Barbara Webb
Minimal Footprint Grasping Inspired by Ants
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Ants are highly capable of grasping objects in clutter, and we have recently observed that this involves substantial use of their forelegs. The forelegs, more specifically the tarsi, have high friction microstructures (setal pads), are covered in hairs, and have a flexible under-actuated tip. Here we abstract these features to test their functional advantages for a novel low-cost gripper design, suitable for bin-picking applications. In our implementation, the gripper legs are long and slim, with high friction gripping pads, low friction hairs and single-segment tarsus-like structure to mimic the insect's setal pads, hairs, and the tarsi's interactive compliance. Experimental evaluation shows this design is highly robust for grasping a wide variety of individual consumer objects, with all grasp attempts successful. In addition, we demonstrate this design is effective for picking single objects from dense clutter, a task at which ants also show high competence. The work advances grasping technology and shed new light on the mechanical importance of hairy structures and tarsal flexibility in insects.
An Efficient Insect-inspired Approach for Visual Point-goal Navigation
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:In this work we develop a novel insect-inspired agent for visual point-goal navigation. This combines abstracted models of two insect brain structures that have been implicated, respectively, in associative learning and path integration. We draw an analogy between the formal benchmark of the Habitat point-goal navigation task and the ability of insects to learn and refine visually guided paths around obstacles between a discovered food location and their nest. We demonstrate that the simple insect-inspired agent exhibits performance comparable to recent SOTA models at many orders of magnitude less computational cost. Testing in a more realistic simulated environment shows the approach is robust to perturbations.
AntGrip -- Boosting Parallel Plate Gripper Performance Inspired by the Internal Hairs of Ant Mandibles
Dec 08, 2023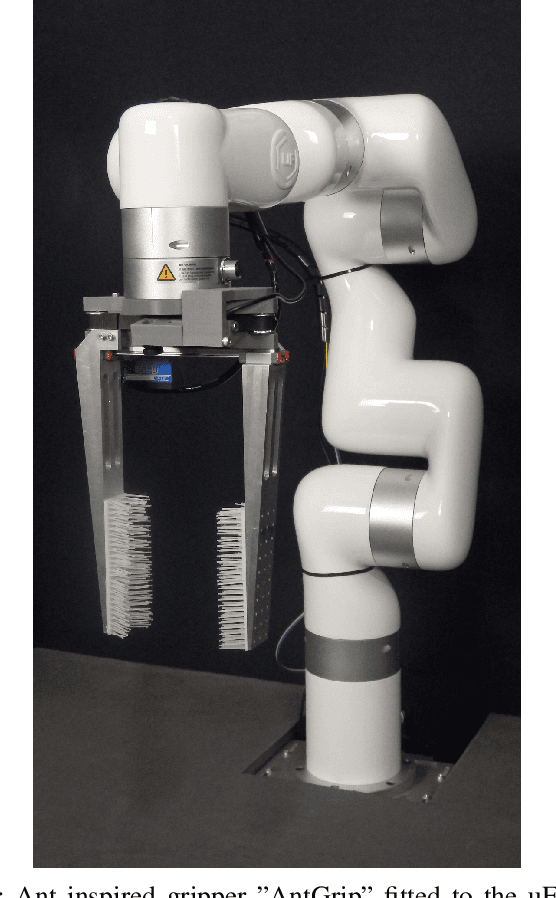
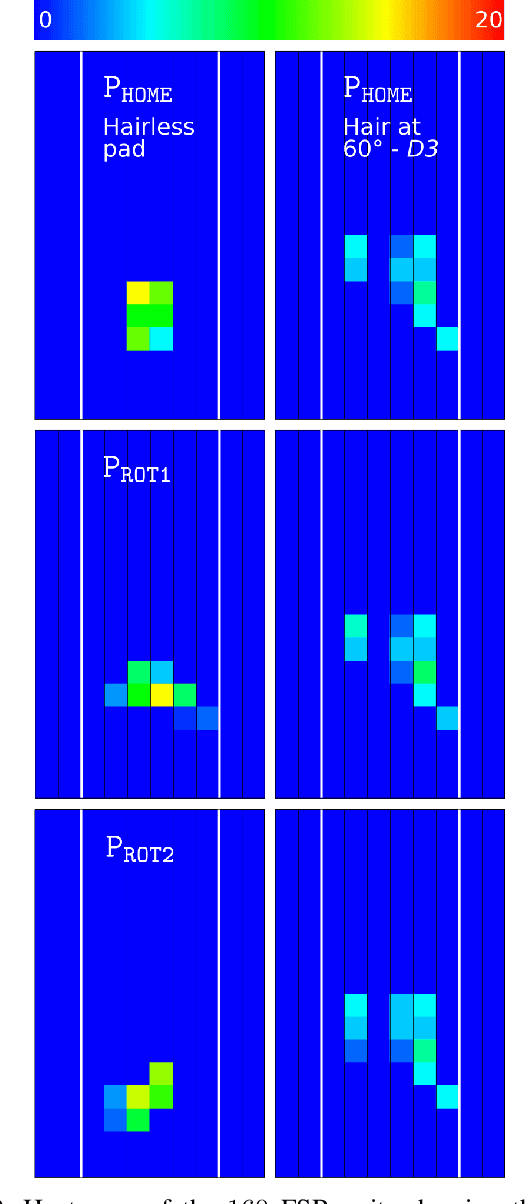
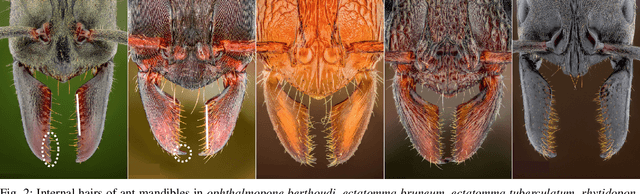
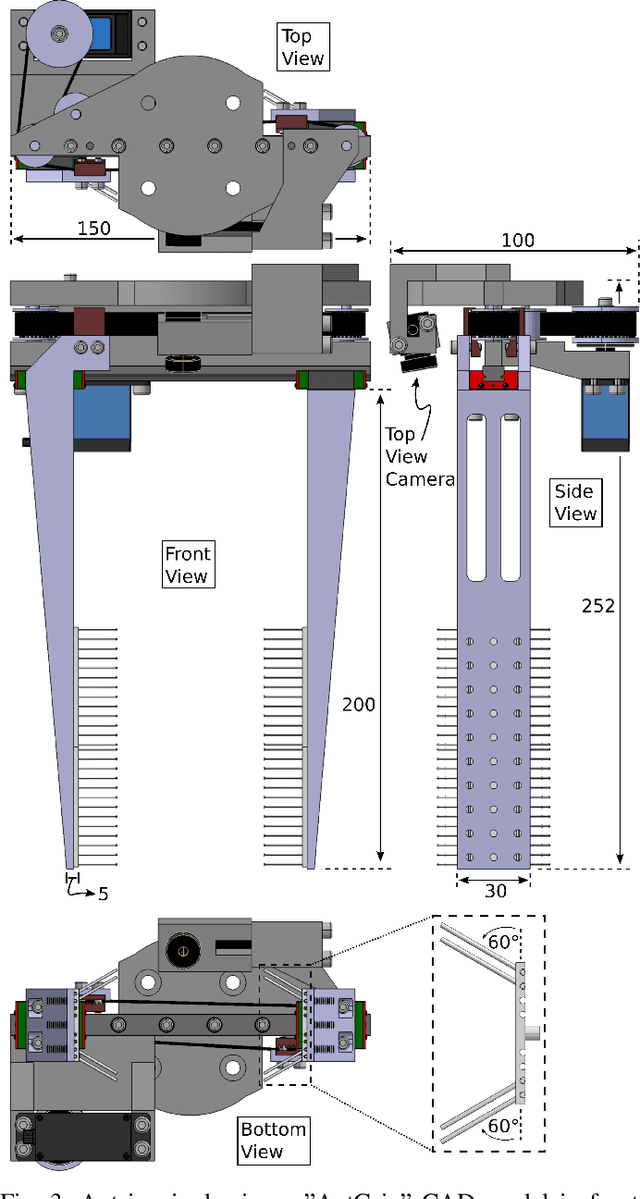
Abstract:Ants use their mandibles - effectively a two-finger gripper - for a wide range of grasping activities. Here we investigate whether mimicking the internal hairs found on ant mandibles can improve performance of a two-finger parallel plate robot gripper. With bin picking applications in mind, the gripper fingers are long and slim, with interchangeable soft gripping pads that can be hairy or hairless. A total of 2400 video-documented experiments have been conducted, comparing hairless to hairy pads with different hair patterns. Simply by adding hairs, the grasp success rate was increased by at least 29%, and the number of objects that remain securely gripped during manipulation more than doubled. This result not only advances the state of the art in grasping technology, but also provides novel insight into the mechanical role of mandible hairs in ant biology.
Vision-based route following by an embodied insect-inspired sparse neural network
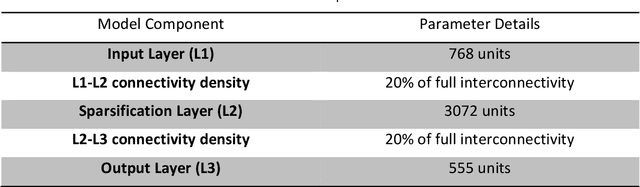
Mar 31, 2023Abstract:We compared the efficiency of the FlyHash model, an insect-inspired sparse neural network (Dasgupta et al., 2017), to similar but non-sparse models in an embodied navigation task. This requires a model to control steering by comparing current visual inputs to memories stored along a training route. We concluded the FlyHash model is more efficient than others, especially in terms of data encoding.
Visual Appearance Analysis of Forest Scenes for Monocular SLAM
Jul 05, 2019
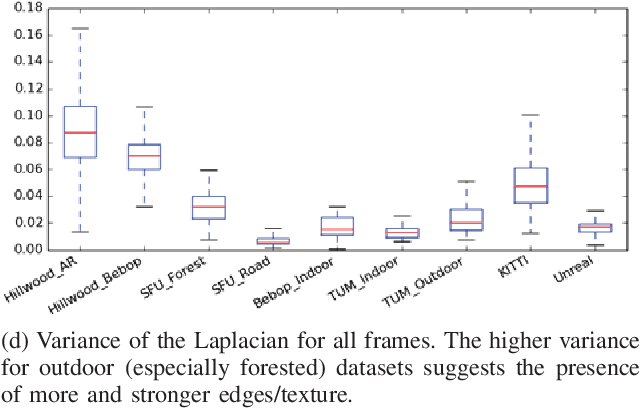
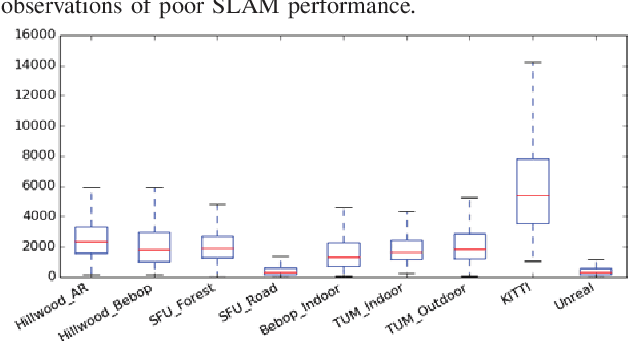

Abstract:Monocular simultaneous localisation and mapping (SLAM) is a cheap and energy efficient way to enable Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) to safely navigate managed forests and gather data crucial for monitoring tree health. SLAM research, however, has mostly been conducted in structured human environments, and as such is poorly adapted to unstructured forests. In this paper, we compare the performance of state of the art monocular SLAM systems on forest data and use visual appearance statistics to characterise the differences between forests and other environments, including a photorealistic simulated forest. We find that SLAM systems struggle with all but the most straightforward forest terrain and identify key attributes (lighting changes and in-scene motion) which distinguish forest scenes from "classic" urban datasets. These differences offer an insight into what makes forests harder to map and open the way for targeted improvements. We also demonstrate that even simulations that look impressive to the human eye can fail to properly reflect the difficult attributes of the environment they simulate, and provide suggestions for more closely mimicking natural scenes.
Place Recognition with Event-based Cameras and a Neural Implementation of SeqSLAM
May 18, 2015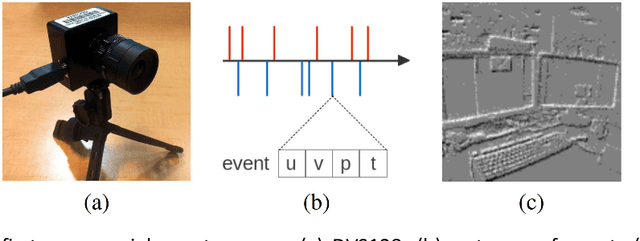
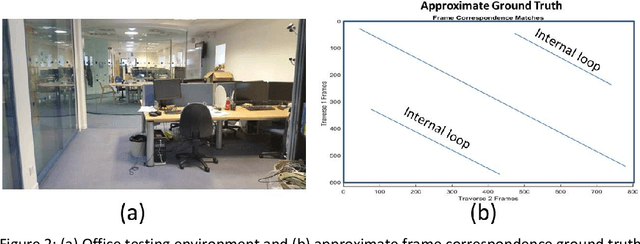
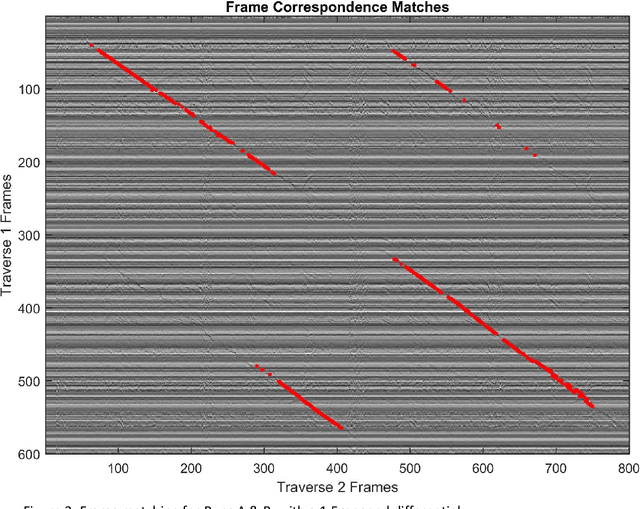
Abstract:Event-based cameras offer much potential to the fields of robotics and computer vision, in part due to their large dynamic range and extremely high "frame rates". These attributes make them, at least in theory, particularly suitable for enabling tasks like navigation and mapping on high speed robotic platforms under challenging lighting conditions, a task which has been particularly challenging for traditional algorithms and camera sensors. Before these tasks become feasible however, progress must be made towards adapting and innovating current RGB-camera-based algorithms to work with event-based cameras. In this paper we present ongoing research investigating two distinct approaches to incorporating event-based cameras for robotic navigation: the investigation of suitable place recognition / loop closure techniques, and the development of efficient neural implementations of place recognition techniques that enable the possibility of place recognition using event-based cameras at very high frame rates using neuromorphic computing hardware.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge