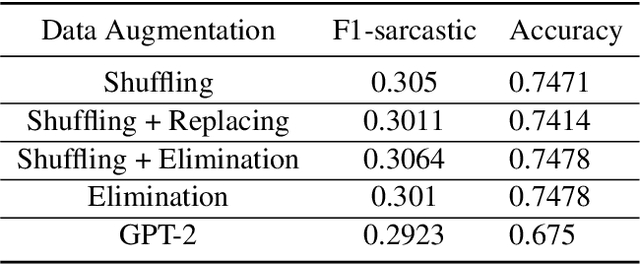
Abstract:Sarcasm is a term that refers to the use of words to mock, irritate, or amuse someone. It is commonly used on social media. The metaphorical and creative nature of sarcasm presents a significant difficulty for sentiment analysis systems based on affective computing. The methodology and results of our team, UTNLP, in the SemEval-2022 shared task 6 on sarcasm detection are presented in this paper. We put different models, and data augmentation approaches to the test and report on which one works best. The tests begin with traditional machine learning models and progress to transformer-based and attention-based models. We employed data augmentation based on data mutation and data generation. Using RoBERTa and mutation-based data augmentation, our best approach achieved an F1-sarcastic of 0.38 in the competition's evaluation phase. After the competition, we fixed our model's flaws and achieved an F1-sarcastic of 0.414.
UTNLP at SemEval-2021 Task 5: A Comparative Analysis of Toxic Span Detection using Attention-based, Named Entity Recognition, and Ensemble Models
Apr 10, 2021
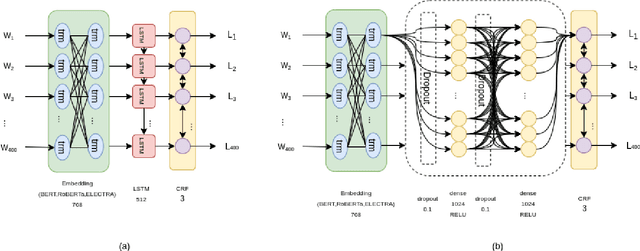
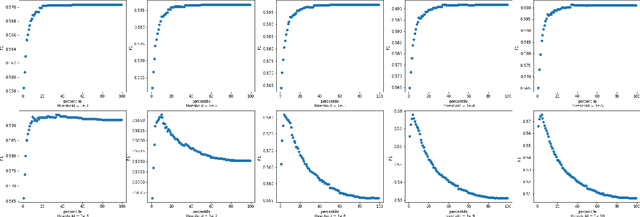
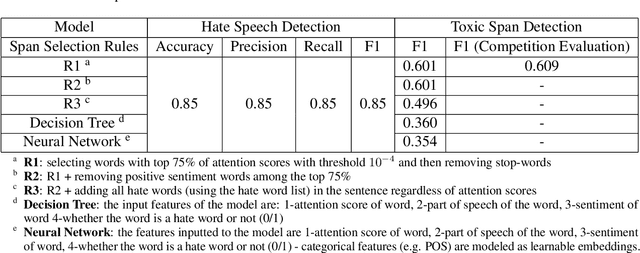
Abstract:Detecting which parts of a sentence contribute to that sentence's toxicity -- rather than providing a sentence-level verdict of hatefulness -- would increase the interpretability of models and allow human moderators to better understand the outputs of the system. This paper presents our team's, UTNLP, methodology and results in the SemEval-2021 shared task 5 on toxic spans detection. We test multiple models and contextual embeddings and report the best setting out of all. The experiments start with keyword-based models and are followed by attention-based, named entity-based, transformers-based, and ensemble models. Our best approach, an ensemble model, achieves an F1 of 0.684 in the competition's evaluation phase.
Sentiment Analysis of Persian-English Code-mixed Texts
Feb 25, 2021
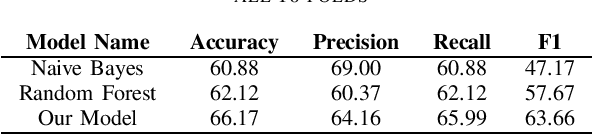
Abstract:The rapid production of data on the internet and the need to understand how users are feeling from a business and research perspective has prompted the creation of numerous automatic monolingual sentiment detection systems. More recently however, due to the unstructured nature of data on social media, we are observing more instances of multilingual and code-mixed texts. This development in content type has created a new demand for code-mixed sentiment analysis systems. In this study we collect, label and thus create a dataset of Persian-English code-mixed tweets. We then proceed to introduce a model which uses BERT pretrained embeddings as well as translation models to automatically learn the polarity scores of these Tweets. Our model outperforms the baseline models that use Na\"ive Bayes and Random Forest methods.
Hybrid Model for Anomaly Detection on Call Detail Records by Time Series Forecasting
Jun 07, 2020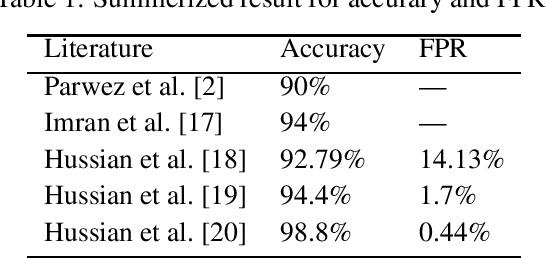
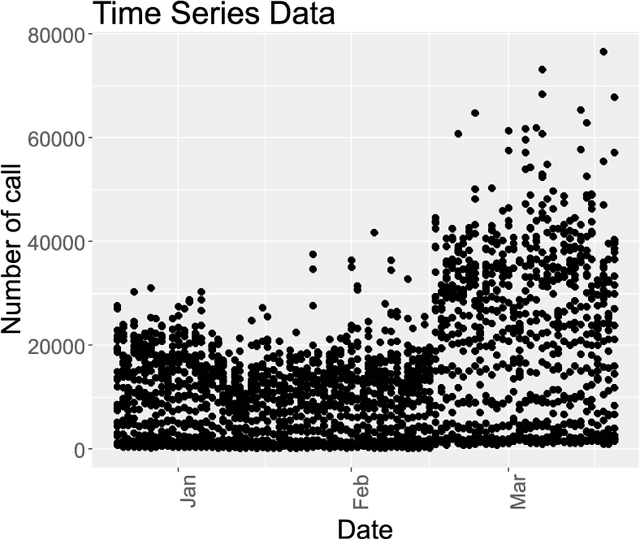
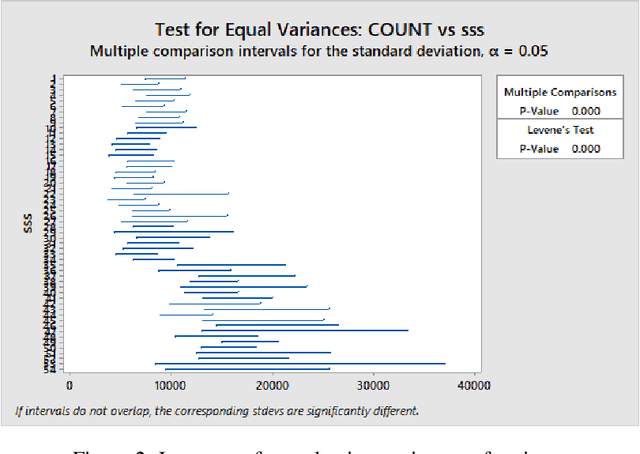
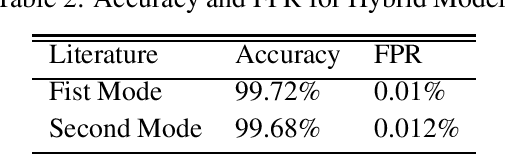
Abstract:Mobile network operators store an enormous amount of information like log files that describe various events and users' activities. Analysis of these logs might be used in many critical applications such as detecting cyber-attacks, finding behavioral patterns of users, security incident response, network forensics, etc. In a cellular network Call Detail Records (CDR) is one type of such logs containing metadata of calls and usually includes valuable information about contact such as the phone numbers of originating and receiving subscribers, call duration, the area of activity, type of call (SMS or voice call) and a timestamp. With anomaly detection, it is possible to determine abnormal reduction or increment of network traffic in an area or for a particular person. This paper's primary goal is to study subscribers' behavior in a cellular network, mainly predicting the number of calls in a region and detecting anomalies in the network traffic. In this paper, a new hybrid method is proposed based on various anomaly detection methods such as GARCH, K-means, and Neural Network to determine the anomalous data. Moreover, we have discussed the possible causes of such anomalies.
A Regression Framework for Predicting User's Next Location using Call Detail Records
Dec 22, 2019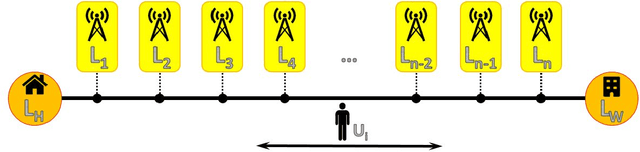
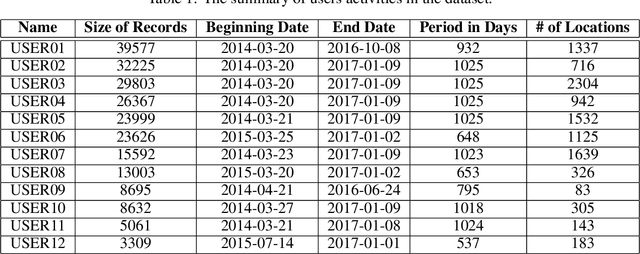
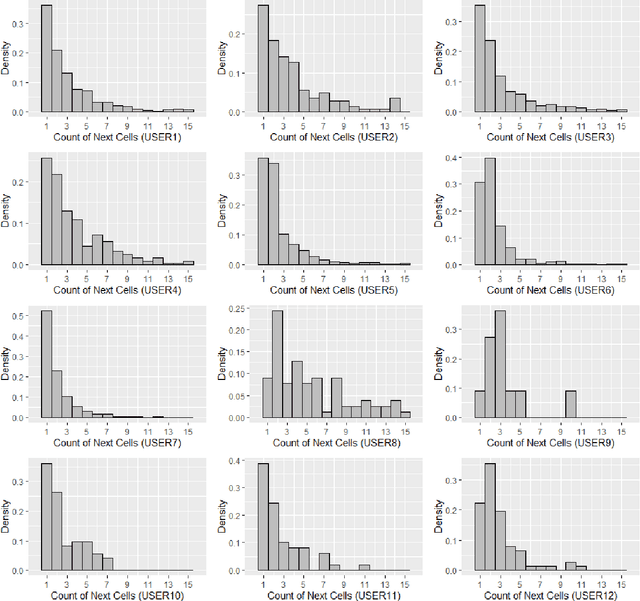
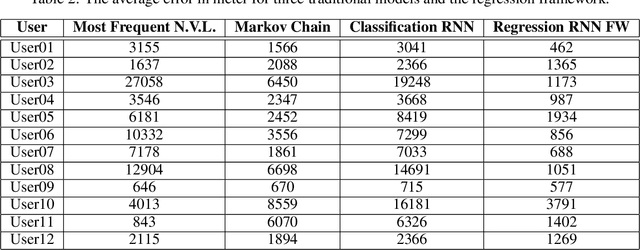
Abstract:With the growth of using cell phones and the increase in diversity of smart mobile devices, a massive volume of data is generated continuously in the process of using these devices. Among these data, Call Detail Records, CDR, is highly remarkable. Since CDR contains both temporal and spatial labels, mobility analysis of CDR is one of the favorite subjects of study among the researchers. The user next location prediction is one of the main problems in the field of human mobility analysis. In this paper, we propose a data processing framework to predict user next location. We propose domain-specific data processing strategies and design a deep neural network model which is based on recurrent neurons and perform regression tasks. Using this prediction framework, the error of the prediction decreases from 74% to 55% in comparison to the worst and best performing traditional models. Methods, strategies, the framework and the results of this paper can be helpful in many applications such as urban planning and digital marketing.
Real-time Travel Time Estimation Using Matrix Factorization
Dec 01, 2019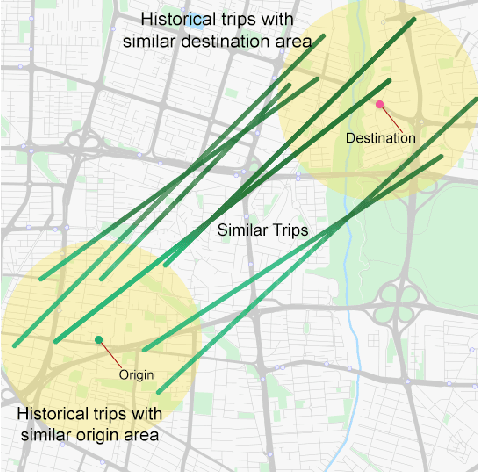
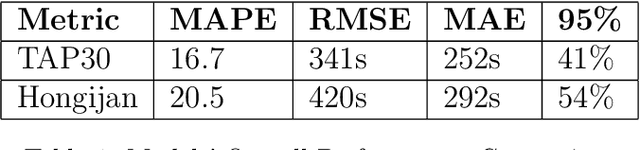
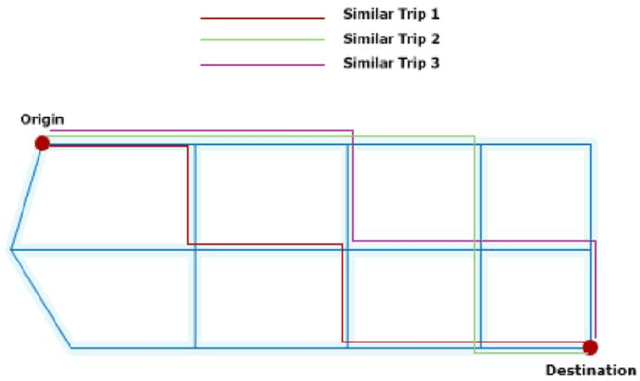
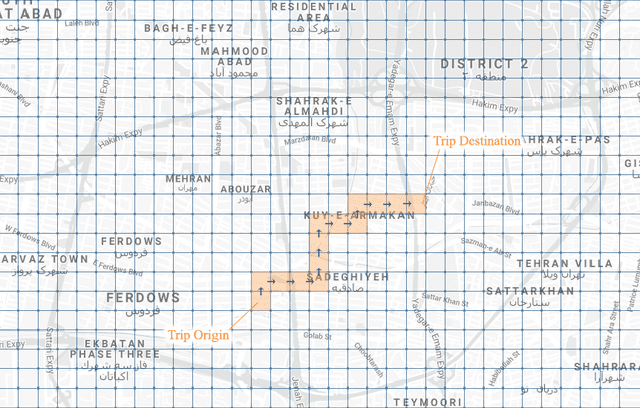
Abstract:Estimating the travel time of any route is of great importance for trip planners, traffic operators, online taxi dispatching and ride-sharing platforms, and navigation provider systems. With the advance of technology, many traveling cars, including online taxi dispatch systems' vehicles are equipped with Global Positioning System (GPS) devices that can report the location of the vehicle every few seconds. This paper uses GPS data and the Matrix Factorization techniques to estimate the travel times on all road segments and time intervals simultaneously. We aggregate GPS data into a matrix, where each cell of the original matrix contains the average vehicle speed for a segment and a specific time interval. One of the problems with this matrix is its high sparsity. We use Alternating Least Squares (ALS) method along with a regularization term to factorize the matrix. Since this approach can solve the sparsity problem that arises from the absence of cars in many road segments in a specific time interval, matrix factorization is suitable for estimating the travel time. Our comprehensive evaluation results using real data provided by one of the largest online taxi dispatching systems in Iran, shows the strength of our proposed method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge