Apostol Vassilev
On the Assessment of Sensitivity of Autonomous Vehicle Perception
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:The viability of automated driving is heavily dependent on the performance of perception systems to provide real-time accurate and reliable information for robust decision-making and maneuvers. These systems must perform reliably not only under ideal conditions, but also when challenged by natural and adversarial driving factors. Both of these types of interference can lead to perception errors and delays in detection and classification. Hence, it is essential to assess the robustness of the perception systems of automated vehicles (AVs) and explore strategies for making perception more reliable. We approach this problem by evaluating perception performance using predictive sensitivity quantification based on an ensemble of models, capturing model disagreement and inference variability across multiple models, under adverse driving scenarios in both simulated environments and real-world conditions. A notional architecture for assessing perception performance is proposed. A perception assessment criterion is developed based on an AV's stopping distance at a stop sign on varying road surfaces, such as dry and wet asphalt, and vehicle speed. Five state-of-the-art computer vision models are used, including YOLO (v8-v9), DEtection TRansformer (DETR50, DETR101), Real-Time DEtection TRansformer (RT-DETR)in our experiments. Diminished lighting conditions, e.g., resulting from the presence of fog and low sun altitude, have the greatest impact on the performance of the perception models. Additionally, adversarial road conditions such as occlusions of roadway objects increase perception sensitivity and model performance drops when faced with a combination of adversarial road conditions and inclement weather conditions. Also, it is demonstrated that the greater the distance to a roadway object, the greater the impact on perception performance, hence diminished perception robustness.
Robust AI Security and Alignment: A Sisyphean Endeavor?
Dec 10, 2025
Abstract:This manuscript establishes information-theoretic limitations for robustness of AI security and alignment by extending Gödel's incompleteness theorem to AI. Knowing these limitations and preparing for the challenges they bring is critically important for the responsible adoption of the AI technology. Practical approaches to dealing with these challenges are provided as well. Broader implications for cognitive reasoning limitations of AI systems are also proven.
Meta learning with language models: Challenges and opportunities in the classification of imbalanced text
Oct 24, 2023Abstract:Detecting out of policy speech (OOPS) content is important but difficult. While machine learning is a powerful tool to tackle this challenging task, it is hard to break the performance ceiling due to factors like quantity and quality limitations on training data and inconsistencies in OOPS definition and data labeling. To realize the full potential of available limited resources, we propose a meta learning technique (MLT) that combines individual models built with different text representations. We analytically show that the resulting technique is numerically stable and produces reasonable combining weights. We combine the MLT with a threshold-moving (TM) technique to further improve the performance of the combined predictor on highly-imbalanced in-distribution and out-of-distribution datasets. We also provide computational results to show the statistically significant advantages of the proposed MLT approach. All authors contributed equally to this work.
Evaluating the Social Impact of Generative AI Systems in Systems and Society
Jun 12, 2023Abstract:Generative AI systems across modalities, ranging from text, image, audio, and video, have broad social impacts, but there exists no official standard for means of evaluating those impacts and which impacts should be evaluated. We move toward a standard approach in evaluating a generative AI system for any modality, in two overarching categories: what is able to be evaluated in a base system that has no predetermined application and what is able to be evaluated in society. We describe specific social impact categories and how to approach and conduct evaluations in the base technical system, then in people and society. Our framework for a base system defines seven categories of social impact: bias, stereotypes, and representational harms; cultural values and sensitive content; disparate performance; privacy and data protection; financial costs; environmental costs; and data and content moderation labor costs. Suggested methods for evaluation apply to all modalities and analyses of the limitations of existing evaluations serve as a starting point for necessary investment in future evaluations. We offer five overarching categories for what is able to be evaluated in society, each with their own subcategories: trustworthiness and autonomy; inequality, marginalization, and violence; concentration of authority; labor and creativity; and ecosystem and environment. Each subcategory includes recommendations for mitigating harm. We are concurrently crafting an evaluation repository for the AI research community to contribute existing evaluations along the given categories. This version will be updated following a CRAFT session at ACM FAccT 2023.
Can you tell? SSNet -- a Sagittal Stratum-inspired Neural Network Framework for Sentiment Analysis
Jun 23, 2020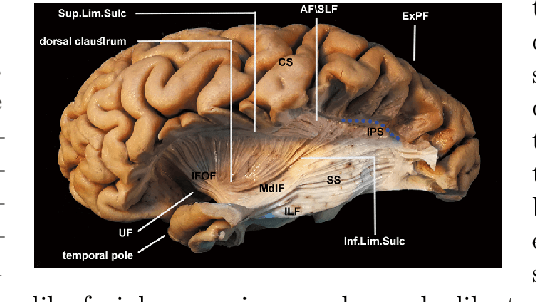
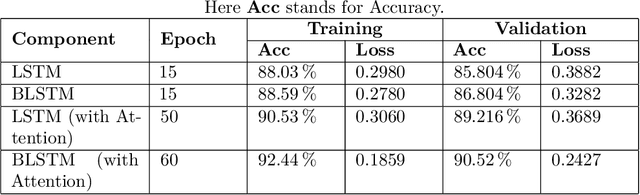
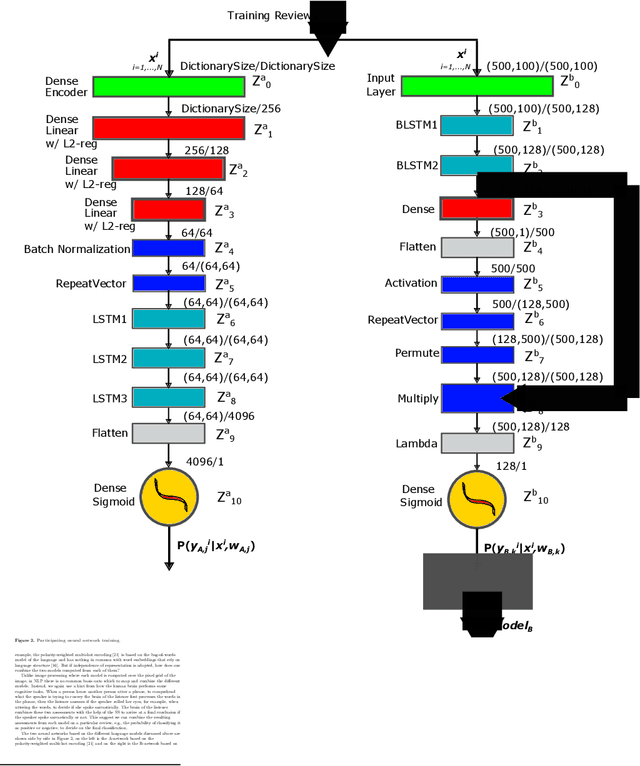

Abstract:When people try to understand nuanced language they typically process multiple input sensor modalities to complete this cognitive task. It turns out the human brain has even a specialized neuron formation, called sagittal stratum, to help us understand sarcasm. We use this biological formation as the inspiration for designing a neural network architecture that combines predictions of different models on the same text to construct a robust, accurate and computationally efficient classifier for sentiment analysis. Experimental results on representative benchmark datasets and comparisons to other methods1show the advantages of the new network architecture.
BowTie - A deep learning feedforward neural network for sentiment analysis
Apr 18, 2019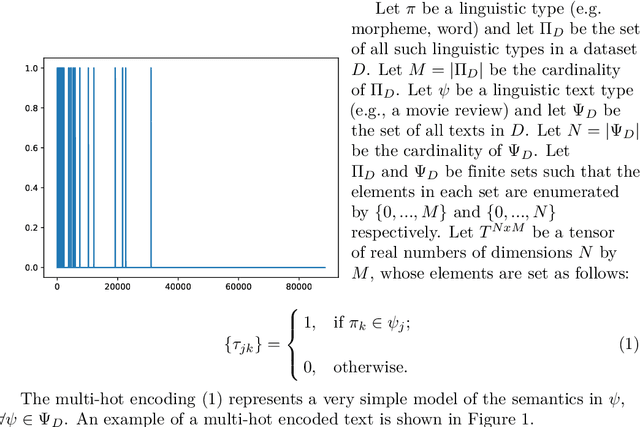
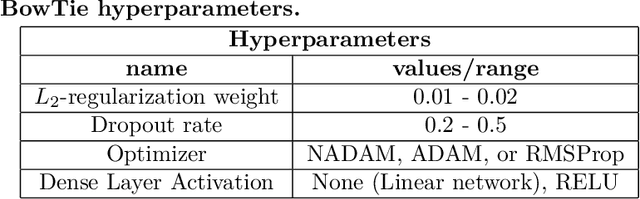
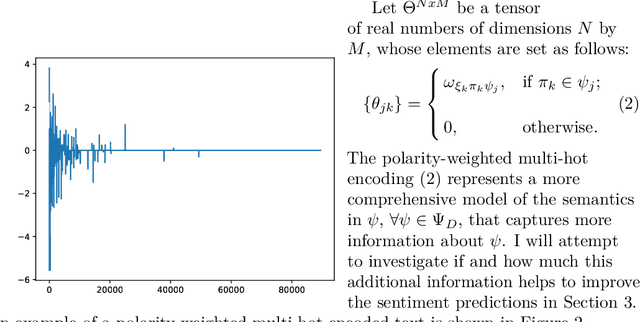
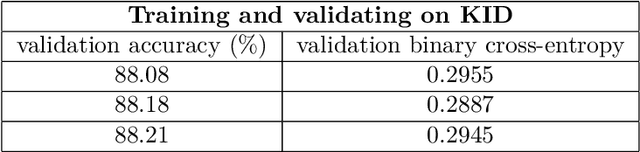
Abstract:How to model and encode the semantics of human-written text and select the type of neural network to process it are not settled issues in sentiment analysis. Accuracy and transferability are critical issues in machine learning in general. These properties are closely related to the loss estimates for the trained model. I present a computationally-efficient and accurate feedforward neural network for sentiment prediction capable of maintaining low losses. When coupled with an effective semantics model of the text, it provides highly accurate models with low losses. Experimental results on representative benchmark datasets and comparisons to other methods show the advantages of the new approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge