Arman Shojaeifard
ISAC Channel Modelling -- Perspectives from ETSI
May 15, 2025Abstract:Integrated Sensing and Communications (ISAC) is defined as one of six usage scenarios in the ITU-R International Mobile Telecommunications (IMT) 2030 framework for 6G. ISAC is envisioned to introduce the sensing capability into the cellular network, where sensing may be obtained using the cellular radio frequency (RF) signals with or without additional auxiliary sensors. To enable ISAC, specification bodies such as European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) and Third Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) have already started to look into detailed ISAC use cases, their requirements, and the channel models and evaluation methodologies that are necessary to design and evaluate ISAC performance. With focus on the channel model, the current communication-centric channel models like those specified in 3GPP technical report (TR) 38.901 do not cover the RF signals interactions between the transmitter, target object, receiver and their surrounding environment. To bridge this gap, 3GPP has been looking into the basic changes that are necessary to make to their TR38.901 channel model with focus on selected use cases from the 3GPP SA1 5G-Advanced feasibility study. In parallel, ETSI ISAC Industry Specification Group (ISG) has been studying the more advanced ISAC channel modelling features that are needed to support the variety of ISAC use cases envisioned in 6G. In this paper, we present the baseline and advanced features developed thus far in 3GPP and ETSI ISAC ISG, respectively, towards a comprehensive view of the ISAC channel model in 6G.
Achievable Rate Analysis of Intelligent Omni-Surface Assisted NOMA Holographic MIMO Systems
May 02, 2024


Abstract:An intelligent omni-surface (IOS) assisted holographic multiple-input and multiple-output architecture is conceived for $360^\circ$ full-space coverage at a low energy consumption. The theoretical ergodic rate lower bound of our non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) scheme is derived based on the moment matching approximation method, while considering the signal distortion at transceivers imposed by hardware impairments (HWIs). Furthermore, the asymptotically ergodic rate lower bound is derived both for an infinite number of IOS elements and for continuous aperture surfaces. Both the theoretical analysis and the simulation results show that the achievable rate of the NOMA scheme is higher than that of its orthogonal multiple access counterpart. Furthermore, owing to the HWIs at the transceivers, the achievable rate saturates at high signal-to-noise ratio region, instead of reaching its theoretical maximum.
Energy-Efficient Reconfigurable Holographic Surfaces Operating in the Presence of Realistic Hardware Impairments
May 02, 2024



Abstract:Reconfigurable holographic surfaces (RHSs) constitute a promising technique of supporting energy-efficient communications. In this paper, we formulate the energy efficiency maximization problem of the switch-controlled RHS-aided beamforming architecture by alternately optimizing the holographic beamformer at the RHS, the digital beamformer, the total transmit power and the power sharing ratio of each user. Specifically, to deal with this challenging non-convex optimization problem, we decouple it into three sub-problems. Firstly, the coefficients of RHS elements responsible for the holographic beamformer are optimized to maximize the sum of the eigen-channel gains of all users by our proposed low-complexity eigen-decomposition (ED) method. Then, the digital beamformer is designed by the singular value decomposition (SVD) method to support multi-user information transfer. Finally, the total transmit power and the power sharing ratio are alternately optimized, while considering the effect of transceiver hardware impairments (HWI). We theoretically derive the spectral efficiency and energy efficiency performance upper bound for the RHS-based beamforming architectures in the presence of HWIs. Our simulation results show that the switch-controlled RHS-aided beamforming architecture achieves higher energy efficiency than the conventional fully digital beamformer and the hybrid beamformer based on phase shift arrays (PSA). Moreover, considering the effect of HWI in the beamforming design can bring about further energy efficiency enhancements.
Achievable Rate Analysis of the STAR-RIS Aided NOMA Uplink in the Face of Imperfect CSI and Hardware Impairments
Jun 14, 2023


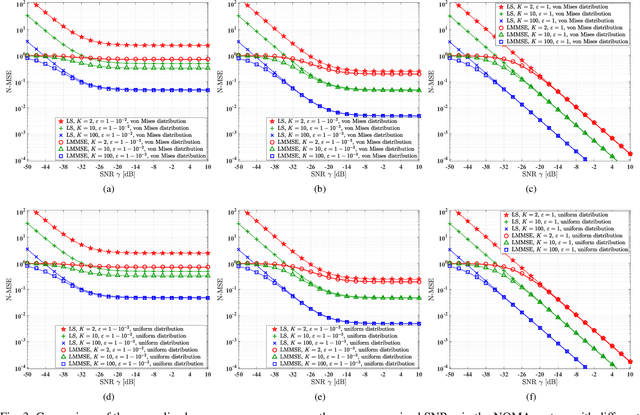
Abstract:Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RIS) are capable of beneficially ameliorating the propagation environment by appropriately controlling the passive reflecting elements. To extend the coverage area, the concept of simultaneous transmitting and reflecting reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (STAR-RIS) has been proposed, yielding supporting 360^circ coverage user equipment (UE) located on both sides of the RIS. In this paper, we theoretically formulate the ergodic sum-rate of the STAR-RIS assisted non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) uplink in the face of channel estimation errors and hardware impairments (HWI). Specifically, the STAR-RIS phase shift is configured based on the statistical channel state information (CSI), followed by linear minimum mean square error (LMMSE) channel estimation of the equivalent channel spanning from the UEs to the access point (AP). Afterwards, successive interference cancellation (SIC) is employed at the AP using the estimated instantaneous CSI, and we derive the theoretical ergodic sum-rate upper bound for both perfect and imperfect SIC decoding algorithm. The theoretical analysis and the simulation results show that both the channel estimation and the ergodic sum-rate have performance floor at high transmit power region caused by transceiver hardware impairments.
Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface Aided Amplitude- and Phase-Modulated Downlink Transmission
Jan 23, 2023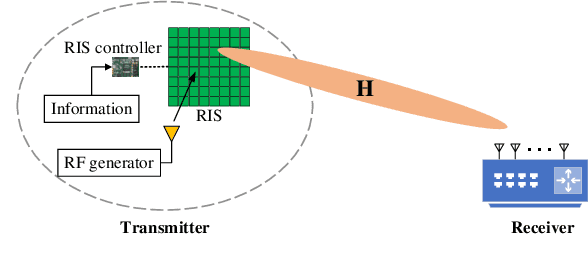
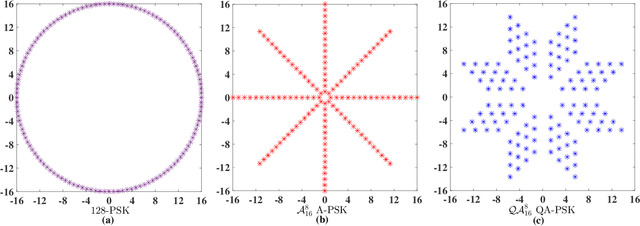
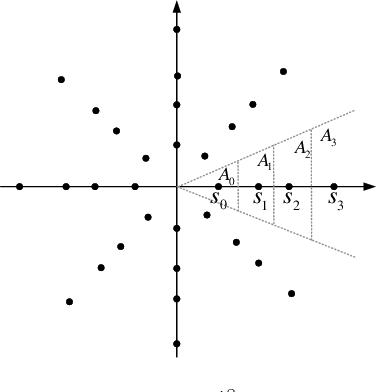
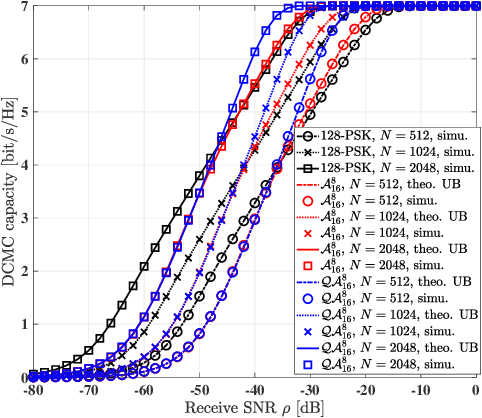
Abstract:New reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) based amplitude and phase modulation schemes are proposed as an evolution how the phase-only modulation schemes available in the literature. Explicitly, both the amplitude-phase shift keying (A-PSK) and quadrature amplitude-phase shift keying (QA-PSK) are conceived, where the RIS is assumed to be part of a transmitter to deliver information to the multi-antenna aided downlink receiver. In the proposed design, the RIS is partitioned into multiple blocks, and the information bits are conveyed by controlling both the ON-OFF state and the phase shift of the RIS elements in each block. Since the propagation paths spanning from each RIS block to the receiver can be coherently combined as a benefit of appropriately configuring the phase of the RIS elements, the received signal constellations can be designed by controlling both the ON-OFF pattern of the RIS blocks as well as the phase shift of the RIS elements. Both the theoretical analysis and the simulation results show that our proposed RIS-aided modulation schemes outperform the state-of-the-art RIS-based PSK modulation both in terms of its discrete-input-continuous-output memoryless channel (DCMC) capacity and its symbol error probability, especially in the high signal-to-noise-ratio (SNR) region, when considering realistic finite resolution RIS phase shifts.
Performance Analysis of Active RIS-aided Systems in the Face of Imperfect CSI and Phase Shift Noise
Jan 23, 2023



Abstract:The linear minimal mean square error (LMMSE) estimator for active reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS)-aided wireless systems is formulated. Furthermore, based on the moment-matching method, we employ the Gamma distribution to approximate the distribution of the instantaneous received signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio (SINR), and then derive the closed-form outage probability and ergodic channel capacity in the presence of realistic channel estimation errors, the thermal noise of RIS amplifiers and the RIS phase shift noise. Our theoretical analysis and simulation results show that the introduction of RIS amplifiers is equivalent to increasing of the transmit power, and also present the performance degradation resulting from the channel estimation error and the RIS phase noise.
Statistical CSI-based Beamforming for RIS-Aided Multiuser MISO Systems using Deep Reinforcement Learning
Sep 03, 2022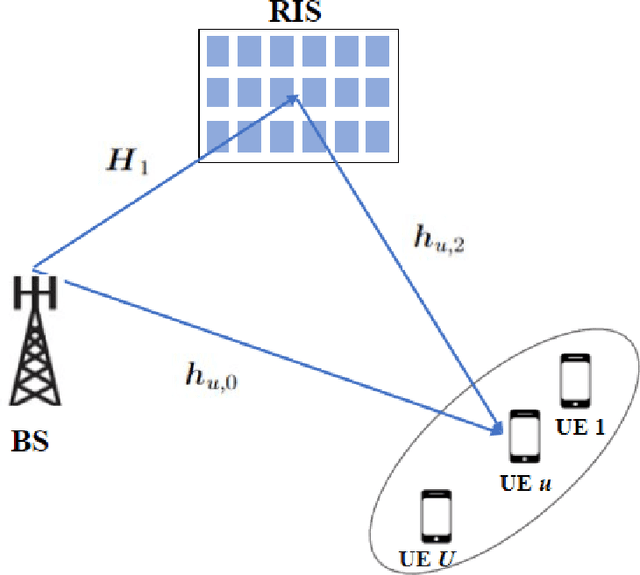
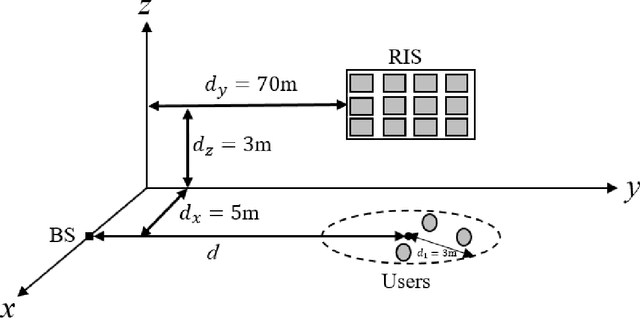
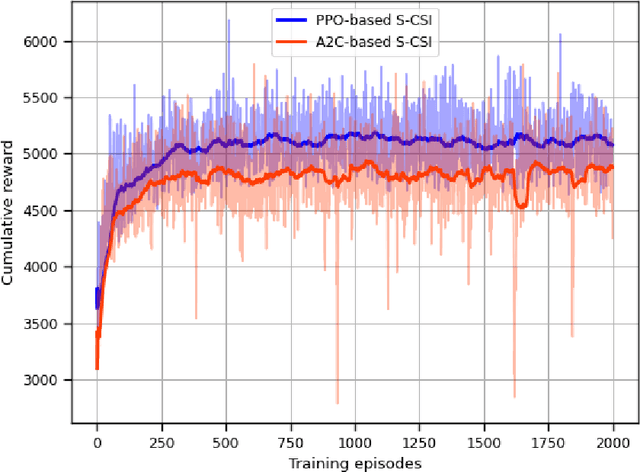
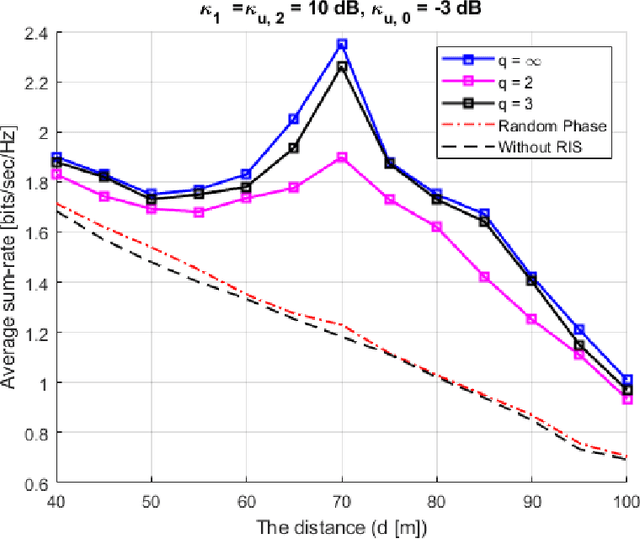
Abstract:The paper presents a joint beamforming algorithm using statistical channel state information (S-CSI) for reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RIS) for multiuser MISO wireless communications. We used S-CSI, which is a long-term average of the cascaded channel as opposed to instantaneous CSI utilized in most existing works. Through this method, the overhead of channel estimation is dramatically reduced. We propose a proximal policy optimization (PPO) algorithm which is a well-known actor-critic based reinforcement learning (RL) algorithm to solve the optimization problem. To test the efficacy of this algorithm, simulation results are presented along with evaluations of key system parameters, including the Rician factor and RIS location, on the achievable sum rate of the users.
Sim2real for Reinforcement Learning Driven Next Generation Networks
Jun 08, 2022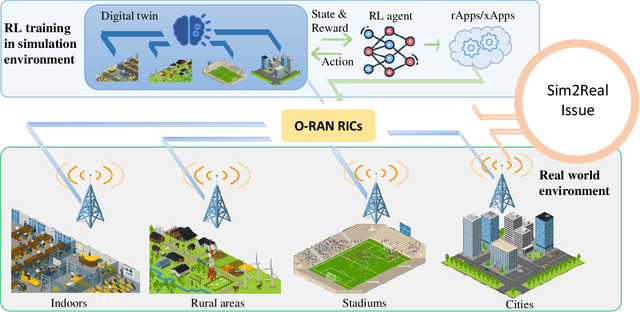
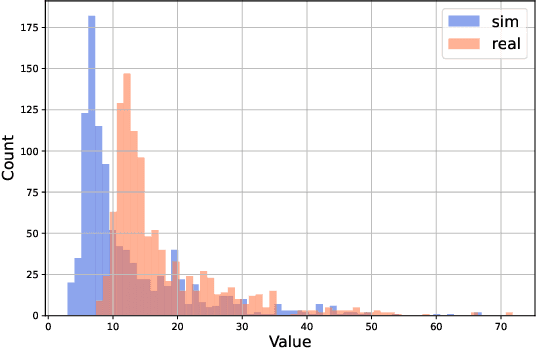
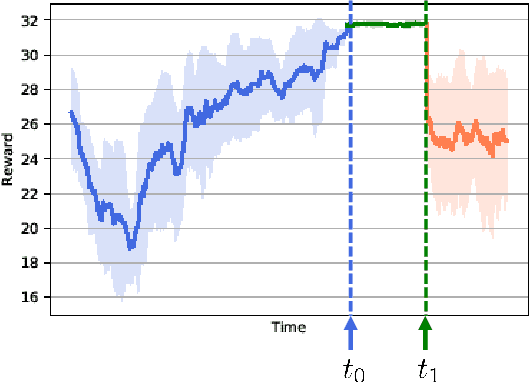

Abstract:The next generation of networks will actively embrace artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies for automation networks and optimal network operation strategies. The emerging network structure represented by Open RAN (O-RAN) conforms to this trend, and the radio intelligent controller (RIC) at the centre of its specification serves as an ML applications host. Various ML models, especially Reinforcement Learning (RL) models, are regarded as the key to solving RAN-related multi-objective optimization problems. However, it should be recognized that most of the current RL successes are confined to abstract and simplified simulation environments, which may not directly translate to high performance in complex real environments. One of the main reasons is the modelling gap between the simulation and the real environment, which could make the RL agent trained by simulation ill-equipped for the real environment. This issue is termed as the sim2real gap. This article brings to the fore the sim2real challenge within the context of O-RAN. Specifically, it emphasizes the characteristics, and benefits that the digital twins (DT) could have as a place for model development and verification. Several use cases are presented to exemplify and demonstrate failure modes of the simulations trained RL model in real environments. The effectiveness of DT in assisting the development of RL algorithms is discussed. Then the current state of the art learning-based methods commonly used to overcome the sim2real challenge are presented. Finally, the development and deployment concerns for the RL applications realisation in O-RAN are discussed from the view of the potential issues like data interaction, environment bottlenecks, and algorithm design.
Smart Interference Management xApp using Deep Reinforcement Learning
Apr 12, 2022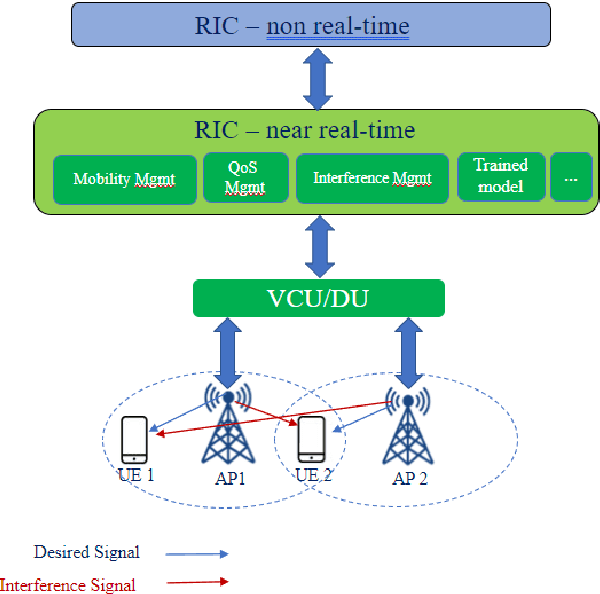
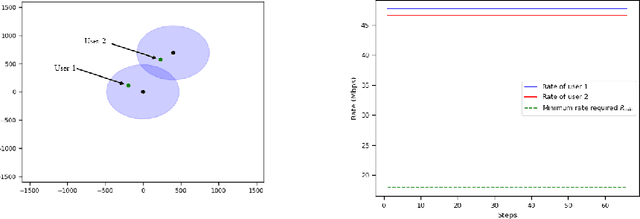
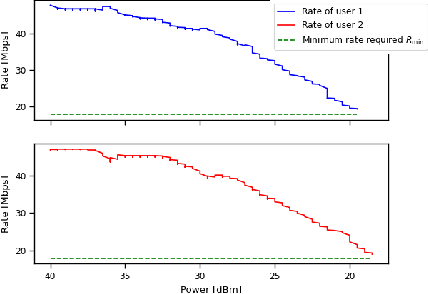

Abstract:Interference continues to be a key limiting factor in cellular radio access network (RAN) deployments. Effective, data-driven, self-adapting radio resource management (RRM) solutions are essential for tackling interference, and thus achieving the desired performance levels particularly at the cell-edge. In future network architecture, RAN intelligent controller (RIC) running with near-real-time applications, called xApps, is considered as a potential component to enable RRM. In this paper, based on deep reinforcement learning (RL) xApp, a joint sub-band masking and power management is proposed for smart interference management. The sub-band resource masking problem is formulated as a Markov Decision Process (MDP) that can be solved employing deep RL to approximate the policy functions as well as to avoid extremely high computational and storage costs of conventional tabular-based approaches. The developed xApp is scalable in both storage and computation. Simulation results demonstrate advantages of the proposed approach over decentralized baselines in terms of the trade-off between cell-centre and cell-edge user rates, energy efficiency and computational efficiency.
Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces Relying on Non-Diagonal Phase Shift Matrices
Mar 15, 2022
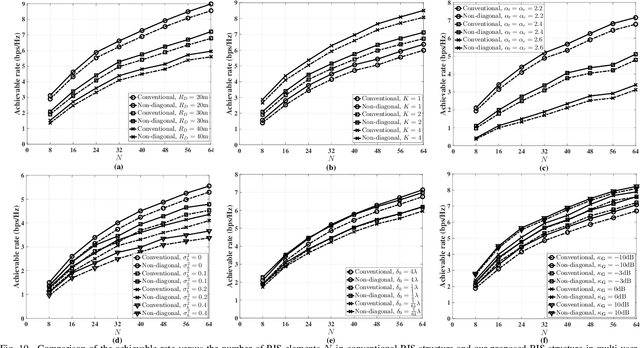


Abstract:Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RIS) have been actively researched as a potential technique for future wireless communications, which intelligently ameliorate the signal propagation environment. In the conventional design, each RIS element configures and reflects its received signal independently of all other RIS elements, which results in a diagonal phase shift matrix. By contrast, we propose a novel RIS architecture, where the incident signal impinging on one element can be reflected from another element after an appropriate phase shift adjustment, which increases the flexibility in the design of RIS phase shifts, hence, potentially improving the system performance. The resultant RIS phase shift matrix also has off-diagonal elements, as opposed to the pure diagonal structure of the conventional design. Compared to the state-of-art fully-connected/group-connected RIS structures, our proposed RIS architecture has lower complexity, while attaining a higher channel gain than the group-connected RIS structure, and approaching that of the fully-connected RIS structure. We formulate and solve the problem of maximizing the achievable rate of our proposed RIS architecture by jointly optimizing the transmit beamforming and the non-diagonal phase shift matrix based on alternating optimization and semi-define relaxation (SDR) methods. Moreover, the closed-form expressions of the channel gain, the outage probability and bit error ratio (BER) are derived. Simulation results demonstrate that our proposed RIS architecture results in an improved performance in terms of the achievable rate compared to the conventional architecture, both in single-user as well as in multi-user scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge