Munawar Hasan
Department of Computer Science, IIIT-Delhi, India
On the Assessment of Sensitivity of Autonomous Vehicle Perception
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:The viability of automated driving is heavily dependent on the performance of perception systems to provide real-time accurate and reliable information for robust decision-making and maneuvers. These systems must perform reliably not only under ideal conditions, but also when challenged by natural and adversarial driving factors. Both of these types of interference can lead to perception errors and delays in detection and classification. Hence, it is essential to assess the robustness of the perception systems of automated vehicles (AVs) and explore strategies for making perception more reliable. We approach this problem by evaluating perception performance using predictive sensitivity quantification based on an ensemble of models, capturing model disagreement and inference variability across multiple models, under adverse driving scenarios in both simulated environments and real-world conditions. A notional architecture for assessing perception performance is proposed. A perception assessment criterion is developed based on an AV's stopping distance at a stop sign on varying road surfaces, such as dry and wet asphalt, and vehicle speed. Five state-of-the-art computer vision models are used, including YOLO (v8-v9), DEtection TRansformer (DETR50, DETR101), Real-Time DEtection TRansformer (RT-DETR)in our experiments. Diminished lighting conditions, e.g., resulting from the presence of fog and low sun altitude, have the greatest impact on the performance of the perception models. Additionally, adversarial road conditions such as occlusions of roadway objects increase perception sensitivity and model performance drops when faced with a combination of adversarial road conditions and inclement weather conditions. Also, it is demonstrated that the greater the distance to a roadway object, the greater the impact on perception performance, hence diminished perception robustness.
Meta learning with language models: Challenges and opportunities in the classification of imbalanced text
Oct 24, 2023Abstract:Detecting out of policy speech (OOPS) content is important but difficult. While machine learning is a powerful tool to tackle this challenging task, it is hard to break the performance ceiling due to factors like quantity and quality limitations on training data and inconsistencies in OOPS definition and data labeling. To realize the full potential of available limited resources, we propose a meta learning technique (MLT) that combines individual models built with different text representations. We analytically show that the resulting technique is numerically stable and produces reasonable combining weights. We combine the MLT with a threshold-moving (TM) technique to further improve the performance of the combined predictor on highly-imbalanced in-distribution and out-of-distribution datasets. We also provide computational results to show the statistically significant advantages of the proposed MLT approach. All authors contributed equally to this work.
Can you tell? SSNet -- a Sagittal Stratum-inspired Neural Network Framework for Sentiment Analysis
Jun 23, 2020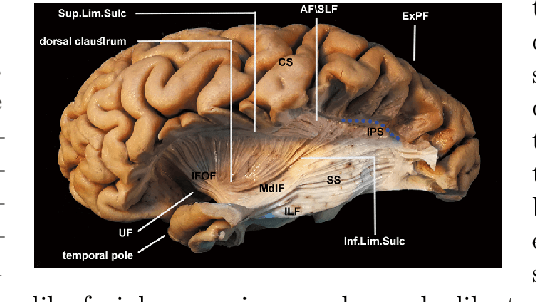
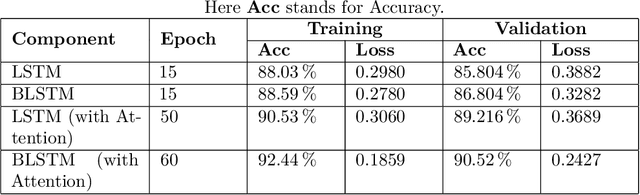
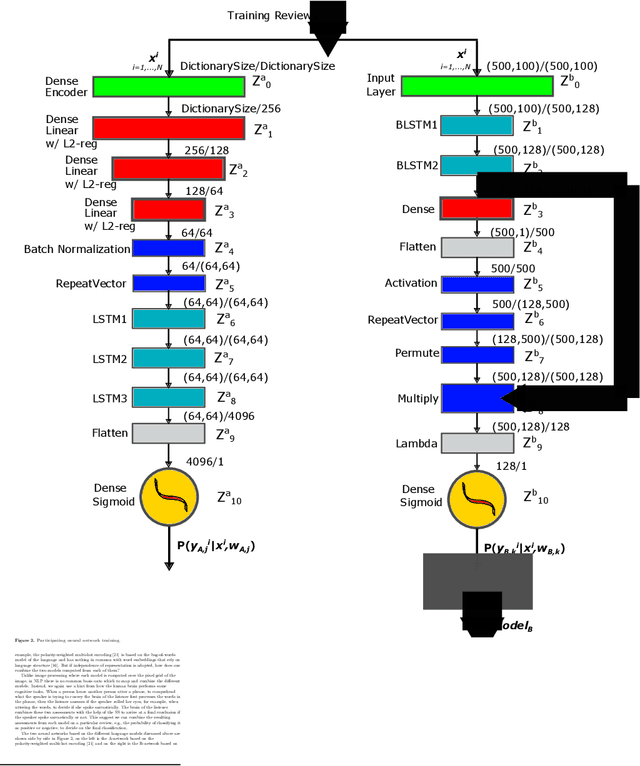

Abstract:When people try to understand nuanced language they typically process multiple input sensor modalities to complete this cognitive task. It turns out the human brain has even a specialized neuron formation, called sagittal stratum, to help us understand sarcasm. We use this biological formation as the inspiration for designing a neural network architecture that combines predictions of different models on the same text to construct a robust, accurate and computationally efficient classifier for sentiment analysis. Experimental results on representative benchmark datasets and comparisons to other methods1show the advantages of the new network architecture.
Multi-lane Detection Using Instance Segmentation and Attentive Voting
Jan 01, 2020



Abstract:Autonomous driving is becoming one of the leading industrial research areas. Therefore many automobile companies are coming up with semi to fully autonomous driving solutions. Among these solutions, lane detection is one of the vital driver-assist features that play a crucial role in the decision-making process of the autonomous vehicle. A variety of solutions have been proposed to detect lanes on the road, which ranges from using hand-crafted features to the state-of-the-art end-to-end trainable deep learning architectures. Most of these architectures are trained in a traffic constrained environment. In this paper, we propose a novel solution to multi-lane detection, which outperforms state of the art methods in terms of both accuracy and speed. To achieve this, we also offer a dataset with a more intuitive labeling scheme as compared to other benchmark datasets. Using our approach, we are able to obtain a lane segmentation accuracy of 99.87% running at 54.53 fps (average).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge