Axel von Arnim
EEvAct: Early Event-Based Action Recognition with High-Rate Two-Stream Spiking Neural Networks
Jul 10, 2025Abstract:Recognizing human activities early is crucial for the safety and responsiveness of human-robot and human-machine interfaces. Due to their high temporal resolution and low latency, event-based vision sensors are a perfect match for this early recognition demand. However, most existing processing approaches accumulate events to low-rate frames or space-time voxels which limits the early prediction capabilities. In contrast, spiking neural networks (SNNs) can process the events at a high-rate for early predictions, but most works still fall short on final accuracy. In this work, we introduce a high-rate two-stream SNN which closes this gap by outperforming previous work by 2% in final accuracy on the large-scale THU EACT-50 dataset. We benchmark the SNNs within a novel early event-based recognition framework by reporting Top-1 and Top-5 recognition scores for growing observation time. Finally, we exemplify the impact of these methods on a real-world task of early action triggering for human motion capture in sports.
Scaling Up Resonate-and-Fire Networks for Fast Deep Learning
Apr 01, 2025Abstract:Spiking neural networks (SNNs) present a promising computing paradigm for neuromorphic processing of event-based sensor data. The resonate-and-fire (RF) neuron, in particular, appeals through its biological plausibility, complex dynamics, yet computational simplicity. Despite theoretically predicted benefits, challenges in parameter initialization and efficient learning inhibited the implementation of RF networks, constraining their use to a single layer. In this paper, we address these shortcomings by deriving the RF neuron as a structured state space model (SSM) from the HiPPO framework. We introduce S5-RF, a new SSM layer comprised of RF neurons based on the S5 model, that features a generic initialization scheme and fast training within a deep architecture. S5-RF scales for the first time a RF network to a deep SNN with up to four layers and achieves with 78.8% a new state-of-the-art result for recurrent SNNs on the Spiking Speech Commands dataset in under three hours of training time. Moreover, compared to the reference SNNs that solve our benchmarking tasks, it achieves similar performance with much fewer spiking operations. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/ThomasEHuber/s5-rf.
* 19 pages, 3 figures
Neuromorphic force-control in an industrial task: validating energy and latency benefits
Mar 13, 2024Abstract:As robots become smarter and more ubiquitous, optimizing the power consumption of intelligent compute becomes imperative towards ensuring the sustainability of technological advancements. Neuromorphic computing hardware makes use of biologically inspired neural architectures to achieve energy and latency improvements compared to conventional von Neumann computing architecture. Applying these benefits to robots has been demonstrated in several works in the field of neurorobotics, typically on relatively simple control tasks. Here, we introduce an example of neuromorphic computing applied to the real-world industrial task of object insertion. We trained a spiking neural network (SNN) to perform force-torque feedback control using a reinforcement learning approach in simulation. We then ported the SNN to the Intel neuromorphic research chip Loihi interfaced with a KUKA robotic arm. At inference time we show latency competitive with current CPU/GPU architectures, two orders of magnitude less energy usage in comparison to traditional low-energy edge-hardware. We offer this example as a proof of concept implementation of a neuromoprhic controller in real-world robotic setting, highlighting the benefits of neuromorphic hardware for the development of intelligent controllers for robots.
Neuromorphic Optical Flow and Real-time Implementation with Event Cameras
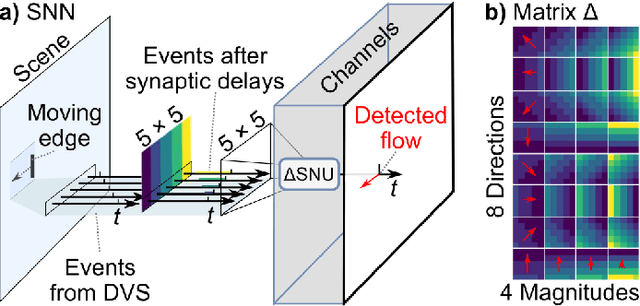
Apr 14, 2023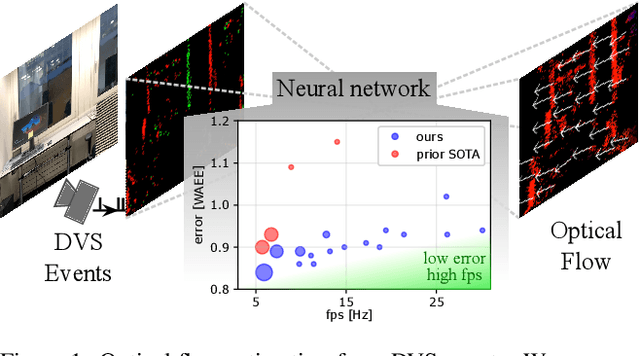
Abstract:Optical flow provides information on relative motion that is an important component in many computer vision pipelines. Neural networks provide high accuracy optical flow, yet their complexity is often prohibitive for application at the edge or in robots, where efficiency and latency play crucial role. To address this challenge, we build on the latest developments in event-based vision and spiking neural networks. We propose a new network architecture, inspired by Timelens, that improves the state-of-the-art self-supervised optical flow accuracy when operated both in spiking and non-spiking mode. To implement a real-time pipeline with a physical event camera, we propose a methodology for principled model simplification based on activity and latency analysis. We demonstrate high speed optical flow prediction with almost two orders of magnitude reduced complexity while maintaining the accuracy, opening the path for real-time deployments.
Dynamic Event-based Optical Identification and Communication
Mar 14, 2023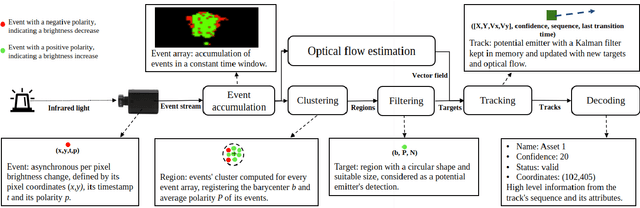
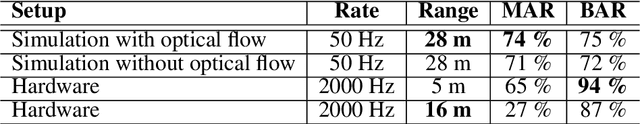
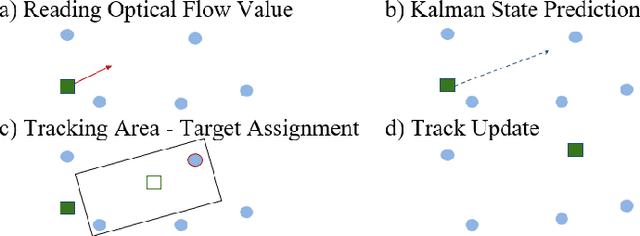
Abstract:Optical identification is often done with spatial or temporal visual pattern recognition and localization. Temporal pattern recognition, depending on the technology, involves a trade-off between communication frequency, range and accurate tracking. We propose a solution with light-emitting beacons that improves this trade-off by exploiting fast event-based cameras and, for tracking, sparse neuromorphic optical flow computed with spiking neurons. In an asset monitoring use case, we demonstrate that the system, embedded in a simulated drone, is robust to relative movements and enables simultaneous communication with, and tracking of, multiple moving beacons. Finally, in a hardware lab prototype, we achieve state-of-the-art optical camera communication frequencies in the kHz magnitude.
A Spiking Central Pattern Generator for the control of a simulated lamprey robot running on SpiNNaker and Loihi neuromorphic boards
Jan 18, 2021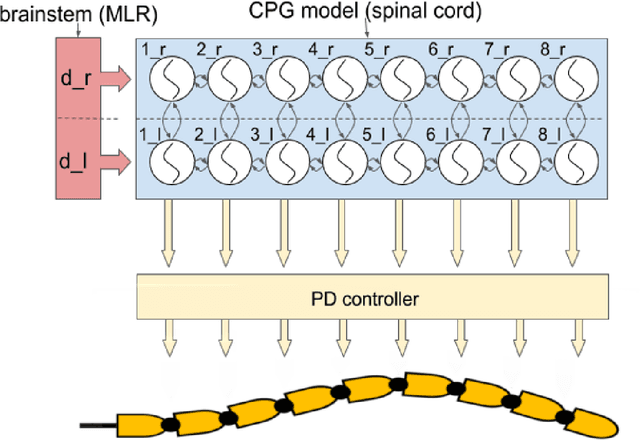
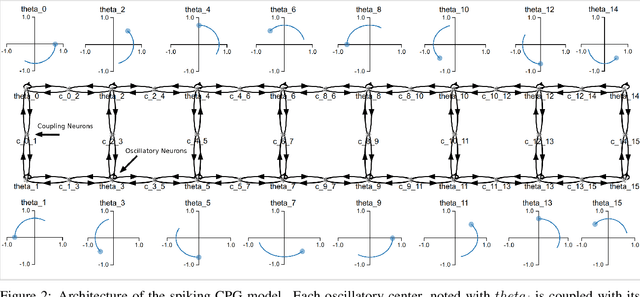
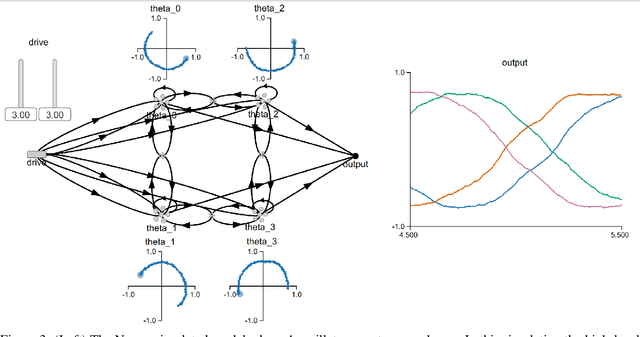
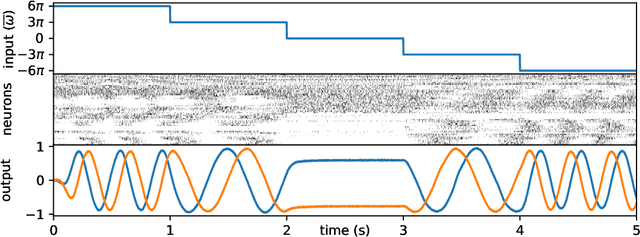
Abstract:Central Pattern Generators (CPGs) models have been long used to investigate both the neural mechanisms that underlie animal locomotion as well as a tool for robotic research. In this work we propose a spiking CPG neural network and its implementation on neuromorphic hardware as a means to control a simulated lamprey model. To construct our CPG model, we employ the naturally emerging dynamical systems that arise through the use of recurrent neural populations in the Neural Engineering Framework (NEF). We define the mathematical formulation behind our model, which consists of a system of coupled abstract oscillators modulated by high-level signals, capable of producing a variety of output gaits. We show that with this mathematical formulation of the Central Pattern Generator model, the model can be turned into a Spiking Neural Network (SNN) that can be easily simulated with Nengo, an SNN simulator. The spiking CPG model is then used to produce the swimming gaits of a simulated lamprey robot model in various scenarios. We show that by modifying the input to the network, which can be provided by sensory information, the robot can be controlled dynamically in direction and pace. The proposed methodology can be generalized to other types of CPGs suitable for both engineering applications and scientific research. We test our system on two neuromorphic platforms, SpiNNaker and Loihi. Finally, we show that this category of spiking algorithms shows a promising potential to exploit the theoretical advantages of neuromorphic hardware in terms of energy efficiency and computational speed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge