Rui Inacio
Federated Meta-Learning for Traffic Steering in O-RAN
Sep 13, 2022



Abstract:The vision of 5G lies in providing high data rates, low latency (for the aim of near-real-time applications), significantly increased base station capacity, and near-perfect quality of service (QoS) for users, compared to LTE networks. In order to provide such services, 5G systems will support various combinations of access technologies such as LTE, NR, NR-U and Wi-Fi. Each radio access technology (RAT) provides different types of access, and these should be allocated and managed optimally among the users. Besides resource management, 5G systems will also support a dual connectivity service. The orchestration of the network therefore becomes a more difficult problem for system managers with respect to legacy access technologies. In this paper, we propose an algorithm for RAT allocation based on federated meta-learning (FML), which enables RAN intelligent controllers (RICs) to adapt more quickly to dynamically changing environments. We have designed a simulation environment which contains LTE and 5G NR service technologies. In the simulation, our objective is to fulfil UE demands within the deadline of transmission to provide higher QoS values. We compared our proposed algorithm with a single RL agent, the Reptile algorithm and a rule-based heuristic method. Simulation results show that the proposed FML method achieves higher caching rates at first deployment round 21% and 12% respectively. Moreover, proposed approach adapts to new tasks and environments most quickly amongst the compared methods.
Sim2real for Reinforcement Learning Driven Next Generation Networks
Jun 08, 2022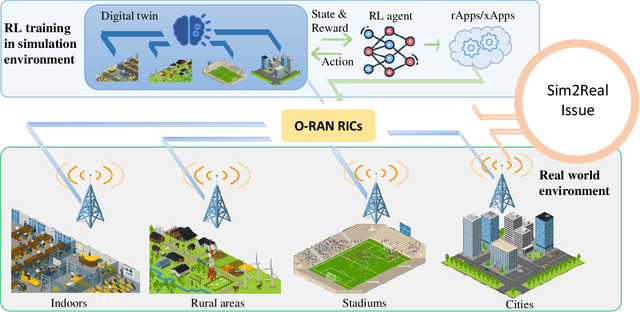
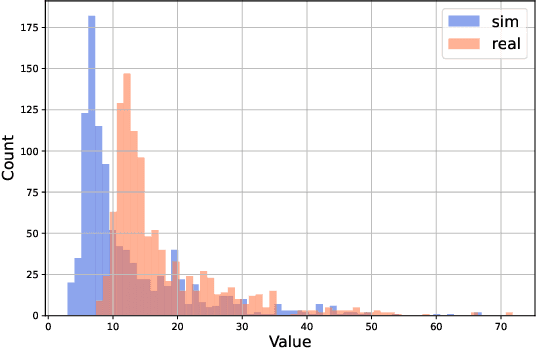
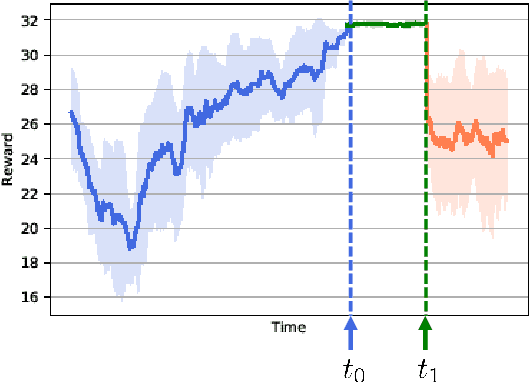

Abstract:The next generation of networks will actively embrace artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies for automation networks and optimal network operation strategies. The emerging network structure represented by Open RAN (O-RAN) conforms to this trend, and the radio intelligent controller (RIC) at the centre of its specification serves as an ML applications host. Various ML models, especially Reinforcement Learning (RL) models, are regarded as the key to solving RAN-related multi-objective optimization problems. However, it should be recognized that most of the current RL successes are confined to abstract and simplified simulation environments, which may not directly translate to high performance in complex real environments. One of the main reasons is the modelling gap between the simulation and the real environment, which could make the RL agent trained by simulation ill-equipped for the real environment. This issue is termed as the sim2real gap. This article brings to the fore the sim2real challenge within the context of O-RAN. Specifically, it emphasizes the characteristics, and benefits that the digital twins (DT) could have as a place for model development and verification. Several use cases are presented to exemplify and demonstrate failure modes of the simulations trained RL model in real environments. The effectiveness of DT in assisting the development of RL algorithms is discussed. Then the current state of the art learning-based methods commonly used to overcome the sim2real challenge are presented. Finally, the development and deployment concerns for the RL applications realisation in O-RAN are discussed from the view of the potential issues like data interaction, environment bottlenecks, and algorithm design.
RLOps: Development Life-cycle of Reinforcement Learning Aided Open RAN
Nov 12, 2021
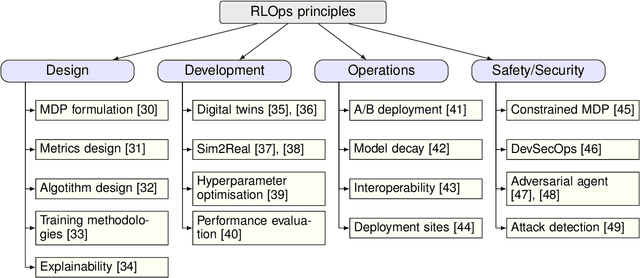

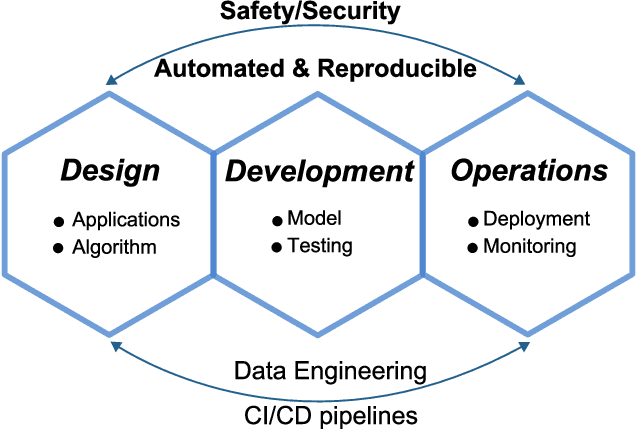
Abstract:Radio access network (RAN) technologies continue to witness massive growth, with Open RAN gaining the most recent momentum. In the O-RAN specifications, the RAN intelligent controller (RIC) serves as an automation host. This article introduces principles for machine learning (ML), in particular, reinforcement learning (RL) relevant for the O-RAN stack. Furthermore, we review state-of-the-art research in wireless networks and cast it onto the RAN framework and the hierarchy of the O-RAN architecture. We provide a taxonomy of the challenges faced by ML/RL models throughout the development life-cycle: from the system specification to production deployment (data acquisition, model design, testing and management, etc.). To address the challenges, we integrate a set of existing MLOps principles with unique characteristics when RL agents are considered. This paper discusses a systematic life-cycle model development, testing and validation pipeline, termed: RLOps. We discuss all fundamental parts of RLOps, which include: model specification, development and distillation, production environment serving, operations monitoring, safety/security and data engineering platform. Based on these principles, we propose the best practices for RLOps to achieve an automated and reproducible model development process.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge