András Juhász
Data for Mathematical Copilots: Better Ways of Presenting Proofs for Machine Learning
Dec 19, 2024

Abstract:The suite of datasets commonly used to train and evaluate the mathematical capabilities of AI-based mathematical copilots (primarily large language models) exhibit several shortcomings. These limitations include a restricted scope of mathematical complexity, typically not exceeding lower undergraduate-level mathematics, binary rating protocols and other issues, which makes comprehensive proof-based evaluation suites difficult. We systematically explore these limitations and contend that enhancing the capabilities of large language models, or any forthcoming advancements in AI-based mathematical assistants (copilots or "thought partners"), necessitates a paradigm shift in the design of mathematical datasets and the evaluation criteria of mathematical ability: It is necessary to move away from result-based datasets (theorem statement to theorem proof) and convert the rich facets of mathematical research practice to data LLMs can train on. Examples of these are mathematical workflows (sequences of atomic, potentially subfield-dependent tasks that are often performed when creating new mathematics), which are an important part of the proof-discovery process. Additionally, we advocate for mathematical dataset developers to consider the concept of "motivated proof", introduced by G. P\'olya in 1949, which can serve as a blueprint for datasets that offer a better proof learning signal, alleviating some of the mentioned limitations. Lastly, we introduce math datasheets for datasets, extending the general, dataset-agnostic variants of datasheets: We provide a questionnaire designed specifically for math datasets that we urge dataset creators to include with their datasets. This will make creators aware of potential limitations of their datasets while at the same time making it easy for readers to assess it from the point of view of training and evaluating mathematical copilots.
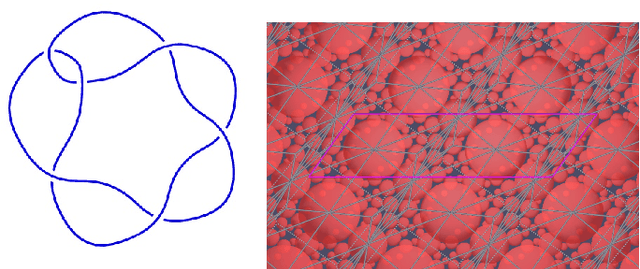
The unknotting number, hard unknot diagrams, and reinforcement learning
Sep 13, 2024



Abstract:We have developed a reinforcement learning agent that often finds a minimal sequence of unknotting crossing changes for a knot diagram with up to 200 crossings, hence giving an upper bound on the unknotting number. We have used this to determine the unknotting number of 57k knots. We took diagrams of connected sums of such knots with oppositely signed signatures, where the summands were overlaid. The agent has found examples where several of the crossing changes in an unknotting collection of crossings result in hyperbolic knots. Based on this, we have shown that, given knots $K$ and $K'$ that satisfy some mild assumptions, there is a diagram of their connected sum and $u(K) + u(K')$ unknotting crossings such that changing any one of them results in a prime knot. As a by-product, we have obtained a dataset of 2.6 million distinct hard unknot diagrams; most of them under 35 crossings. Assuming the additivity of the unknotting number, we have determined the unknotting number of 43 at most 12-crossing knots for which the unknotting number is unknown.
The signature and cusp geometry of hyperbolic knots
Nov 30, 2021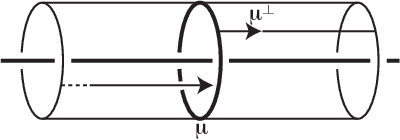
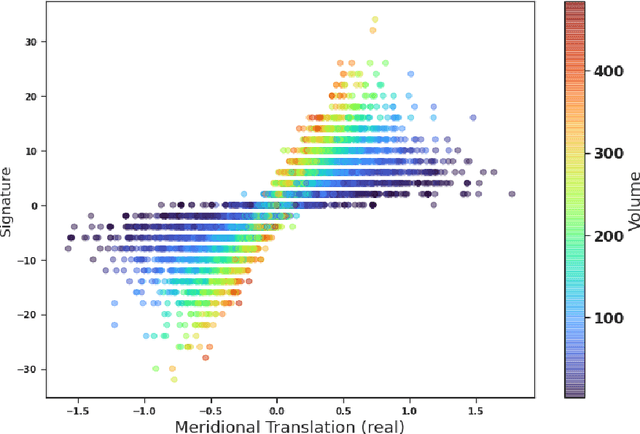

Abstract:We introduce a new real-valued invariant called the natural slope of a hyperbolic knot in the 3-sphere, which is defined in terms of its cusp geometry. We show that twice the knot signature and the natural slope differ by at most a constant times the hyperbolic volume divided by the cube of the injectivity radius. This inequality was discovered using machine learning to detect relationships between various knot invariants. It has applications to Dehn surgery and to 4-ball genus. We also show a refined version of the inequality where the upper bound is a linear function of the volume, and the slope is corrected by terms corresponding to short geodesics that link the knot an odd number of times.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge