Artur Garcez
The Misclassification Likelihood Matrix: Some Classes Are More Likely To Be Misclassified Than Others
Jul 10, 2024Abstract:This study introduces the Misclassification Likelihood Matrix (MLM) as a novel tool for quantifying the reliability of neural network predictions under distribution shifts. The MLM is obtained by leveraging softmax outputs and clustering techniques to measure the distances between the predictions of a trained neural network and class centroids. By analyzing these distances, the MLM provides a comprehensive view of the model's misclassification tendencies, enabling decision-makers to identify the most common and critical sources of errors. The MLM allows for the prioritization of model improvements and the establishment of decision thresholds based on acceptable risk levels. The approach is evaluated on the MNIST dataset using a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) and a perturbed version of the dataset to simulate distribution shifts. The results demonstrate the effectiveness of the MLM in assessing the reliability of predictions and highlight its potential in enhancing the interpretability and risk mitigation capabilities of neural networks. The implications of this work extend beyond image classification, with ongoing applications in autonomous systems, such as self-driving cars, to improve the safety and reliability of decision-making in complex, real-world environments.
When to Accept Automated Predictions and When to Defer to Human Judgment?
Jul 10, 2024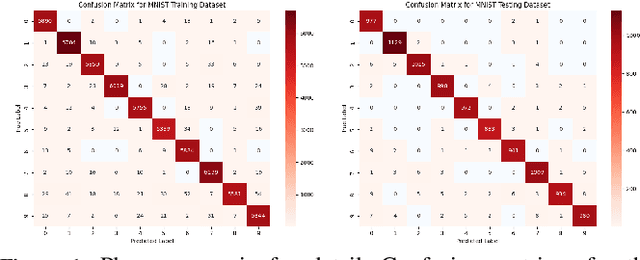
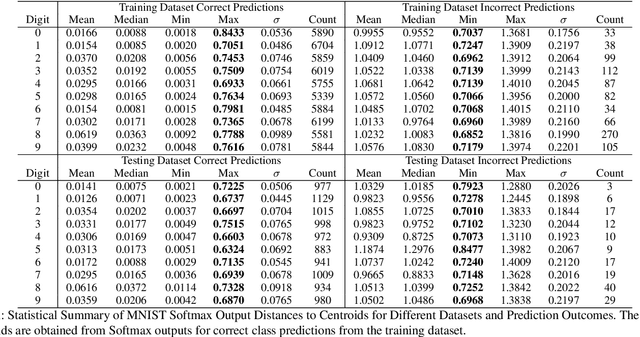
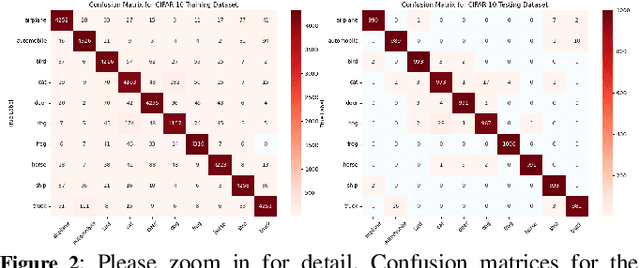
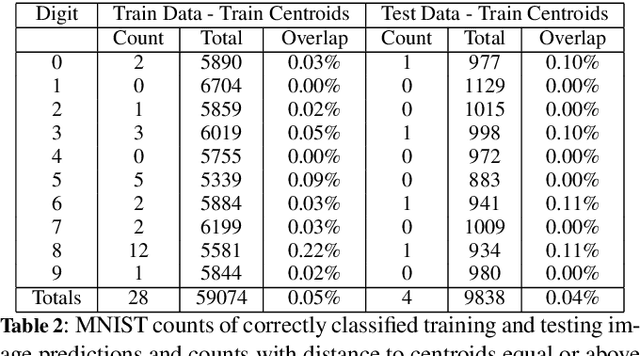
Abstract:Ensuring the reliability and safety of automated decision-making is crucial. It is well-known that data distribution shifts in machine learning can produce unreliable outcomes. This paper proposes a new approach for measuring the reliability of predictions under distribution shifts. We analyze how the outputs of a trained neural network change using clustering to measure distances between outputs and class centroids. We propose this distance as a metric to evaluate the confidence of predictions under distribution shifts. We assign each prediction to a cluster with centroid representing the mean softmax output for all correct predictions of a given class. We then define a safety threshold for a class as the smallest distance from an incorrect prediction to the given class centroid. We evaluate the approach on the MNIST and CIFAR-10 datasets using a Convolutional Neural Network and a Vision Transformer, respectively. The results show that our approach is consistent across these data sets and network models, and indicate that the proposed metric can offer an efficient way of determining when automated predictions are acceptable and when they should be deferred to human operators given a distribution shift.
Evaluation of autonomous systems under data distribution shifts
Jun 28, 2024



Abstract:We posit that data can only be safe to use up to a certain threshold of the data distribution shift, after which control must be relinquished by the autonomous system and operation halted or handed to a human operator. With the use of a computer vision toy example we demonstrate that network predictive accuracy is impacted by data distribution shifts and propose distance metrics between training and testing data to define safe operation limits within said shifts. We conclude that beyond an empirically obtained threshold of the data distribution shift, it is unreasonable to expect network predictive accuracy not to degrade
Neural-Symbolic Relational Reasoning on Graph Models: Effective Link Inference and Computation from Knowledge Bases
May 05, 2020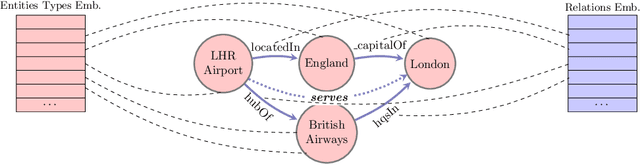
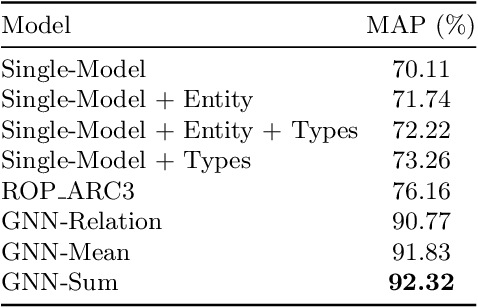
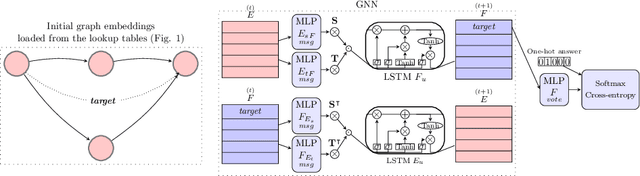
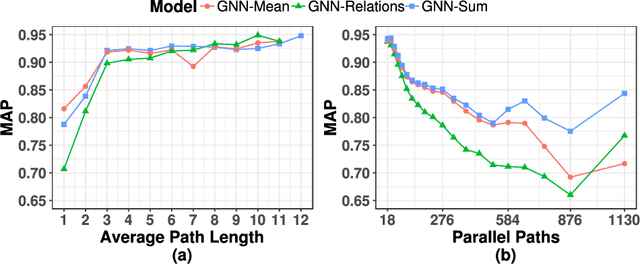
Abstract:The recent developments and growing interest in neural-symbolic models has shown that hybrid approaches can offer richer models for Artificial Intelligence. The integration of effective relational learning and reasoning methods is one of the key challenges in this direction, as neural learning and symbolic reasoning offer complementary characteristics that can benefit the development of AI systems. Relational labelling or link prediction on knowledge graphs has become one of the main problems in deep learning-based natural language processing research. Moreover, other fields which make use of neural-symbolic techniques may also benefit from such research endeavours. There have been several efforts towards the identification of missing facts from existing ones in knowledge graphs. Two lines of research try and predict knowledge relations between two entities by considering all known facts connecting them or several paths of facts connecting them. We propose a neural-symbolic graph neural network which applies learning over all the paths by feeding the model with the embedding of the minimal subset of the knowledge graph containing such paths. By learning to produce representations for entities and facts corresponding to word embeddings, we show how the model can be trained end-to-end to decode these representations and infer relations between entities in a multitask approach. Our contribution is two-fold: a neural-symbolic methodology leverages the resolution of relational inference in large graphs, and we also demonstrate that such neural-symbolic model is shown more effective than path-based approaches
Graph Neural Networks Meet Neural-Symbolic Computing: A Survey and Perspective
Mar 11, 2020
Abstract:Neural-symbolic computing has now become the subject of interest of both academic and industry research laboratories. Graph Neural Networks (GNN) have been widely used in relational and symbolic domains, with widespread application of GNNs in combinatorial optimization, constraint satisfaction, relational reasoning and other scientific domains. The need for improved explainability, interpretability and trust of AI systems in general demands principled methodologies, as suggested by neural-symbolic computing. In this paper, we review the state-of-the-art on the use of GNNs as a model of neural-symbolic computing. This includes the application of GNNs in several domains as well as its relationship to current developments in neural-symbolic computing.
Linear-Time Sequence Classification using Restricted Boltzmann Machines
Mar 08, 2018



Abstract:Classification of sequence data is the topic of interest for dynamic Bayesian models and Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs). While the former can explicitly model the temporal dependencies between class variables, the latter have a capability of learning representations. Several attempts have been made to improve performance by combining these two approaches or increasing the processing capability of the hidden units in RNNs. This often results in complex models with a large number of learning parameters. In this paper, a compact model is proposed which offers both representation learning and temporal inference of class variables by rolling Restricted Boltzmann Machines (RBMs) and class variables over time. We address the key issue of intractability in this variant of RBMs by optimising a conditional distribution, instead of a joint distribution. Experiments reported in the paper on melody modelling and optical character recognition show that the proposed model can outperform the state-of-the-art. Also, the experimental results on optical character recognition, part-of-speech tagging and text chunking demonstrate that our model is comparable to recurrent neural networks with complex memory gates while requiring far fewer parameters.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge