Junchen Liu
Beyond Conditional Computation: Retrieval-Augmented Genomic Foundation Models with Gengram
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Current genomic foundation models (GFMs) rely on extensive neural computation to implicitly approximate conserved biological motifs from single-nucleotide inputs. We propose Gengram, a conditional memory module that introduces an explicit and highly efficient lookup primitive for multi-base motifs via a genomic-specific hashing scheme, establishing genomic "syntax". Integrated into the backbone of state-of-the-art GFMs, Gengram achieves substantial gains (up to 14%) across several functional genomics tasks. The module demonstrates robust architectural generalization, while further inspection of Gengram's latent space reveals the emergence of meaningful representations that align closely with fundamental biological knowledge. By establishing structured motif memory as a modeling primitive, Gengram simultaneously boosts empirical performance and mechanistic interpretability, providing a scalable and biology-aligned pathway for the next generation of GFMs. The code is available at https://github.com/zhejianglab/Genos, and the model checkpoint is available at https://huggingface.co/ZhejiangLab/Gengram.
Beyond One-Way Pruning: Bidirectional Pruning-Regrowth for Extreme Accuracy-Sparsity Tradeoff
Nov 11, 2025Abstract:As a widely adopted model compression technique, model pruning has demonstrated strong effectiveness across various architectures. However, we observe that when sparsity exceeds a certain threshold, both iterative and one-shot pruning methods lead to a steep decline in model performance. This rapid degradation limits the achievable compression ratio and prevents models from meeting the stringent size constraints required by certain hardware platforms, rendering them inoperable. To overcome this limitation, we propose a bidirectional pruning-regrowth strategy. Starting from an extremely compressed network that satisfies hardware constraints, the method selectively regenerates critical connections to recover lost performance, effectively mitigating the sharp accuracy drop commonly observed under high sparsity conditions.
A Novel Multi-Reference-Point Modeling Framework for Monostatic Background Channel: Toward 3GPP ISAC Standardization
Nov 05, 2025Abstract:Integrated Sensing and Communication (ISAC) has been identified as a key 6G application by ITU and 3GPP. A realistic, standard-compatible channel model is essential for ISAC system design. To characterize the impact of Sensing Targets (STs), 3GPP defines ISAC channel as a combination of target and background channels, comprising multipath components related to STs and those originating solely from the environment, respectively. Although the background channel does not carry direct ST information, its accurate modeling is critical for evaluating sensing performance, especially in complex environments. Existing communication standards characterize propagation between separated transmitter (Tx) and receiver (Rx). However, modeling background channels in the ISAC monostatic mode, where the Tx and Rx are co-located, remains a pressing challenge. In this paper, we firstly conduct ISAC monostatic background channel measurements for an indoor scenario at 28 GHz. Realistic channel parameters are extracted, revealing pronounced single-hop propagation and discrete multipath distribution. Inspired by these properties, a novel stochastic model is proposed to characterizing the ISAC monostatic background channel as the superposition of sub-channels between the monostatic Tx&Rx and multiple communication Rx-like Reference Points (RPs). This model is compatible with standardizations, and a 3GPP-extended implementation framework is introduced. Finally, a genetic algorithm-based method is proposed to extract the optimal number and placement of multi-RPs. The optimization approach and modeling framework are validated by comparing measured and simulated channel parameters. Results demonstrate that the proposed model effectively captures monostatic background channel characteristics, addresses a critical gap in ISAC channel modeling, and supports 6G standardization.
SmallThinker: A Family of Efficient Large Language Models Natively Trained for Local Deployment
Jul 28, 2025Abstract:While frontier large language models (LLMs) continue to push capability boundaries, their deployment remains confined to GPU-powered cloud infrastructure. We challenge this paradigm with SmallThinker, a family of LLMs natively designed - not adapted - for the unique constraints of local devices: weak computational power, limited memory, and slow storage. Unlike traditional approaches that mainly compress existing models built for clouds, we architect SmallThinker from the ground up to thrive within these limitations. Our innovation lies in a deployment-aware architecture that transforms constraints into design principles. First, We introduce a two-level sparse structure combining fine-grained Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) with sparse feed-forward networks, drastically reducing computational demands without sacrificing model capacity. Second, to conquer the I/O bottleneck of slow storage, we design a pre-attention router that enables our co-designed inference engine to prefetch expert parameters from storage while computing attention, effectively hiding storage latency that would otherwise cripple on-device inference. Third, for memory efficiency, we utilize NoPE-RoPE hybrid sparse attention mechanism to slash KV cache requirements. We release SmallThinker-4B-A0.6B and SmallThinker-21B-A3B, which achieve state-of-the-art performance scores and even outperform larger LLMs. Remarkably, our co-designed system mostly eliminates the need for expensive GPU hardware: with Q4_0 quantization, both models exceed 20 tokens/s on ordinary consumer CPUs, while consuming only 1GB and 8GB of memory respectively. SmallThinker is publicly available at hf.co/PowerInfer/SmallThinker-4BA0.6B-Instruct and hf.co/PowerInfer/SmallThinker-21BA3B-Instruct.
ISAC Channel Modelling -- Perspectives from ETSI
May 15, 2025Abstract:Integrated Sensing and Communications (ISAC) is defined as one of six usage scenarios in the ITU-R International Mobile Telecommunications (IMT) 2030 framework for 6G. ISAC is envisioned to introduce the sensing capability into the cellular network, where sensing may be obtained using the cellular radio frequency (RF) signals with or without additional auxiliary sensors. To enable ISAC, specification bodies such as European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) and Third Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) have already started to look into detailed ISAC use cases, their requirements, and the channel models and evaluation methodologies that are necessary to design and evaluate ISAC performance. With focus on the channel model, the current communication-centric channel models like those specified in 3GPP technical report (TR) 38.901 do not cover the RF signals interactions between the transmitter, target object, receiver and their surrounding environment. To bridge this gap, 3GPP has been looking into the basic changes that are necessary to make to their TR38.901 channel model with focus on selected use cases from the 3GPP SA1 5G-Advanced feasibility study. In parallel, ETSI ISAC Industry Specification Group (ISG) has been studying the more advanced ISAC channel modelling features that are needed to support the variety of ISAC use cases envisioned in 6G. In this paper, we present the baseline and advanced features developed thus far in 3GPP and ETSI ISAC ISG, respectively, towards a comprehensive view of the ISAC channel model in 6G.
Light-R1: Curriculum SFT, DPO and RL for Long COT from Scratch and Beyond
Mar 13, 2025Abstract:This paper presents our work on the Light-R1 series, with models, data, and code all released. We first focus on training long COT models from scratch, specifically starting from models initially lacking long COT capabilities. Using a curriculum training recipe consisting of two-stage SFT and semi-on-policy DPO, we train our model Light-R1-32B from Qwen2.5-32B-Instruct, resulting in superior math performance compared to DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-32B. Despite being trained exclusively on math data, Light-R1-32B shows strong generalization across other domains. In the subsequent phase of this work, we highlight the significant benefit of the 3k dataset constructed for the second SFT stage on enhancing other models. By fine-tuning DeepSeek-R1-Distilled models using this dataset, we obtain new SOTA models in 7B and 14B, while the 32B model, Light-R1-32B-DS performed comparably to QwQ-32B and DeepSeek-R1. Furthermore, we extend our work by applying reinforcement learning, specifically GRPO, on long-COT models to further improve reasoning performance. We successfully train our final Light-R1-14B-DS with RL, achieving SOTA performance among 14B parameter models in math. With AIME24 & 25 scores of 74.0 and 60.2 respectively, Light-R1-14B-DS surpasses even many 32B models and DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Llama-70B. Its RL training also exhibits well expected behavior, showing simultaneous increase in response length and reward score. The Light-R1 series of work validates training long-COT models from scratch, showcases the art in SFT data and releases SOTA models from RL.
Rip-NeRF: Anti-aliasing Radiance Fields with Ripmap-Encoded Platonic Solids
May 03, 2024



Abstract:Despite significant advancements in Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs), the renderings may still suffer from aliasing and blurring artifacts, since it remains a fundamental challenge to effectively and efficiently characterize anisotropic areas induced by the cone-casting procedure. This paper introduces a Ripmap-Encoded Platonic Solid representation to precisely and efficiently featurize 3D anisotropic areas, achieving high-fidelity anti-aliasing renderings. Central to our approach are two key components: Platonic Solid Projection and Ripmap encoding. The Platonic Solid Projection factorizes the 3D space onto the unparalleled faces of a certain Platonic solid, such that the anisotropic 3D areas can be projected onto planes with distinguishable characterization. Meanwhile, each face of the Platonic solid is encoded by the Ripmap encoding, which is constructed by anisotropically pre-filtering a learnable feature grid, to enable featurzing the projected anisotropic areas both precisely and efficiently by the anisotropic area-sampling. Extensive experiments on both well-established synthetic datasets and a newly captured real-world dataset demonstrate that our Rip-NeRF attains state-of-the-art rendering quality, particularly excelling in the fine details of repetitive structures and textures, while maintaining relatively swift training times.
NeRRF: 3D Reconstruction and View Synthesis for Transparent and Specular Objects with Neural Refractive-Reflective Fields
Sep 22, 2023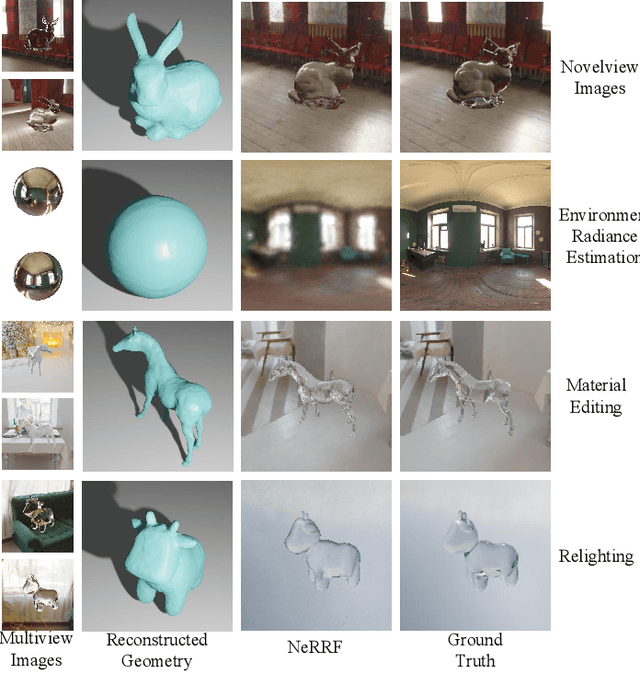
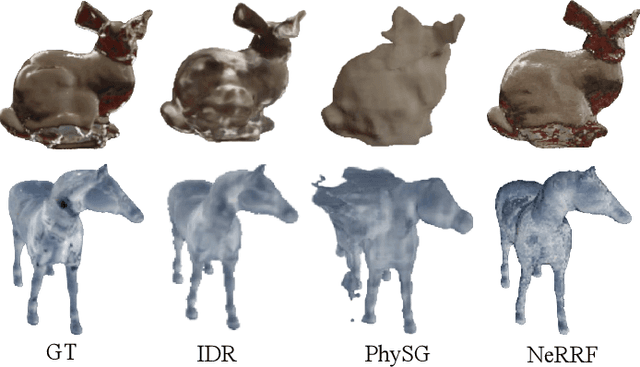

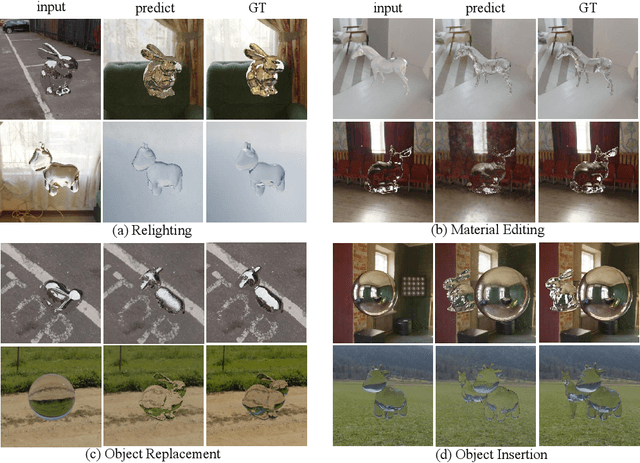
Abstract:Neural radiance fields (NeRF) have revolutionized the field of image-based view synthesis. However, NeRF uses straight rays and fails to deal with complicated light path changes caused by refraction and reflection. This prevents NeRF from successfully synthesizing transparent or specular objects, which are ubiquitous in real-world robotics and A/VR applications. In this paper, we introduce the refractive-reflective field. Taking the object silhouette as input, we first utilize marching tetrahedra with a progressive encoding to reconstruct the geometry of non-Lambertian objects and then model refraction and reflection effects of the object in a unified framework using Fresnel terms. Meanwhile, to achieve efficient and effective anti-aliasing, we propose a virtual cone supersampling technique. We benchmark our method on different shapes, backgrounds and Fresnel terms on both real-world and synthetic datasets. We also qualitatively and quantitatively benchmark the rendering results of various editing applications, including material editing, object replacement/insertion, and environment illumination estimation. Codes and data are publicly available at https://github.com/dawning77/NeRRF.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge