Baoyang Chen
Learning to Generate Poetic Chinese Landscape Painting with Calligraphy
May 08, 2023



Abstract:In this paper, we present a novel system (denoted as Polaca) to generate poetic Chinese landscape painting with calligraphy. Unlike previous single image-to-image painting generation, Polaca takes the classic poetry as input and outputs the artistic landscape painting image with the corresponding calligraphy. It is equipped with three different modules to complete the whole piece of landscape painting artwork: the first one is a text-to-image module to generate landscape painting image, the second one is an image-to-image module to generate stylistic calligraphy image, and the third one is an image fusion module to fuse the two images into a whole piece of aesthetic artwork.
SE-GAN: Skeleton Enhanced GAN-based Model for Brush Handwriting Font Generation
Apr 22, 2022



Abstract:Previous works on font generation mainly focus on the standard print fonts where character's shape is stable and strokes are clearly separated. There is rare research on brush handwriting font generation, which involves holistic structure changes and complex strokes transfer. To address this issue, we propose a novel GAN-based image translation model by integrating the skeleton information. We first extract the skeleton from training images, then design an image encoder and a skeleton encoder to extract corresponding features. A self-attentive refined attention module is devised to guide the model to learn distinctive features between different domains. A skeleton discriminator is involved to first synthesize the skeleton image from the generated image with a pre-trained generator, then to judge its realness to the target one. We also contribute a large-scale brush handwriting font image dataset with six styles and 15,000 high-resolution images. Both quantitative and qualitative experimental results demonstrate the competitiveness of our proposed model.
Brain-Inspired Inference on Missing Video Sequence
Dec 15, 2019
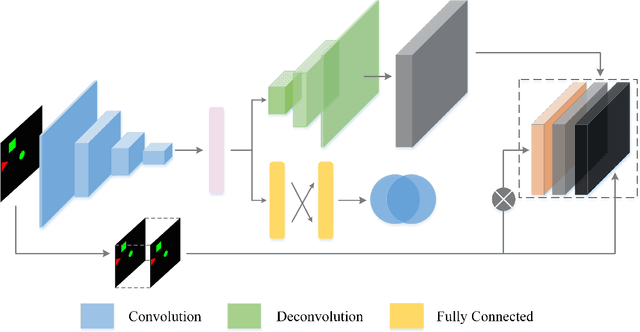
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel end-to-end architecture that could generate a variety of plausible video sequences correlating two given discontinuous frames. Our work is inspired by the human ability of inference. Specifically, given two static images, human are capable of inferring what might happen in between as well as present diverse versions of their inference. We firstly train our model to learn the transformation to understand the movement trends within given frames. For the sake of imitating the inference of human, we introduce a latent variable sampled from Gaussian distribution. By means of integrating different latent variables with learned transformation features, the model could learn more various possible motion modes. Then applying these motion modes on the original frame, we could acquire various corresponding intermediate video sequence. Moreover, the framework is trained in adversarial fashion with unsupervised learning. Evaluating on the moving Mnist dataset and the 2D Shapes dataset, we show that our model is capable of imitating the human inference to some extent.
Mappa Mundi: An Interactive Artistic Mind Map Generator with Artificial Imagination
May 09, 2019

Abstract:We present a novel real-time, collaborative, and interactive AI painting system, Mappa Mundi, for artistic Mind Map creation. The system consists of a voice-based input interface, an automatic topic expansion module, and an image projection module. The key innovation is to inject Artificial Imagination into painting creation by considering lexical and phonological similarities of language, learning and inheriting artist's original painting style, and applying the principles of Dadaism and impossibility of improvisation. Our system indicates that AI and artist can collaborate seamlessly to create imaginative artistic painting and Mappa Mundi has been applied in art exhibition in UCCA, Beijing
From Knowledge Map to Mind Map: Artificial Imagination
Mar 06, 2019



Abstract:Imagination is one of the most important factors which makes an artistic painting unique and impressive. With the rapid development of Artificial Intelligence, more and more researchers try to create painting with AI technology automatically. However, lacking of imagination is still a main problem for AI painting. In this paper, we propose a novel approach to inject rich imagination into a special painting art Mind Map creation. We firstly consider lexical and phonological similarities of seed word, then learn and inherit original painting style of the author, and finally apply Dadaism and impossibility of improvisation principles into painting process. We also design several metrics for imagination evaluation. Experimental results show that our proposed method can increase imagination of painting and also improve its overall quality.
Video Imagination from a Single Image with Transformation Generation
Jun 15, 2017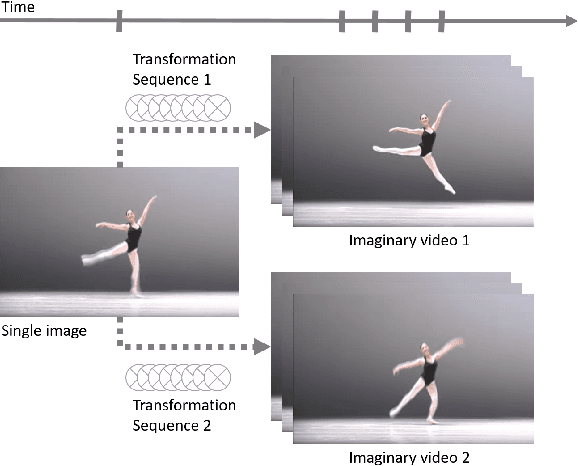
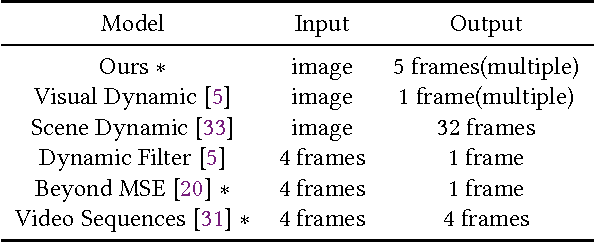
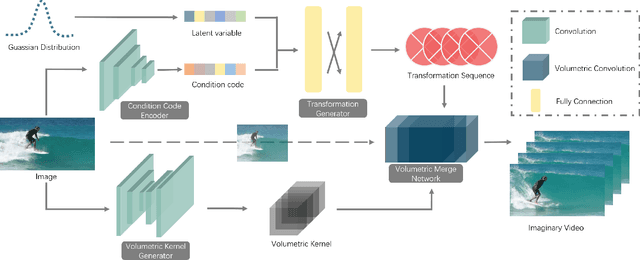
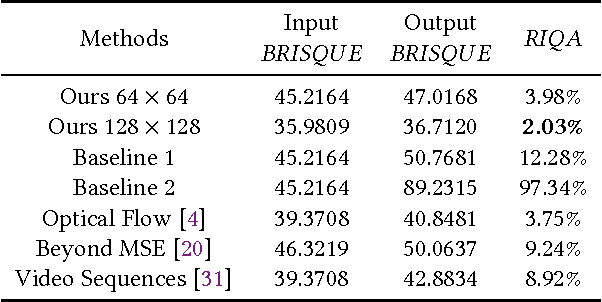
Abstract:In this work, we focus on a challenging task: synthesizing multiple imaginary videos given a single image. Major problems come from high dimensionality of pixel space and the ambiguity of potential motions. To overcome those problems, we propose a new framework that produce imaginary videos by transformation generation. The generated transformations are applied to the original image in a novel volumetric merge network to reconstruct frames in imaginary video. Through sampling different latent variables, our method can output different imaginary video samples. The framework is trained in an adversarial way with unsupervised learning. For evaluation, we propose a new assessment metric $RIQA$. In experiments, we test on 3 datasets varying from synthetic data to natural scene. Our framework achieves promising performance in image quality assessment. The visual inspection indicates that it can successfully generate diverse five-frame videos in acceptable perceptual quality.
Long-Term Video Interpolation with Bidirectional Predictive Network
Jun 13, 2017

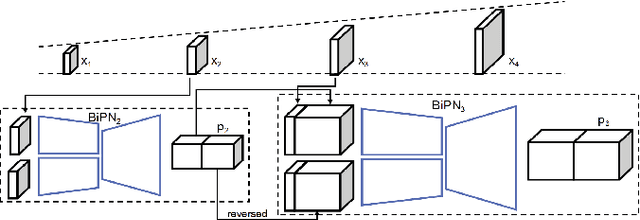

Abstract:This paper considers the challenging task of long-term video interpolation. Unlike most existing methods that only generate few intermediate frames between existing adjacent ones, we attempt to speculate or imagine the procedure of an episode and further generate multiple frames between two non-consecutive frames in videos. In this paper, we present a novel deep architecture called bidirectional predictive network (BiPN) that predicts intermediate frames from two opposite directions. The bidirectional architecture allows the model to learn scene transformation with time as well as generate longer video sequences. Besides, our model can be extended to predict multiple possible procedures by sampling different noise vectors. A joint loss composed of clues in image and feature spaces and adversarial loss is designed to train our model. We demonstrate the advantages of BiPN on two benchmarks Moving 2D Shapes and UCF101 and report competitive results to recent approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge