Ava Pettet
Online Decision-Making Under Uncertainty for Vehicle-to-Building Systems
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Vehicle-to-building (V2B) systems integrate physical infrastructures, such as smart buildings and electric vehicles (EVs) connected to chargers at the building, with digital control mechanisms to manage energy use. By utilizing EVs as flexible energy reservoirs, buildings can dynamically charge and discharge them to optimize energy use and cut costs under time-variable pricing and demand charge policies. This setup leads to the V2B optimization problem, where buildings coordinate EV charging and discharging to minimize total electricity costs while meeting users' charging requirements. However, the V2B optimization problem is challenging because of: (1) fluctuating electricity pricing, which includes both energy charges ($/kWh) and demand charges ($/kW); (2) long planning horizons (typically over 30 days); (3) heterogeneous chargers with varying charging rates, controllability, and directionality (i.e., unidirectional or bidirectional); and (4) user-specific battery levels at departure to ensure user requirements are met. In contrast to existing approaches that often model this setting as a single-shot combinatorial optimization problem, we highlight critical limitations in prior work and instead model the V2B optimization problem as a Markov decision process (MDP), i.e., a stochastic control process. Solving the resulting MDP is challenging due to the large state and action spaces. To address the challenges of the large state space, we leverage online search, and we counter the action space by using domain-specific heuristics to prune unpromising actions. We validate our approach in collaboration with Nissan Advanced Technology Center - Silicon Valley. Using data from their EV testbed, we show that the proposed framework significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods.
* 17 pages, 2 figures, 10 tables. Published in the Proceedings of the 16th ACM/IEEE International Conference on Cyber-Physical Systems (ICCPS '25), May 06--09, 2025, Irvine, CA, USA
CONSENT: A Negotiation Framework for Leveraging User Flexibility in Vehicle-to-Building Charging under Uncertainty
Jan 04, 2026Abstract:The growth of Electric Vehicles (EVs) creates a conflict in vehicle-to-building (V2B) settings between building operators, who face high energy costs from uncoordinated charging, and drivers, who prioritize convenience and a full charge. To resolve this, we propose a negotiation-based framework that, by design, guarantees voluntary participation, strategy-proofness, and budget feasibility. It transforms EV charging into a strategic resource by offering drivers a range of incentive-backed options for modest flexibility in their departure time or requested state of charge (SoC). Our framework is calibrated with user survey data and validated using real operational data from a commercial building and an EV manufacturer. Simulations show that our negotiation protocol creates a mutually beneficial outcome: lowering the building operator's costs by over 3.5\% compared to an optimized, non-negotiating smart charging policy, while simultaneously reducing user charging expenses by 22\% below the utility's retail energy rate. By aligning operator and EV user objectives, our framework provides a strategic bridge between energy and mobility systems, transforming EV charging from a source of operational friction into a platform for collaboration and shared savings.
Scalable Decision-Making in Stochastic Environments through Learned Temporal Abstraction
Feb 28, 2025Abstract:Sequential decision-making in high-dimensional continuous action spaces, particularly in stochastic environments, faces significant computational challenges. We explore this challenge in the traditional offline RL setting, where an agent must learn how to make decisions based on data collected through a stochastic behavior policy. We present \textit{Latent Macro Action Planner} (L-MAP), which addresses this challenge by learning a set of temporally extended macro-actions through a state-conditional Vector Quantized Variational Autoencoder (VQ-VAE), effectively reducing action dimensionality. L-MAP employs a (separate) learned prior model that acts as a latent transition model and allows efficient sampling of plausible actions. During planning, our approach accounts for stochasticity in both the environment and the behavior policy by using Monte Carlo tree search (MCTS). In offline RL settings, including stochastic continuous control tasks, L-MAP efficiently searches over discrete latent actions to yield high expected returns. Empirical results demonstrate that L-MAP maintains low decision latency despite increased action dimensionality. Notably, across tasks ranging from continuous control with inherently stochastic dynamics to high-dimensional robotic hand manipulation, L-MAP significantly outperforms existing model-based methods and performs on-par with strong model-free actor-critic baselines, highlighting the effectiveness of the proposed approach in planning in complex and stochastic environments with high-dimensional action spaces.
Reinforcement Learning-based Approach for Vehicle-to-Building Charging with Heterogeneous Agents and Long Term Rewards
Feb 24, 2025Abstract:Strategic aggregation of electric vehicle batteries as energy reservoirs can optimize power grid demand, benefiting smart and connected communities, especially large office buildings that offer workplace charging. This involves optimizing charging and discharging to reduce peak energy costs and net peak demand, monitored over extended periods (e.g., a month), which involves making sequential decisions under uncertainty and delayed and sparse rewards, a continuous action space, and the complexity of ensuring generalization across diverse conditions. Existing algorithmic approaches, e.g., heuristic-based strategies, fall short in addressing real-time decision-making under dynamic conditions, and traditional reinforcement learning (RL) models struggle with large state-action spaces, multi-agent settings, and the need for long-term reward optimization. To address these challenges, we introduce a novel RL framework that combines the Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient approach (DDPG) with action masking and efficient MILP-driven policy guidance. Our approach balances the exploration of continuous action spaces to meet user charging demands. Using real-world data from a major electric vehicle manufacturer, we show that our approach comprehensively outperforms many well-established baselines and several scalable heuristic approaches, achieving significant cost savings while meeting all charging requirements. Our results show that the proposed approach is one of the first scalable and general approaches to solving the V2B energy management challenge.
Decision Making in Non-Stationary Environments with Policy-Augmented Search
Jan 06, 2024


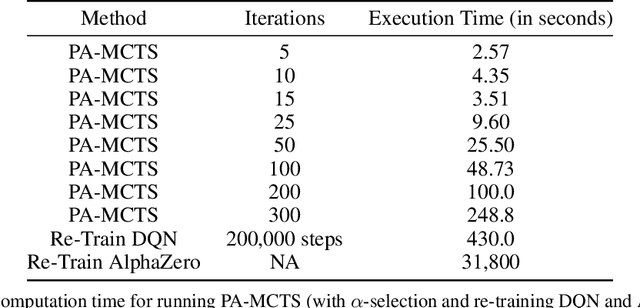
Abstract:Sequential decision-making under uncertainty is present in many important problems. Two popular approaches for tackling such problems are reinforcement learning and online search (e.g., Monte Carlo tree search). While the former learns a policy by interacting with the environment (typically done before execution), the latter uses a generative model of the environment to sample promising action trajectories at decision time. Decision-making is particularly challenging in non-stationary environments, where the environment in which an agent operates can change over time. Both approaches have shortcomings in such settings -- on the one hand, policies learned before execution become stale when the environment changes and relearning takes both time and computational effort. Online search, on the other hand, can return sub-optimal actions when there are limitations on allowed runtime. In this paper, we introduce \textit{Policy-Augmented Monte Carlo tree search} (PA-MCTS), which combines action-value estimates from an out-of-date policy with an online search using an up-to-date model of the environment. We prove theoretical results showing conditions under which PA-MCTS selects the one-step optimal action and also bound the error accrued while following PA-MCTS as a policy. We compare and contrast our approach with AlphaZero, another hybrid planning approach, and Deep Q Learning on several OpenAI Gym environments. Through extensive experiments, we show that under non-stationary settings with limited time constraints, PA-MCTS outperforms these baselines.
Dynamic Simplex: Balancing Safety and Performance in Autonomous Cyber Physical Systems
Feb 20, 2023



Abstract:Learning Enabled Components (LEC) have greatly assisted cyber-physical systems in achieving higher levels of autonomy. However, LEC's susceptibility to dynamic and uncertain operating conditions is a critical challenge for the safety of these systems. Redundant controller architectures have been widely adopted for safety assurance in such contexts. These architectures augment LEC "performant" controllers that are difficult to verify with "safety" controllers and the decision logic to switch between them. While these architectures ensure safety, we point out two limitations. First, they are trained offline to learn a conservative policy of always selecting a controller that maintains the system's safety, which limits the system's adaptability to dynamic and non-stationary environments. Second, they do not support reverse switching from the safety controller to the performant controller, even when the threat to safety is no longer present. To address these limitations, we propose a dynamic simplex strategy with an online controller switching logic that allows two-way switching. We consider switching as a sequential decision-making problem and model it as a semi-Markov decision process. We leverage a combination of a myopic selector using surrogate models (for the forward switch) and a non-myopic planner (for the reverse switch) to balance safety and performance. We evaluate this approach using an autonomous vehicle case study in the CARLA simulator using different driving conditions, locations, and component failures. We show that the proposed approach results in fewer collisions and higher performance than state-of-the-art alternatives.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge