Andreas Grivas
Fast and Expressive Multi-Token Prediction with Probabilistic Circuits
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:Multi-token prediction (MTP) is a prominent strategy to significantly speed up generation in large language models (LLMs), including byte-level LLMs, which are tokeniser-free but prohibitively slow. However, existing MTP methods often sacrifice expressiveness by assuming independence between future tokens. In this work, we investigate the trade-off between expressiveness and latency in MTP within the framework of probabilistic circuits (PCs). Our framework, named MTPC, allows one to explore different ways to encode the joint distributions over future tokens by selecting different circuit architectures, generalising classical models such as (hierarchical) mixture models, hidden Markov models and tensor networks. We show the efficacy of MTPC by retrofitting existing byte-level LLMs, such as EvaByte. Our experiments show that, when combined with speculative decoding, MTPC significantly speeds up generation compared to MTP with independence assumptions, while guaranteeing to retain the performance of the original verifier LLM. We also rigorously study the optimal trade-off between expressiveness and latency when exploring the possible parameterisations of MTPC, such as PC architectures and partial layer sharing between the verifier and draft LLMs.
Perceptions of Edinburgh: Capturing Neighbourhood Characteristics by Clustering Geoparsed Local News
Sep 17, 2024



Abstract:The communities that we live in affect our health in ways that are complex and hard to define. Moreover, our understanding of the place-based processes affecting health and inequalities is limited. This undermines the development of robust policy interventions to improve local health and well-being. News media provides social and community information that may be useful in health studies. Here we propose a methodology for characterising neighbourhoods by using local news articles. More specifically, we show how we can use Natural Language Processing (NLP) to unlock further information about neighbourhoods by analysing, geoparsing and clustering news articles. Our work is novel because we combine street-level geoparsing tailored to the locality with clustering of full news articles, enabling a more detailed examination of neighbourhood characteristics. We evaluate our outputs and show via a confluence of evidence, both from a qualitative and a quantitative perspective, that the themes we extract from news articles are sensible and reflect many characteristics of the real world. This is significant because it allows us to better understand the effects of neighbourhoods on health. Our findings on neighbourhood characterisation using news data will support a new generation of place-based research which examines a wider set of spatial processes and how they affect health, enabling new epidemiological research.
Taming the Sigmoid Bottleneck: Provably Argmaxable Sparse Multi-Label Classification
Oct 16, 2023



Abstract:Sigmoid output layers are widely used in multi-label classification (MLC) tasks, in which multiple labels can be assigned to any input. In many practical MLC tasks, the number of possible labels is in the thousands, often exceeding the number of input features and resulting in a low-rank output layer. In multi-class classification, it is known that such a low-rank output layer is a bottleneck that can result in unargmaxable classes: classes which cannot be predicted for any input. In this paper, we show that for MLC tasks, the analogous sigmoid bottleneck results in exponentially many unargmaxable label combinations. We explain how to detect these unargmaxable outputs and demonstrate their presence in three widely used MLC datasets. We then show that they can be prevented in practice by introducing a Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) output layer, which guarantees that all sparse label combinations with up to $k$ active labels are argmaxable. Our DFT layer trains faster and is more parameter efficient, matching the F1@k score of a sigmoid layer while using up to 50% fewer trainable parameters. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/andreasgrv/sigmoid-bottleneck.
Low-Rank Softmax Can Have Unargmaxable Classes in Theory but Rarely in Practice
Mar 21, 2022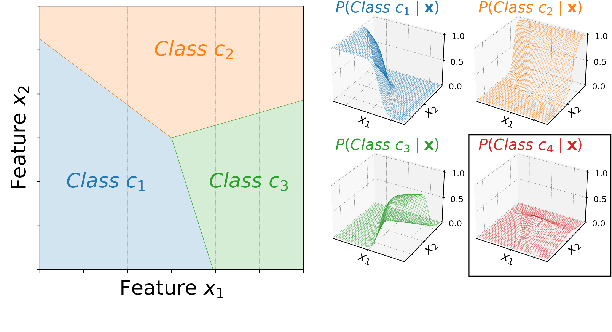
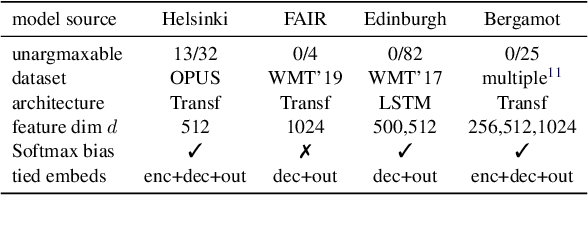
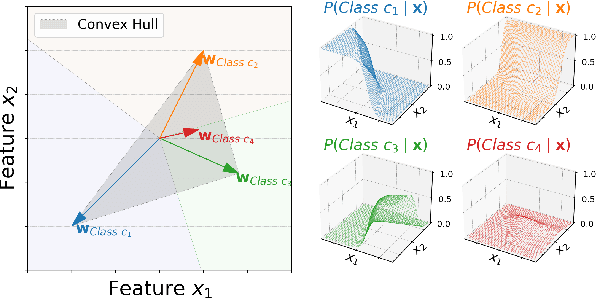
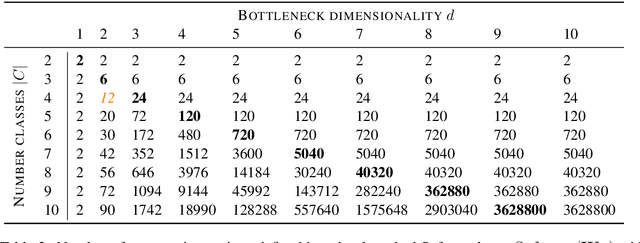
Abstract:Classifiers in natural language processing (NLP) often have a large number of output classes. For example, neural language models (LMs) and machine translation (MT) models both predict tokens from a vocabulary of thousands. The Softmax output layer of these models typically receives as input a dense feature representation, which has much lower dimensionality than the output. In theory, the result is some words may be impossible to be predicted via argmax, irrespective of input features, and empirically, there is evidence this happens in small language models. In this paper we ask whether it can happen in practical large language models and translation models. To do so, we develop algorithms to detect such \emph{unargmaxable} tokens in public models. We find that 13 out of 150 models do indeed have such tokens; however, they are very infrequent and unlikely to impact model quality. We release our code so that others can inspect their models.
A Systematic Review of Natural Language Processing Applied to Radiology Reports
Feb 18, 2021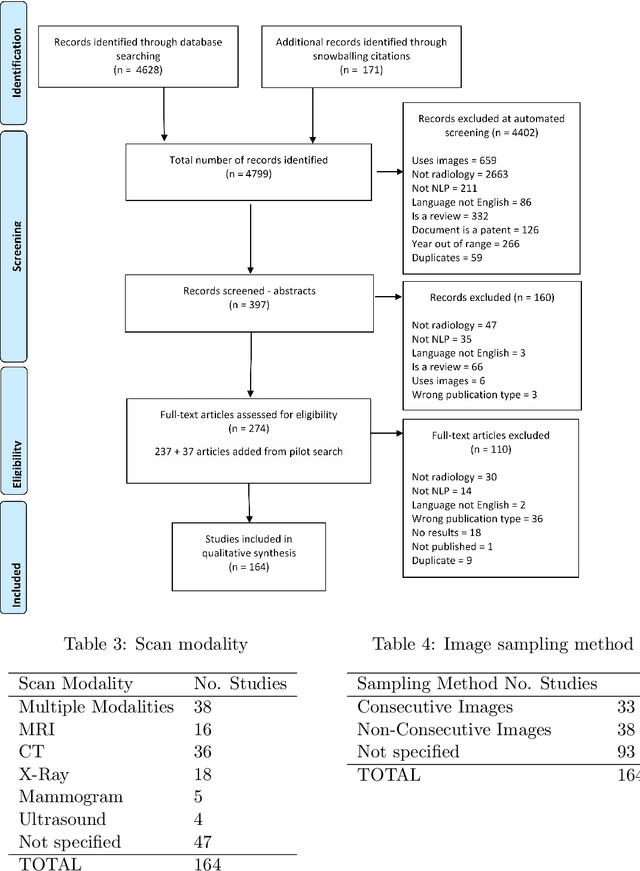
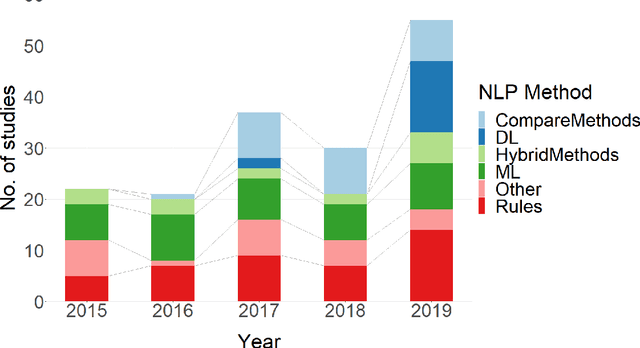
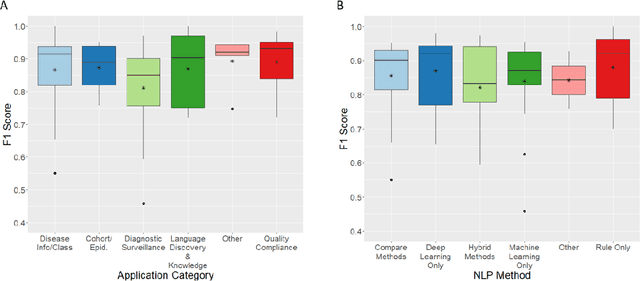
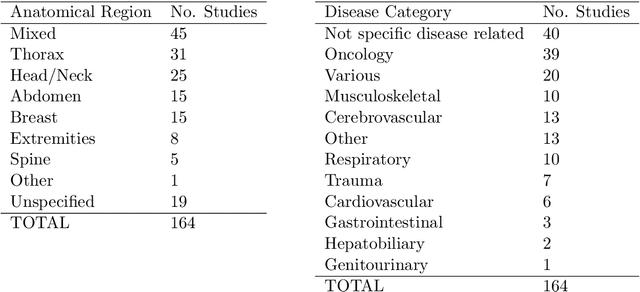
Abstract:NLP has a significant role in advancing healthcare and has been found to be key in extracting structured information from radiology reports. Understanding recent developments in NLP application to radiology is of significance but recent reviews on this are limited. This study systematically assesses recent literature in NLP applied to radiology reports. Our automated literature search yields 4,799 results using automated filtering, metadata enriching steps and citation search combined with manual review. Our analysis is based on 21 variables including radiology characteristics, NLP methodology, performance, study, and clinical application characteristics. We present a comprehensive analysis of the 164 publications retrieved with each categorised into one of 6 clinical application categories. Deep learning use increases but conventional machine learning approaches are still prevalent. Deep learning remains challenged when data is scarce and there is little evidence of adoption into clinical practice. Despite 17% of studies reporting greater than 0.85 F1 scores, it is hard to comparatively evaluate these approaches given that most of them use different datasets. Only 14 studies made their data and 15 their code available with 10 externally validating results. Automated understanding of clinical narratives of the radiology reports has the potential to enhance the healthcare process but reproducibility and explainability of models are important if the domain is to move applications into clinical use. More could be done to share code enabling validation of methods on different institutional data and to reduce heterogeneity in reporting of study properties allowing inter-study comparisons. Our results have significance for researchers providing a systematic synthesis of existing work to build on, identify gaps, opportunities for collaboration and avoid duplication.
What do character-level models learn about morphology? The case of dependency parsing
Aug 28, 2018
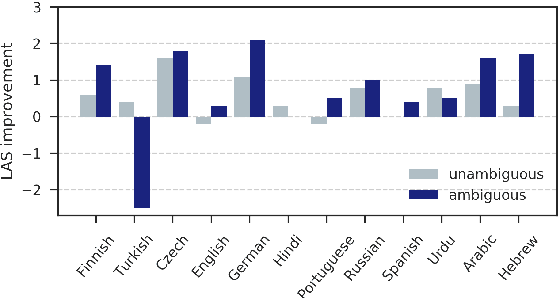

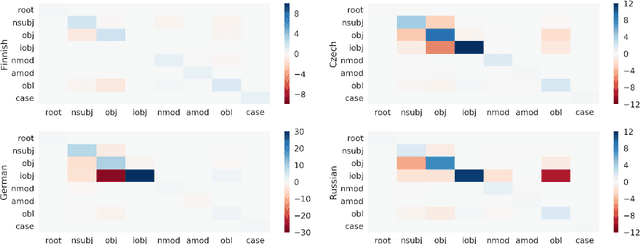
Abstract:When parsing morphologically-rich languages with neural models, it is beneficial to model input at the character level, and it has been claimed that this is because character-level models learn morphology. We test these claims by comparing character-level models to an oracle with access to explicit morphological analysis on twelve languages with varying morphological typologies. Our results highlight many strengths of character-level models, but also show that they are poor at disambiguating some words, particularly in the face of case syncretism. We then demonstrate that explicitly modeling morphological case improves our best model, showing that character-level models can benefit from targeted forms of explicit morphological modeling.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge