Keith Briggs
Monotone Optimisation with Learned Projections
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Monotone optimisation problems admit specialised global solvers such as the Polyblock Outer Approximation (POA) algorithm, but these methods typically require explicit objective and constraint functions. In many applications, these functions are only available through data, making POA difficult to apply directly. We introduce an algorithm-aware learning approach that integrates learned models into POA by directly predicting its projection primitive via the radial inverse, avoiding the costly bisection procedure used in standard POA. We propose Homogeneous-Monotone Radial Inverse (HM-RI) networks, structured neural architectures that enforce key monotonicity and homogeneity properties, enabling fast projection estimation. We provide a theoretical characterisation of radial inverse functions and show that, under mild structural conditions, a HM-RI predictor corresponds to the radial inverse of a valid set of monotone constraints. To reduce training overhead, we further develop relaxed monotonicity conditions that remain compatible with POA. Across multiple monotone optimisation benchmarks (indefinite quadratic programming, multiplicative programming, and transmit power optimisation), our approach yields substantial speed-ups in comparison to direct function estimation while maintaining strong solution quality, outperforming baselines that do not exploit monotonic structure.
Factored Value Functions for Graph-Based Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:Credit assignment is a core challenge in multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL), especially in large-scale systems with structured, local interactions. Graph-based Markov decision processes (GMDPs) capture such settings via an influence graph, but standard critics are poorly aligned with this structure: global value functions provide weak per-agent learning signals, while existing local constructions can be difficult to estimate and ill-behaved in infinite-horizon settings. We introduce the Diffusion Value Function (DVF), a factored value function for GMDPs that assigns to each agent a value component by diffusing rewards over the influence graph with temporal discounting and spatial attenuation. We show that DVF is well-defined, admits a Bellman fixed point, and decomposes the global discounted value via an averaging property. DVF can be used as a drop-in critic in standard RL algorithms and estimated scalably with graph neural networks. Building on DVF, we propose Diffusion A2C (DA2C) and a sparse message-passing actor, Learned DropEdge GNN (LD-GNN), for learning decentralised algorithms under communication costs. Across the firefighting benchmark and three distributed computation tasks (vector graph colouring and two transmit power optimisation problems), DA2C consistently outperforms local and global critic baselines, improving average reward by up to 11%.
Federated Meta-Learning for Traffic Steering in O-RAN
Sep 13, 2022



Abstract:The vision of 5G lies in providing high data rates, low latency (for the aim of near-real-time applications), significantly increased base station capacity, and near-perfect quality of service (QoS) for users, compared to LTE networks. In order to provide such services, 5G systems will support various combinations of access technologies such as LTE, NR, NR-U and Wi-Fi. Each radio access technology (RAT) provides different types of access, and these should be allocated and managed optimally among the users. Besides resource management, 5G systems will also support a dual connectivity service. The orchestration of the network therefore becomes a more difficult problem for system managers with respect to legacy access technologies. In this paper, we propose an algorithm for RAT allocation based on federated meta-learning (FML), which enables RAN intelligent controllers (RICs) to adapt more quickly to dynamically changing environments. We have designed a simulation environment which contains LTE and 5G NR service technologies. In the simulation, our objective is to fulfil UE demands within the deadline of transmission to provide higher QoS values. We compared our proposed algorithm with a single RL agent, the Reptile algorithm and a rule-based heuristic method. Simulation results show that the proposed FML method achieves higher caching rates at first deployment round 21% and 12% respectively. Moreover, proposed approach adapts to new tasks and environments most quickly amongst the compared methods.
Smart Interference Management xApp using Deep Reinforcement Learning
Apr 12, 2022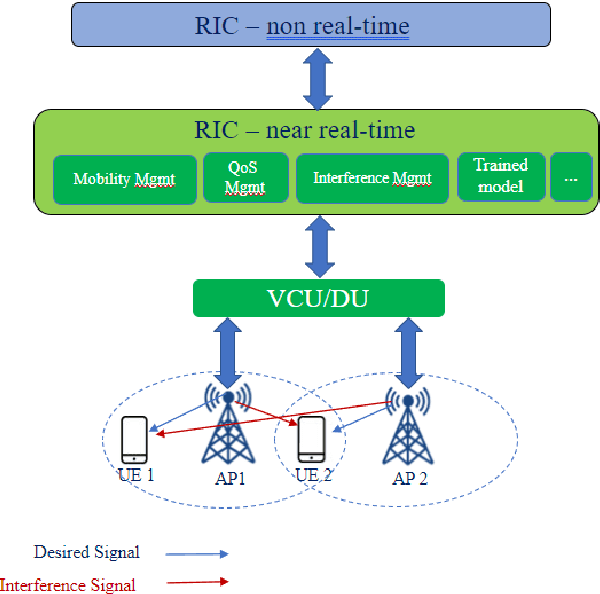
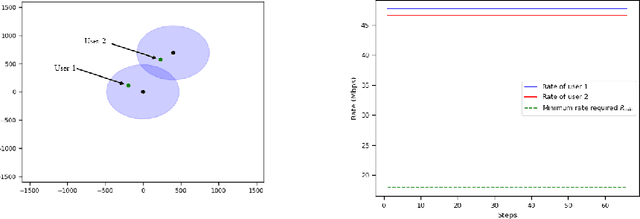
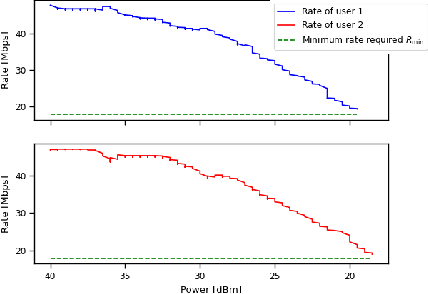

Abstract:Interference continues to be a key limiting factor in cellular radio access network (RAN) deployments. Effective, data-driven, self-adapting radio resource management (RRM) solutions are essential for tackling interference, and thus achieving the desired performance levels particularly at the cell-edge. In future network architecture, RAN intelligent controller (RIC) running with near-real-time applications, called xApps, is considered as a potential component to enable RRM. In this paper, based on deep reinforcement learning (RL) xApp, a joint sub-band masking and power management is proposed for smart interference management. The sub-band resource masking problem is formulated as a Markov Decision Process (MDP) that can be solved employing deep RL to approximate the policy functions as well as to avoid extremely high computational and storage costs of conventional tabular-based approaches. The developed xApp is scalable in both storage and computation. Simulation results demonstrate advantages of the proposed approach over decentralized baselines in terms of the trade-off between cell-centre and cell-edge user rates, energy efficiency and computational efficiency.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge