Amir Tamrakar
Towards Understanding Confusion and Affective States Under Communication Failures in Voice-Based Human-Machine Interaction
Jul 15, 2022



Abstract:We present a series of two studies conducted to understand user's affective states during voice-based human-machine interactions. Emphasis is placed on the cases of communication errors or failures. In particular, we are interested in understanding "confusion" in relation with other affective states. The studies consist of two types of tasks: (1) related to communication with a voice-based virtual agent: speaking to the machine and understanding what the machine says, (2) non-communication related, problem-solving tasks where the participants solve puzzles and riddles but are asked to verbally explain the answers to the machine. We collected audio-visual data and self-reports of affective states of the participants. We report results of two studies and analysis of the collected data. The first study was analyzed based on the annotator's observation, and the second study was analyzed based on the self-report.
"How to best say it?" : Translating Directives in Machine Language into Natural Language in the Blocks World
Jul 14, 2021



Abstract:We propose a method to generate optimal natural language for block placement directives generated by a machine's planner during human-agent interactions in the blocks world. A non user-friendly machine directive, e.g., move(ObjId, toPos), is transformed into visually and contextually grounded referring expressions that are much easier for the user to comprehend. We describe an algorithm that progressively and generatively transforms the machine's directive in ECI (Elementary Composable Ideas)-space, generating many alternative versions of the directive. We then define a cost function to evaluate the ease of comprehension of these alternatives and select the best option. The parameters for this cost function were derived empirically from a user study that measured utterance-to-action timings.
Towards Explainable Student Group Collaboration Assessment Models Using Temporal Representations of Individual Student Roles
Jun 17, 2021
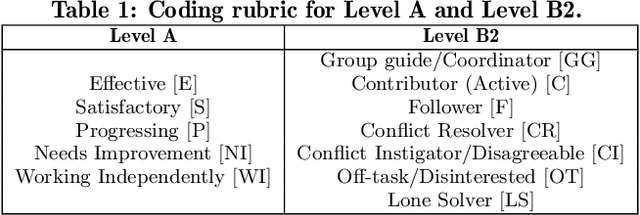

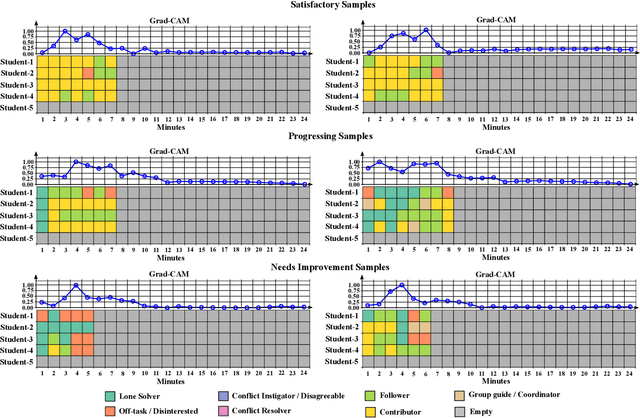
Abstract:Collaboration is identified as a required and necessary skill for students to be successful in the fields of Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM). However, due to growing student population and limited teaching staff it is difficult for teachers to provide constructive feedback and instill collaborative skills using instructional methods. Development of simple and easily explainable machine-learning-based automated systems can help address this problem. Improving upon our previous work, in this paper we propose using simple temporal-CNN deep-learning models to assess student group collaboration that take in temporal representations of individual student roles as input. We check the applicability of dynamically changing feature representations for student group collaboration assessment and how they impact the overall performance. We also use Grad-CAM visualizations to better understand and interpret the important temporal indices that led to the deep-learning model's decision.
ACE-Net: Fine-Level Face Alignment through Anchors and Contours Estimation
Dec 02, 2020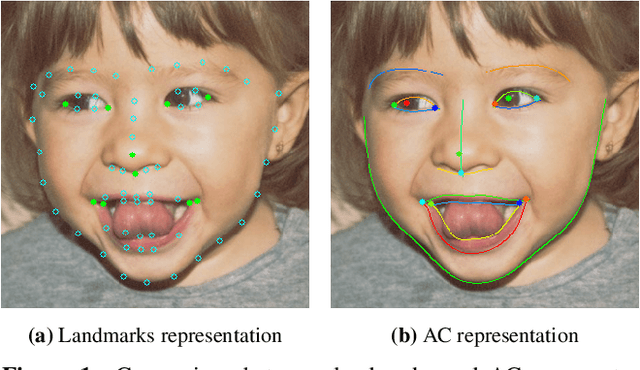

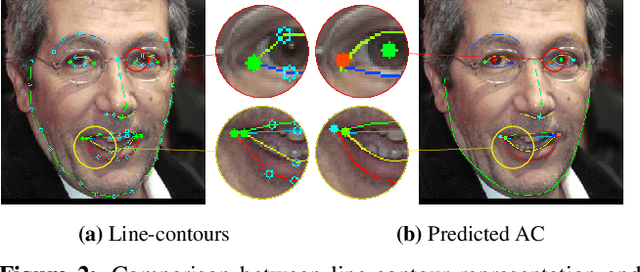

Abstract:We propose a novel facial Anchors and Contours Estimation framework, ACE-Net, for fine-level face alignment tasks. ACE-Net predicts facial anchors and contours that are richer than traditional facial landmarks and more accurate than facial boundaries. In addition, it does not suffer from the ambiguities and inconsistencies in facial-landmarks definitions. We introduce a weakly supervised loss enabling ACE-Net to learn from existing facial landmarks datasets without the need for extra annotations. Synthetic data is also used during training to bridge the density gap between landmarks annotation and true facial contours. We evaluate ACE-Net on commonly used face alignment datasets 300-W and HELEN, and show that ACE-Net achieves significantly higher fine-level face alignment accuracy than landmarks based models, without compromising its performance at the landmarks level. The proposed ACE-Net framework does not rely on any specific network architecture and thus can be applied on top of existing face alignment models for finer face alignment representation.
A Machine Learning Approach to Assess Student Group Collaboration Using Individual Level Behavioral Cues
Aug 05, 2020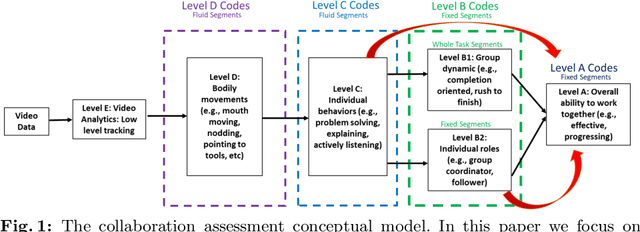


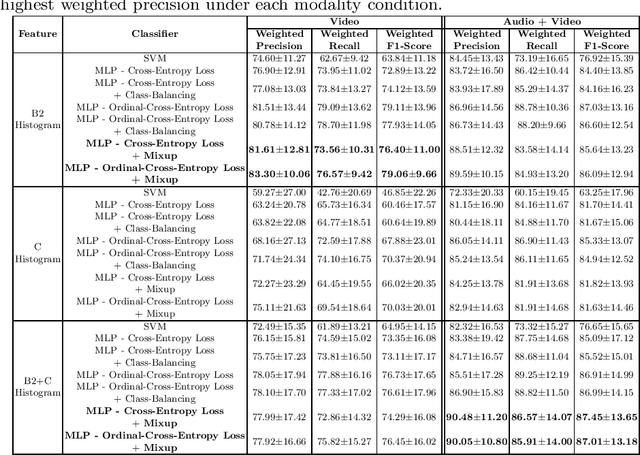
Abstract:K-12 classrooms consistently integrate collaboration as part of their learning experiences. However, owing to large classroom sizes, teachers do not have the time to properly assess each student and give them feedback. In this paper we propose using simple deep-learning-based machine learning models to automatically determine the overall collaboration quality of a group based on annotations of individual roles and individual level behavior of all the students in the group. We come across the following challenges when building these models: 1) Limited training data, 2) Severe class label imbalance. We address these challenges by using a controlled variant of Mixup data augmentation, a method for generating additional data samples by linearly combining different pairs of data samples and their corresponding class labels. Additionally, the label space for our problem exhibits an ordered structure. We take advantage of this fact and also explore using an ordinal-cross-entropy loss function and study its effects with and without Mixup.
Action-Affect Classification and Morphing using Multi-Task Representation Learning
Mar 21, 2016



Abstract:Most recent work focused on affect from facial expressions, and not as much on body. This work focuses on body affect analysis. Affect does not occur in isolation. Humans usually couple affect with an action in natural interactions; for example, a person could be talking and smiling. Recognizing body affect in sequences requires efficient algorithms to capture both the micro movements that differentiate between happy and sad and the macro variations between different actions. We depart from traditional approaches for time-series data analytics by proposing a multi-task learning model that learns a shared representation that is well-suited for action-affect classification as well as generation. For this paper we choose Conditional Restricted Boltzmann Machines to be our building block. We propose a new model that enhances the CRBM model with a factored multi-task component to become Multi-Task Conditional Restricted Boltzmann Machines (MTCRBMs). We evaluate our approach on two publicly available datasets, the Body Affect dataset and the Tower Game dataset, and show superior classification performance improvement over the state-of-the-art, as well as the generative abilities of our model.
Human Social Interaction Modeling Using Temporal Deep Networks
May 28, 2015
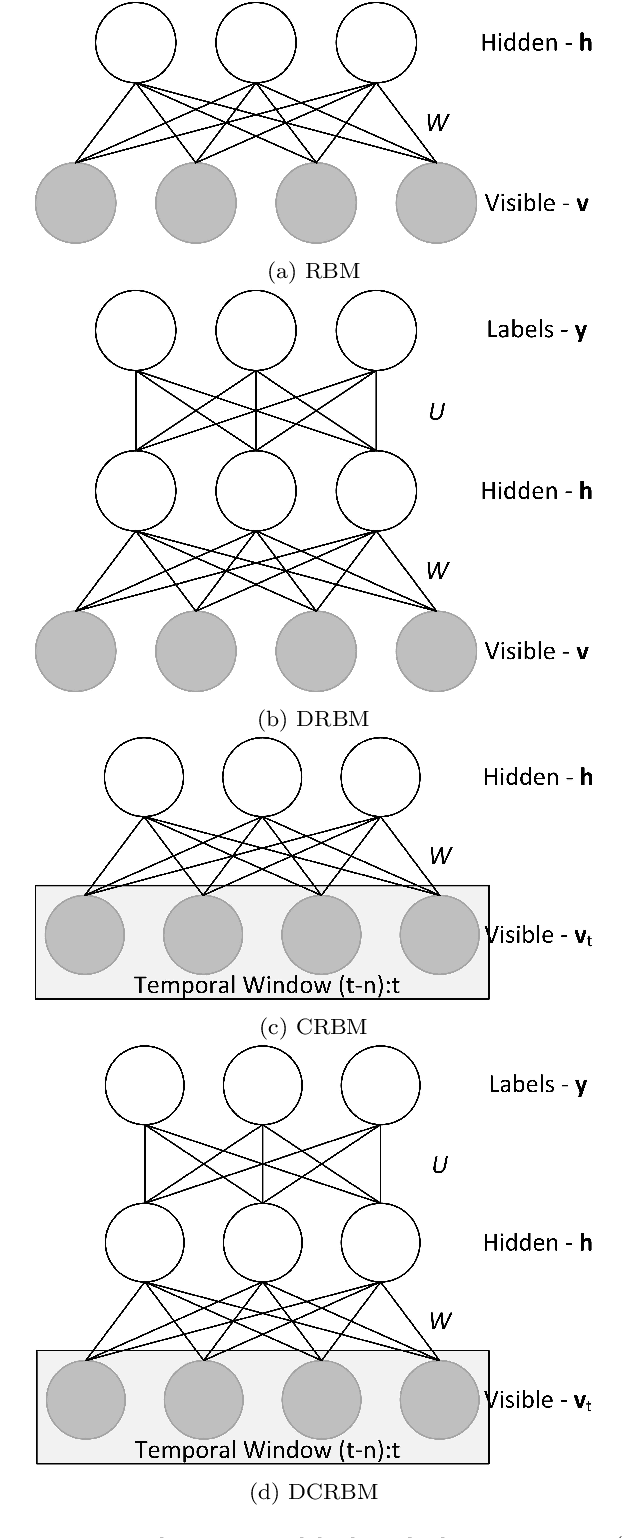
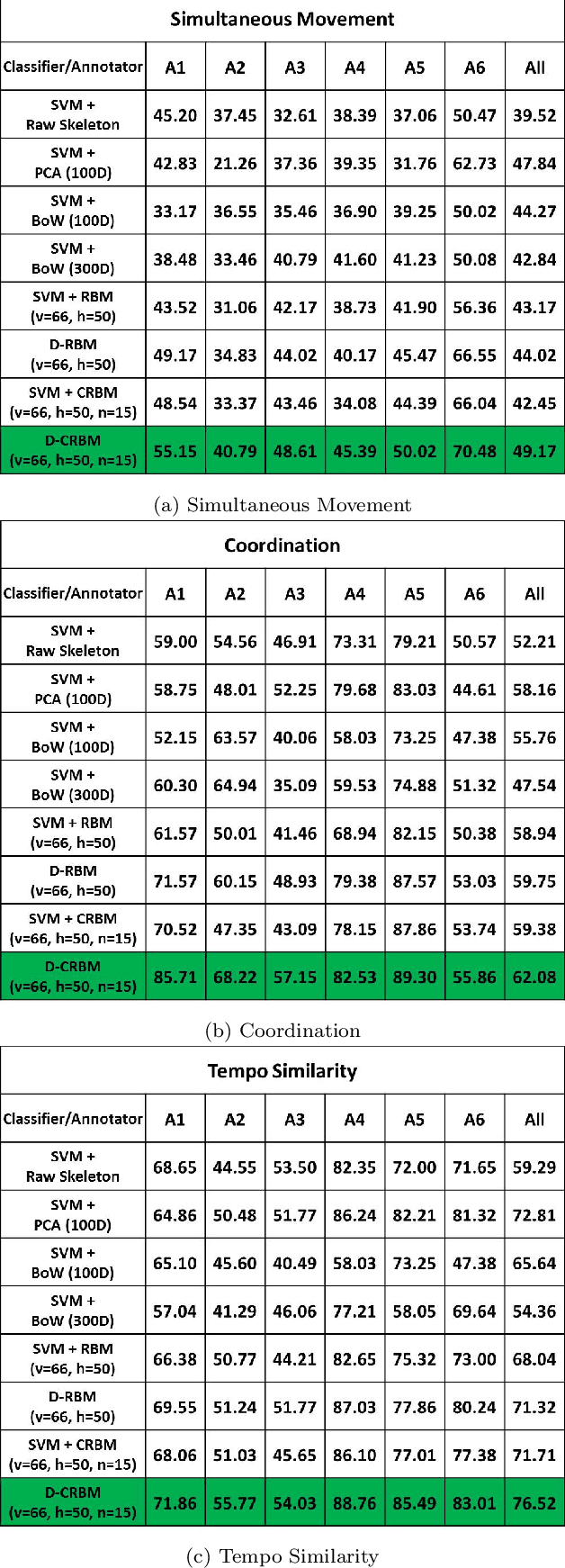
Abstract:We present a novel approach to computational modeling of social interactions based on modeling of essential social interaction predicates (ESIPs) such as joint attention and entrainment. Based on sound social psychological theory and methodology, we collect a new "Tower Game" dataset consisting of audio-visual capture of dyadic interactions labeled with the ESIPs. We expect this dataset to provide a new avenue for research in computational social interaction modeling. We propose a novel joint Discriminative Conditional Restricted Boltzmann Machine (DCRBM) model that combines a discriminative component with the generative power of CRBMs. Such a combination enables us to uncover actionable constituents of the ESIPs in two steps. First, we train the DCRBM model on the labeled data and get accurate (76\%-49\% across various ESIPs) detection of the predicates. Second, we exploit the generative capability of DCRBMs to activate the trained model so as to generate the lower-level data corresponding to the specific ESIP that closely matches the actual training data (with mean square error 0.01-0.1 for generating 100 frames). We are thus able to decompose the ESIPs into their constituent actionable behaviors. Such a purely computational determination of how to establish an ESIP such as engagement is unprecedented.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge