Aniket Deshmukh
Multi-Objective Alignment of Large Language Models Through Hypervolume Maximization
Dec 06, 2024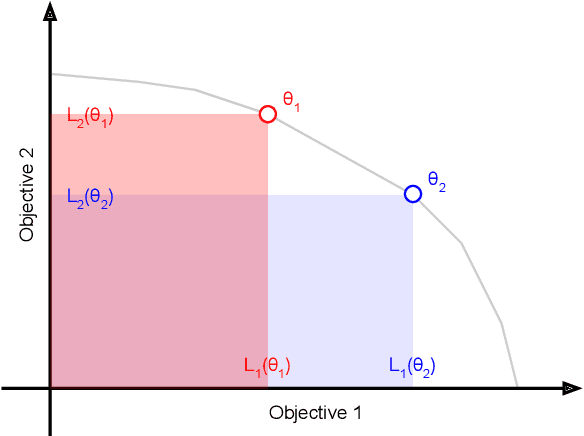

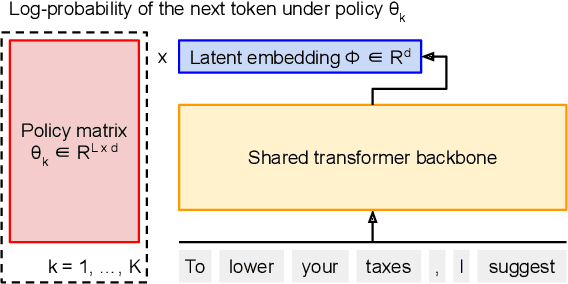

Abstract:Multi-objective alignment from human feedback (MOAHF) in large language models (LLMs) is a challenging problem as human preferences are complex, multifaceted, and often conflicting. Recent works on MOAHF considered a-priori multi-objective optimization (MOO), where human preferences are known at training or inference time. In contrast, when human preferences are unknown or difficult to quantify, a natural approach is to cover the Pareto front by multiple diverse solutions. We propose an algorithm HaM for learning diverse LLM policies that maximizes their hypervolume. This is the first application of a-posteriori MOO to MOAHF. HaM is computationally and space efficient, and empirically superior across objectives such as harmlessness, helpfulness, humor, faithfulness, and hallucination, on various datasets.
Online Posterior Sampling with a Diffusion Prior
Oct 04, 2024
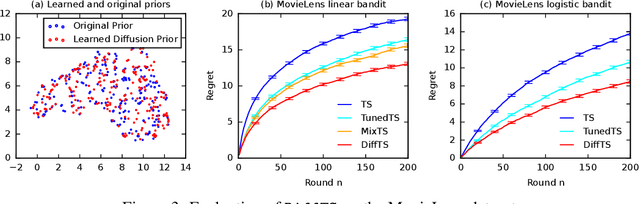


Abstract:Posterior sampling in contextual bandits with a Gaussian prior can be implemented exactly or approximately using the Laplace approximation. The Gaussian prior is computationally efficient but it cannot describe complex distributions. In this work, we propose approximate posterior sampling algorithms for contextual bandits with a diffusion model prior. The key idea is to sample from a chain of approximate conditional posteriors, one for each stage of the reverse process, which are estimated in a closed form using the Laplace approximation. Our approximations are motivated by posterior sampling with a Gaussian prior, and inherit its simplicity and efficiency. They are asymptotically consistent and perform well empirically on a variety of contextual bandit problems.
Optimal Design for Human Feedback
Apr 22, 2024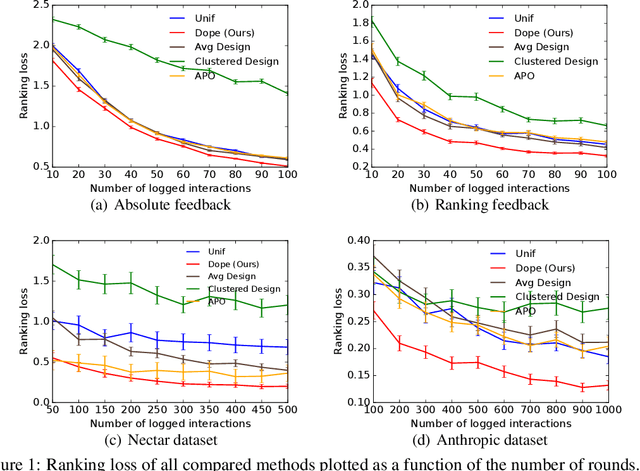
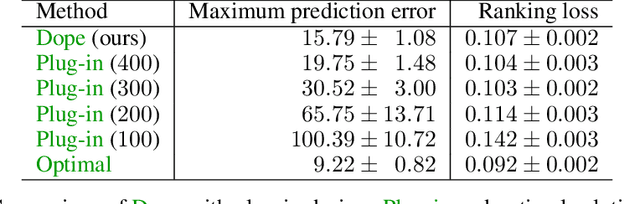
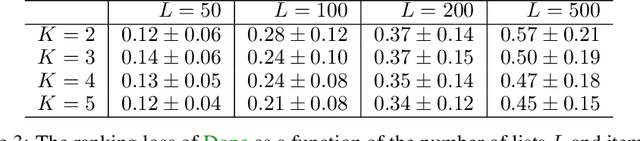
Abstract:Learning of preference models from human feedback has been central to recent advances in artificial intelligence. Motivated by this progress, and the cost of obtaining high-quality human annotations, we study the problem of data collection for learning preference models. The key idea in our work is to generalize optimal designs, a tool for computing efficient data logging policies, to ranked lists. To show the generality of our ideas, we study both absolute and relative feedback on items in the list. We design efficient algorithms for both settings and analyze them. We prove that our preference model estimators improve with more data and so does the ranking error under the estimators. Finally, we experiment with several synthetic and real-world datasets to show the statistical efficiency of our algorithms.
Experimental Design for Active Transductive Inference in Large Language Models
Apr 12, 2024



Abstract:Transduction, the ability to include query-specific examples in the prompt at inference time, is one of the emergent abilities of large language models (LLMs). In this work, we propose a framework for adaptive prompt design called active transductive inference (ATI). We design the LLM prompt by adaptively choosing few-shot examples for a given inference query. The examples are initially unlabeled and we query the user to label the most informative ones, which maximally reduces the uncertainty in the LLM prediction. We propose two algorithms, GO and SAL, which differ in how the few-shot examples are chosen. We analyze these algorithms in linear models: first GO and then use its equivalence with SAL. We experiment with many different tasks and show that GO and SAL outperform other methods for choosing few-shot examples in the LLM prompt at inference time.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge