Andrew H. Beck
PLUTO: Pathology-Universal Transformer
May 13, 2024



Abstract:Pathology is the study of microscopic inspection of tissue, and a pathology diagnosis is often the medical gold standard to diagnose disease. Pathology images provide a unique challenge for computer-vision-based analysis: a single pathology Whole Slide Image (WSI) is gigapixel-sized and often contains hundreds of thousands to millions of objects of interest across multiple resolutions. In this work, we propose PathoLogy Universal TransfOrmer (PLUTO): a light-weight pathology FM that is pre-trained on a diverse dataset of 195 million image tiles collected from multiple sites and extracts meaningful representations across multiple WSI scales that enable a large variety of downstream pathology tasks. In particular, we design task-specific adaptation heads that utilize PLUTO's output embeddings for tasks which span pathology scales ranging from subcellular to slide-scale, including instance segmentation, tile classification, and slide-level prediction. We compare PLUTO's performance to other state-of-the-art methods on a diverse set of external and internal benchmarks covering multiple biologically relevant tasks, tissue types, resolutions, stains, and scanners. We find that PLUTO matches or outperforms existing task-specific baselines and pathology-specific foundation models, some of which use orders-of-magnitude larger datasets and model sizes when compared to PLUTO. Our findings present a path towards a universal embedding to power pathology image analysis, and motivate further exploration around pathology foundation models in terms of data diversity, architectural improvements, sample efficiency, and practical deployability in real-world applications.
Predicting breast tumor proliferation from whole-slide images: the TUPAC16 challenge
Jul 22, 2018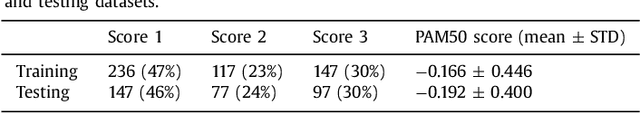
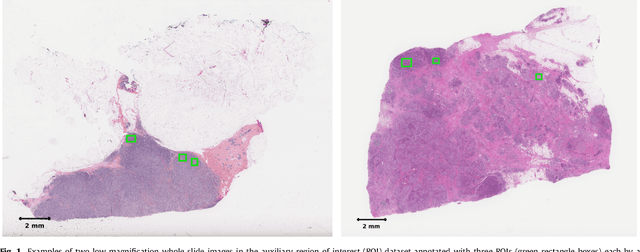
Abstract:Tumor proliferation is an important biomarker indicative of the prognosis of breast cancer patients. Assessment of tumor proliferation in a clinical setting is highly subjective and labor-intensive task. Previous efforts to automate tumor proliferation assessment by image analysis only focused on mitosis detection in predefined tumor regions. However, in a real-world scenario, automatic mitosis detection should be performed in whole-slide images (WSIs) and an automatic method should be able to produce a tumor proliferation score given a WSI as input. To address this, we organized the TUmor Proliferation Assessment Challenge 2016 (TUPAC16) on prediction of tumor proliferation scores from WSIs. The challenge dataset consisted of 500 training and 321 testing breast cancer histopathology WSIs. In order to ensure fair and independent evaluation, only the ground truth for the training dataset was provided to the challenge participants. The first task of the challenge was to predict mitotic scores, i.e., to reproduce the manual method of assessing tumor proliferation by a pathologist. The second task was to predict the gene expression based PAM50 proliferation scores from the WSI. The best performing automatic method for the first task achieved a quadratic-weighted Cohen's kappa score of $\kappa$ = 0.567, 95% CI [0.464, 0.671] between the predicted scores and the ground truth. For the second task, the predictions of the top method had a Spearman's correlation coefficient of r = 0.617, 95% CI [0.581 0.651] with the ground truth. This was the first study that investigated tumor proliferation assessment from WSIs. The achieved results are promising given the difficulty of the tasks and weakly-labelled nature of the ground truth. However, further research is needed to improve the practical utility of image analysis methods for this task.
Crowdsourcing scoring of immunohistochemistry images: Evaluating Performance of the Crowd and an Automated Computational Method
Jun 23, 2016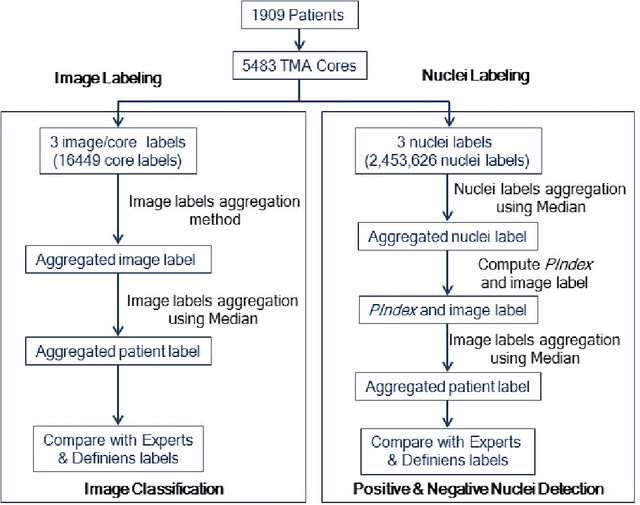
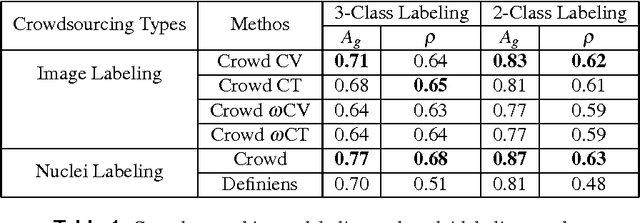
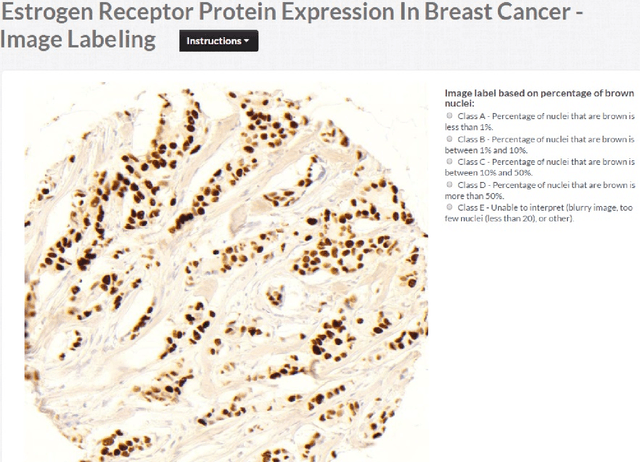
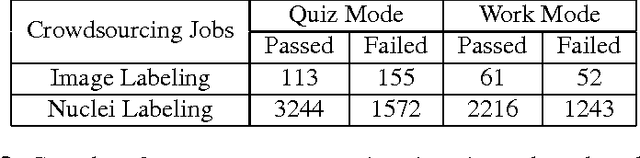
Abstract:The assessment of protein expression in immunohistochemistry (IHC) images provides important diagnostic, prognostic and predictive information for guiding cancer diagnosis and therapy. Manual scoring of IHC images represents a logistical challenge, as the process is labor intensive and time consuming. Since the last decade, computational methods have been developed to enable the application of quantitative methods for the analysis and interpretation of protein expression in IHC images. These methods have not yet replaced manual scoring for the assessment of IHC in the majority of diagnostic laboratories and in many large-scale research studies. An alternative approach is crowdsourcing the quantification of IHC images to an undefined crowd. The aim of this study is to quantify IHC images for labeling of ER status with two different crowdsourcing approaches, image labeling and nuclei labeling, and compare their performance with automated methods. Crowdsourcing-derived scores obtained greater concordance with the pathologist interpretations for both image labeling and nuclei labeling tasks (83% and 87%), as compared to the pathologist concordance achieved by the automated method (81%) on 5,483 TMA images from 1,909 breast cancer patients. This analysis shows that crowdsourcing the scoring of protein expression in IHC images is a promising new approach for large scale cancer molecular pathology studies.
Deep Learning for Identifying Metastatic Breast Cancer
Jun 18, 2016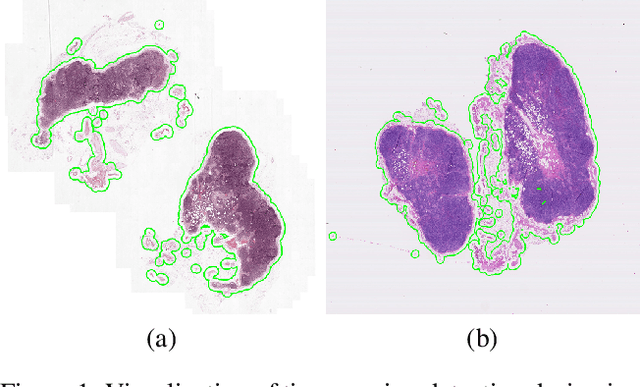
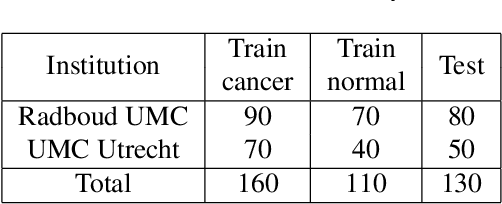
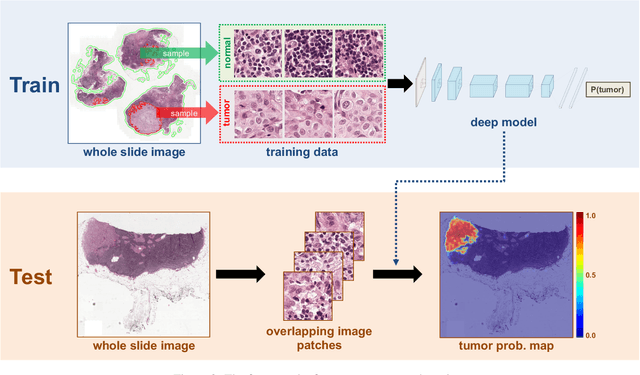
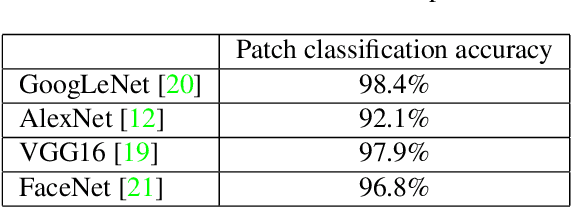
Abstract:The International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI) held a grand challenge to evaluate computational systems for the automated detection of metastatic breast cancer in whole slide images of sentinel lymph node biopsies. Our team won both competitions in the grand challenge, obtaining an area under the receiver operating curve (AUC) of 0.925 for the task of whole slide image classification and a score of 0.7051 for the tumor localization task. A pathologist independently reviewed the same images, obtaining a whole slide image classification AUC of 0.966 and a tumor localization score of 0.733. Combining our deep learning system's predictions with the human pathologist's diagnoses increased the pathologist's AUC to 0.995, representing an approximately 85 percent reduction in human error rate. These results demonstrate the power of using deep learning to produce significant improvements in the accuracy of pathological diagnoses.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge