Béatrice Daille
LINA
FrenchMedMCQA: A French Multiple-Choice Question Answering Dataset for Medical domain
Apr 09, 2023


Abstract:This paper introduces FrenchMedMCQA, the first publicly available Multiple-Choice Question Answering (MCQA) dataset in French for medical domain. It is composed of 3,105 questions taken from real exams of the French medical specialization diploma in pharmacy, mixing single and multiple answers. Each instance of the dataset contains an identifier, a question, five possible answers and their manual correction(s). We also propose first baseline models to automatically process this MCQA task in order to report on the current performances and to highlight the difficulty of the task. A detailed analysis of the results showed that it is necessary to have representations adapted to the medical domain or to the MCQA task: in our case, English specialized models yielded better results than generic French ones, even though FrenchMedMCQA is in French. Corpus, models and tools are available online.
DrBERT: A Robust Pre-trained Model in French for Biomedical and Clinical domains
Apr 03, 2023Abstract:In recent years, pre-trained language models (PLMs) achieve the best performance on a wide range of natural language processing (NLP) tasks. While the first models were trained on general domain data, specialized ones have emerged to more effectively treat specific domains. In this paper, we propose an original study of PLMs in the medical domain on French language. We compare, for the first time, the performance of PLMs trained on both public data from the web and private data from healthcare establishments. We also evaluate different learning strategies on a set of biomedical tasks. In particular, we show that we can take advantage of already existing biomedical PLMs in a foreign language by further pre-train it on our targeted data. Finally, we release the first specialized PLMs for the biomedical field in French, called DrBERT, as well as the largest corpus of medical data under free license on which these models are trained.
The DELICES project: Indexing scientific literature through semantic expansion
Jun 28, 2021
Abstract:Scientific digital libraries play a critical role in the development and dissemination of scientific literature. Despite dedicated search engines, retrieving relevant publications from the ever-growing body of scientific literature remains challenging and time-consuming. Indexing scientific articles is indeed a difficult matter, and current models solely rely on a small portion of the articles (title and abstract) and on author-assigned keyphrases when available. This results in a frustratingly limited access to scientific knowledge. The goal of the DELICES project is to address this pitfall by exploiting semantic relations between scientific articles to both improve and enrich indexing. To this end, we will rely on the latest advances in semantic representations to both increase the relevance of keyphrases extracted from the documents, and extend indexing to new terms borrowed from semantically similar documents.
KPTimes: A Large-Scale Dataset for Keyphrase Generation on News Documents
Nov 28, 2019


Abstract:Keyphrase generation is the task of predicting a set of lexical units that conveys the main content of a source text. Existing datasets for keyphrase generation are only readily available for the scholarly domain and include non-expert annotations. In this paper we present KPTimes, a large-scale dataset of news texts paired with editor-curated keyphrases. Exploring the dataset, we show how editors tag documents, and how their annotations differ from those found in existing datasets. We also train and evaluate state-of-the-art neural keyphrase generation models on KPTimes to gain insights on how well they perform on the news domain. The dataset is available online at https://github.com/ygorg/KPTimes .
Automatic segmentation of texts into units of meaning for reading assistance
Oct 11, 2019
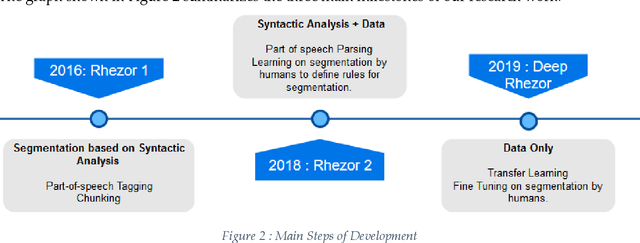
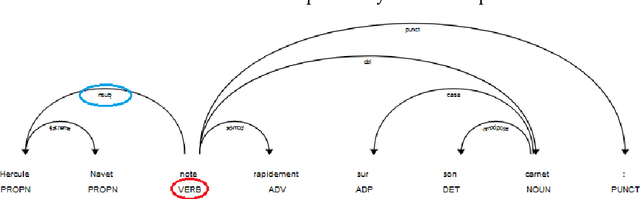
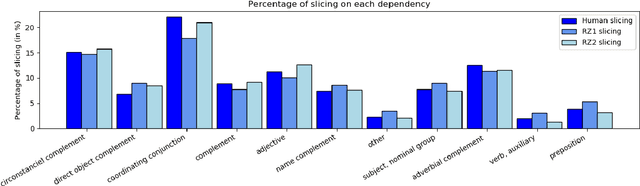
Abstract:The emergence of the digital book is a major step forward in providing access to reading, and therefore often to the common culture and the labour market. By allowing the enrichment of texts with cognitive crutches, EPub 3 compatible accessibility formats such as FROG have proven their effectiveness in alleviating but also reducing dyslexic disorders. In this paper, we show how Artificial Intelligence and particularly Transfer Learning with Google BERT can automate the division into units of meaning, and thus facilitate the creation of enriched digital books at a moderate cost.
Keyphrase Annotation with Graph Co-Ranking
Nov 07, 2016



Abstract:Keyphrase annotation is the task of identifying textual units that represent the main content of a document. Keyphrase annotation is either carried out by extracting the most important phrases from a document, keyphrase extraction, or by assigning entries from a controlled domain-specific vocabulary, keyphrase assignment. Assignment methods are generally more reliable. They provide better-formed keyphrases, as well as keyphrases that do not occur in the document. But they are often silent on the contrary of extraction methods that do not depend on manually built resources. This paper proposes a new method to perform both keyphrase extraction and keyphrase assignment in an integrated and mutual reinforcing manner. Experiments have been carried out on datasets covering different domains of humanities and social sciences. They show statistically significant improvements compared to both keyphrase extraction and keyphrase assignment state-of-the art methods.
Extraction of domain-specific bilingual lexicon from comparable corpora: compositional translation and ranking
Oct 21, 2012



Abstract:This paper proposes a method for extracting translations of morphologically constructed terms from comparable corpora. The method is based on compositional translation and exploits translation equivalences at the morpheme-level, which allows for the generation of "fertile" translations (translation pairs in which the target term has more words than the source term). Ranking methods relying on corpus-based and translation-based features are used to select the best candidate translation. We obtain an average precision of 91% on the Top1 candidate translation. The method was tested on two language pairs (English-French and English-German) and with a small specialized comparable corpora (400k words per language).
* arXiv admin note: substantial text overlap with arXiv:1209.2400
Identification of Fertile Translations in Medical Comparable Corpora: a Morpho-Compositional Approach
Sep 11, 2012



Abstract:This paper defines a method for lexicon in the biomedical domain from comparable corpora. The method is based on compositional translation and exploits morpheme-level translation equivalences. It can generate translations for a large variety of morphologically constructed words and can also generate 'fertile' translations. We show that fertile translations increase the overall quality of the extracted lexicon for English to French translation.
Pattern Based Term Extraction Using ACABIT System
Jul 14, 2009



Abstract:In this paper, we propose a pattern-based term extraction approach for Japanese, applying ACABIT system originally developed for French. The proposed approach evaluates termhood using morphological patterns of basic terms and term variants. After extracting term candidates, ACABIT system filters out non-terms from the candidates based on log-likelihood. This approach is suitable for Japanese term extraction because most of Japanese terms are compound nouns or simple phrasal patterns.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge