Anirudh Nair
Where Did It All Go Wrong? A Hierarchical Look into Multi-Agent Error Attribution
Oct 06, 2025Abstract:Error attribution in Large Language Model (LLM) multi-agent systems presents a significant challenge in debugging and improving collaborative AI systems. Current approaches to pinpointing agent and step level failures in interaction traces - whether using all-at-once evaluation, step-by-step analysis, or binary search - fall short when analyzing complex patterns, struggling with both accuracy and consistency. We present ECHO (Error attribution through Contextual Hierarchy and Objective consensus analysis), a novel algorithm that combines hierarchical context representation, objective analysis-based evaluation, and consensus voting to improve error attribution accuracy. Our approach leverages a positional-based leveling of contextual understanding while maintaining objective evaluation criteria, ultimately reaching conclusions through a consensus mechanism. Experimental results demonstrate that ECHO outperforms existing methods across various multi-agent interaction scenarios, showing particular strength in cases involving subtle reasoning errors and complex interdependencies. Our findings suggest that leveraging these concepts of structured, hierarchical context representation combined with consensus-based objective decision-making, provides a more robust framework for error attribution in multi-agent systems.
Benchmarking Reinforcement Learning Techniques for Autonomous Navigation
Oct 10, 2022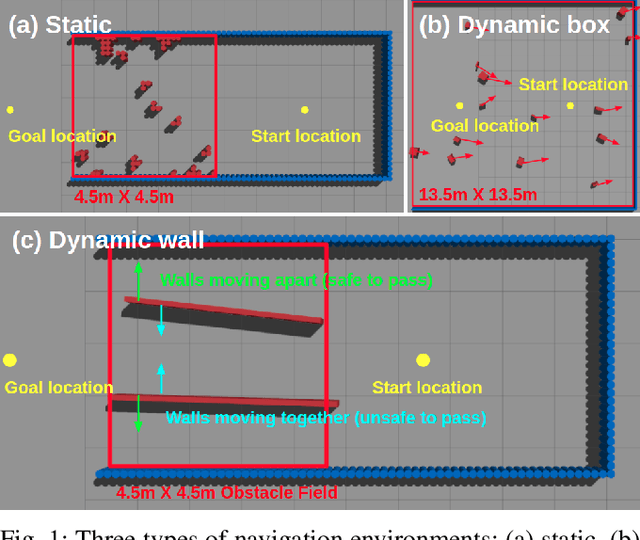
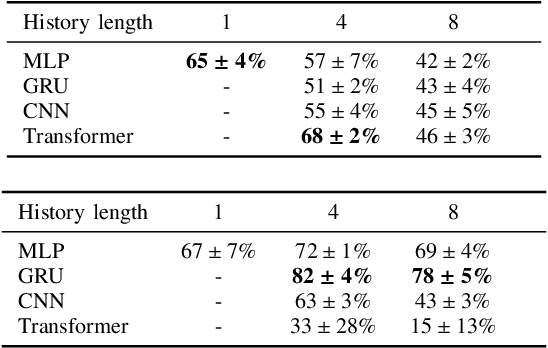
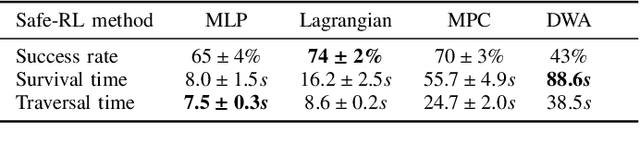
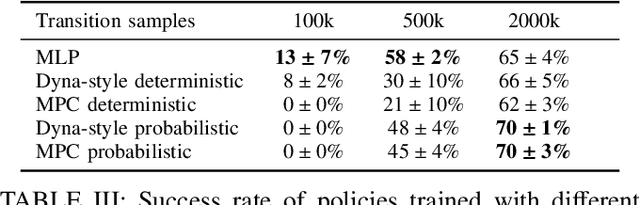
Abstract:Deep reinforcement learning (RL) has brought many successes for autonomous robot navigation. However, there still exists important limitations that prevent real-world use of RL-based navigation systems. For example, most learning approaches lack safety guarantees; and learned navigation systems may not generalize well to unseen environments. Despite a variety of recent learning techniques to tackle these challenges in general, a lack of an open-source benchmark and reproducible learning methods specifically for autonomous navigation makes it difficult for roboticists to choose what learning methods to use for their mobile robots and for learning researchers to identify current shortcomings of general learning methods for autonomous navigation. In this paper, we identify four major desiderata of applying deep RL approaches for autonomous navigation: (D1) reasoning under uncertainty, (D2) safety, (D3) learning from limited trial-and-error data, and (D4) generalization to diverse and novel environments. Then, we explore four major classes of learning techniques with the purpose of achieving one or more of the four desiderata: memory-based neural network architectures (D1), safe RL (D2), model-based RL (D2, D3), and domain randomization (D4). By deploying these learning techniques in a new open-source large-scale navigation benchmark and real-world environments, we perform a comprehensive study aimed at establishing to what extent can these techniques achieve these desiderata for RL-based navigation systems.
Learning Real-world Autonomous Navigation by Self-Supervised Environment Synthesis
Oct 10, 2022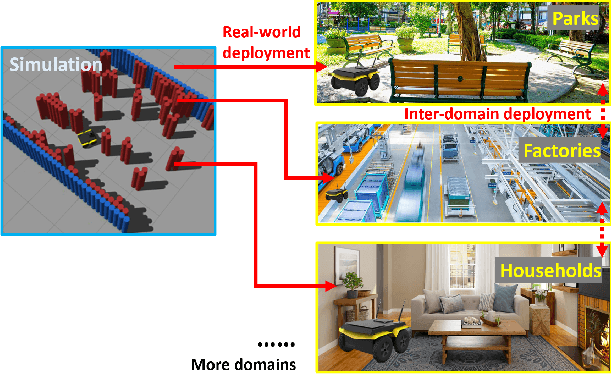
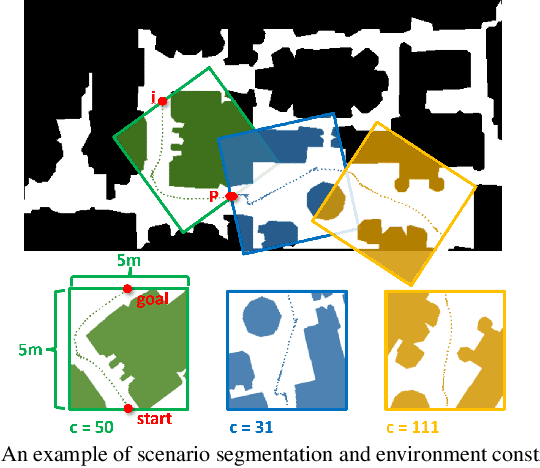
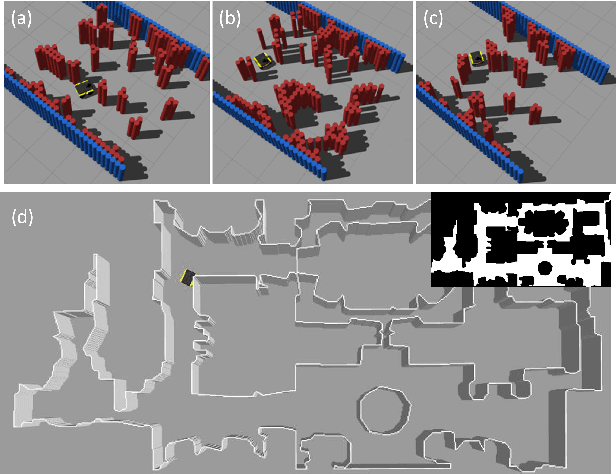

Abstract:Machine learning approaches have recently enabled autonomous navigation for mobile robots in a data-driven manner. Since most existing learning-based navigation systems are trained with data generated in artificially created training environments, during real-world deployment at scale, it is inevitable that robots will encounter unseen scenarios, which are out of the training distribution and therefore lead to poor real-world performance. On the other hand, directly training in the real world is generally unsafe and inefficient. To address this issue, we introduce Self-supervised Environment Synthesis (SES), in which, after real-world deployment with safety and efficiency requirements, autonomous mobile robots can utilize experience from the real-world deployment, reconstruct navigation scenarios, and synthesize representative training environments in simulation. Training in these synthesized environments leads to improved future performance in the real world. The effectiveness of SES at synthesizing representative simulation environments and improving real-world navigation performance is evaluated via a large-scale deployment in a high-fidelity, realistic simulator and a small-scale deployment on a physical robot.
Socially Compliant Navigation Dataset (SCAND): A Large-Scale Dataset of Demonstrations for Social Navigation
Mar 28, 2022


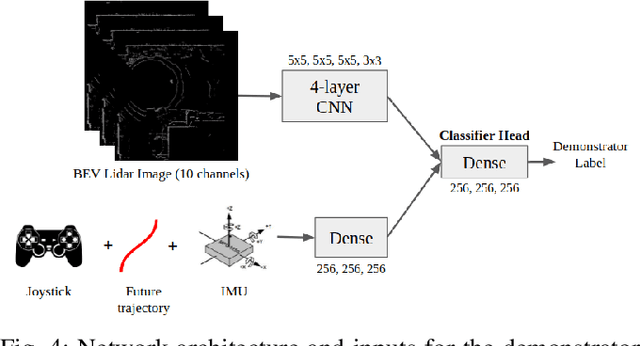
Abstract:Social navigation is the capability of an autonomous agent, such as a robot, to navigate in a 'socially compliant' manner in the presence of other intelligent agents such as humans. With the emergence of autonomously navigating mobile robots in human populated environments (e.g., domestic service robots in homes and restaurants and food delivery robots on public sidewalks), incorporating socially compliant navigation behaviors on these robots becomes critical to ensuring safe and comfortable human robot coexistence. To address this challenge, imitation learning is a promising framework, since it is easier for humans to demonstrate the task of social navigation rather than to formulate reward functions that accurately capture the complex multi objective setting of social navigation. The use of imitation learning and inverse reinforcement learning to social navigation for mobile robots, however, is currently hindered by a lack of large scale datasets that capture socially compliant robot navigation demonstrations in the wild. To fill this gap, we introduce Socially CompliAnt Navigation Dataset (SCAND) a large scale, first person view dataset of socially compliant navigation demonstrations. Our dataset contains 8.7 hours, 138 trajectories, 25 miles of socially compliant, human teleoperated driving demonstrations that comprises multi modal data streams including 3D lidar, joystick commands, odometry, visual and inertial information, collected on two morphologically different mobile robots a Boston Dynamics Spot and a Clearpath Jackal by four different human demonstrators in both indoor and outdoor environments. We additionally perform preliminary analysis and validation through real world robot experiments and show that navigation policies learned by imitation learning on SCAND generate socially compliant behaviors
APPL: Adaptive Planner Parameter Learning
May 17, 2021



Abstract:While current autonomous navigation systems allow robots to successfully drive themselves from one point to another in specific environments, they typically require extensive manual parameter re-tuning by human robotics experts in order to function in new environments. Furthermore, even for just one complex environment, a single set of fine-tuned parameters may not work well in different regions of that environment. These problems prohibit reliable mobile robot deployment by non-expert users. As a remedy, we propose Adaptive Planner Parameter Learning (APPL), a machine learning framework that can leverage non-expert human interaction via several modalities -- including teleoperated demonstrations, corrective interventions, and evaluative feedback -- and also unsupervised reinforcement learning to learn a parameter policy that can dynamically adjust the parameters of classical navigation systems in response to changes in the environment. APPL inherits safety and explainability from classical navigation systems while also enjoying the benefits of machine learning, i.e., the ability to adapt and improve from experience. We present a suite of individual APPL methods and also a unifying cycle-of-learning scheme that combines all the proposed methods in a framework that can improve navigation performance through continual, iterative human interaction and simulation training.
APPLR: Adaptive Planner Parameter Learning from Reinforcement
Nov 01, 2020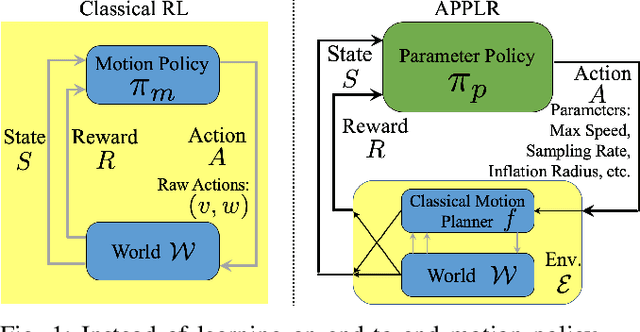

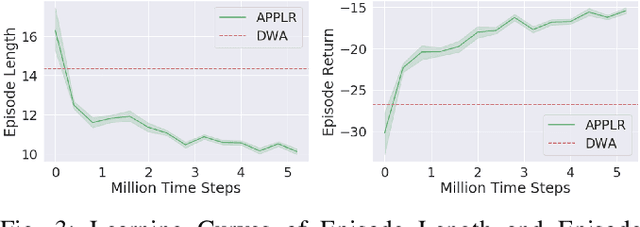
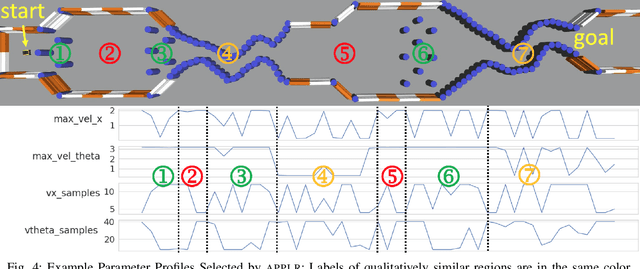
Abstract:Classical navigation systems typically operate using a fixed set of hand-picked parameters (e.g. maximum speed, sampling rate, inflation radius, etc.) and require heavy expert re-tuning in order to work in new environments. To mitigate this requirement, it has been proposed to learn parameters for different contexts in a new environment using human demonstrations collected via teleoperation. However, learning from human demonstration limits deployment to the training environment, and limits overall performance to that of a potentially-suboptimal demonstrator. In this paper, we introduce APPLR, Adaptive Planner Parameter Learning from Reinforcement, which allows existing navigation systems to adapt to new scenarios by using a parameter selection scheme discovered via reinforcement learning (RL) in a wide variety of simulation environments. We evaluate APPLR on a robot in both simulated and physical experiments, and show that it can outperform both a fixed set of hand-tuned parameters and also a dynamic parameter tuning scheme learned from human demonstration.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge