Amir Mohammadi
FantasyID: A dataset for detecting digital manipulations of ID-documents
Jul 28, 2025Abstract:Advancements in image generation led to the availability of easy-to-use tools for malicious actors to create forged images. These tools pose a serious threat to the widespread Know Your Customer (KYC) applications, requiring robust systems for detection of the forged Identity Documents (IDs). To facilitate the development of the detection algorithms, in this paper, we propose a novel publicly available (including commercial use) dataset, FantasyID, which mimics real-world IDs but without tampering with legal documents and, compared to previous public datasets, it does not contain generated faces or specimen watermarks. FantasyID contains ID cards with diverse design styles, languages, and faces of real people. To simulate a realistic KYC scenario, the cards from FantasyID were printed and captured with three different devices, constituting the bonafide class. We have emulated digital forgery/injection attacks that could be performed by a malicious actor to tamper the IDs using the existing generative tools. The current state-of-the-art forgery detection algorithms, such as TruFor, MMFusion, UniFD, and FatFormer, are challenged by FantasyID dataset. It especially evident, in the evaluation conditions close to practical, with the operational threshold set on validation set so that false positive rate is at 10%, leading to false negative rates close to 50% across the board on the test set. The evaluation experiments demonstrate that FantasyID dataset is complex enough to be used as an evaluation benchmark for detection algorithms.
Investigation of Accuracy and Bias in Face Recognition Trained with Synthetic Data
Jul 28, 2025Abstract:Synthetic data has emerged as a promising alternative for training face recognition (FR) models, offering advantages in scalability, privacy compliance, and potential for bias mitigation. However, critical questions remain on whether both high accuracy and fairness can be achieved with synthetic data. In this work, we evaluate the impact of synthetic data on bias and performance of FR systems. We generate balanced face dataset, FairFaceGen, using two state of the art text-to-image generators, Flux.1-dev and Stable Diffusion v3.5 (SD35), and combine them with several identity augmentation methods, including Arc2Face and four IP-Adapters. By maintaining equal identity count across synthetic and real datasets, we ensure fair comparisons when evaluating FR performance on standard (LFW, AgeDB-30, etc.) and challenging IJB-B/C benchmarks and FR bias on Racial Faces in-the-Wild (RFW) dataset. Our results demonstrate that although synthetic data still lags behind the real datasets in the generalization on IJB-B/C, demographically balanced synthetic datasets, especially those generated with SD35, show potential for bias mitigation. We also observe that the number and quality of intra-class augmentations significantly affect FR accuracy and fairness. These findings provide practical guidelines for constructing fairer FR systems using synthetic data.
Second Competition on Presentation Attack Detection on ID Card
Jul 27, 2025Abstract:This work summarises and reports the results of the second Presentation Attack Detection competition on ID cards. This new version includes new elements compared to the previous one. (1) An automatic evaluation platform was enabled for automatic benchmarking; (2) Two tracks were proposed in order to evaluate algorithms and datasets, respectively; and (3) A new ID card dataset was shared with Track 1 teams to serve as the baseline dataset for the training and optimisation. The Hochschule Darmstadt, Fraunhofer-IGD, and Facephi company jointly organised this challenge. 20 teams were registered, and 74 submitted models were evaluated. For Track 1, the "Dragons" team reached first place with an Average Ranking and Equal Error rate (EER) of AV-Rank of 40.48% and 11.44% EER, respectively. For the more challenging approach in Track 2, the "Incode" team reached the best results with an AV-Rank of 14.76% and 6.36% EER, improving on the results of the first edition of 74.30% and 21.87% EER, respectively. These results suggest that PAD on ID cards is improving, but it is still a challenging problem related to the number of images, especially of bona fide images.
Prepended Domain Transformer: Heterogeneous Face Recognition without Bells and Whistles
Oct 12, 2022



Abstract:Heterogeneous Face Recognition (HFR) refers to matching face images captured in different domains, such as thermal to visible images (VIS), sketches to visible images, near-infrared to visible, and so on. This is particularly useful in matching visible spectrum images to images captured from other modalities. Though highly useful, HFR is challenging because of the domain gap between the source and target domain. Often, large-scale paired heterogeneous face image datasets are absent, preventing training models specifically for the heterogeneous task. In this work, we propose a surprisingly simple, yet, very effective method for matching face images across different sensing modalities. The core idea of the proposed approach is to add a novel neural network block called Prepended Domain Transformer (PDT) in front of a pre-trained face recognition (FR) model to address the domain gap. Retraining this new block with few paired samples in a contrastive learning setup was enough to achieve state-of-the-art performance in many HFR benchmarks. The PDT blocks can be retrained for several source-target combinations using the proposed general framework. The proposed approach is architecture agnostic, meaning they can be added to any pre-trained FR models. Further, the approach is modular and the new block can be trained with a minimal set of paired samples, making it much easier for practical deployment. The source code and protocols will be made available publicly.
Iris Liveness Detection Competition (LivDet-Iris) -- The 2020 Edition
Sep 01, 2020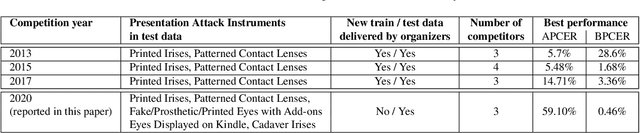
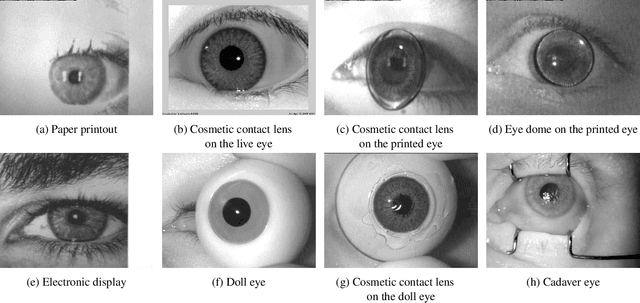
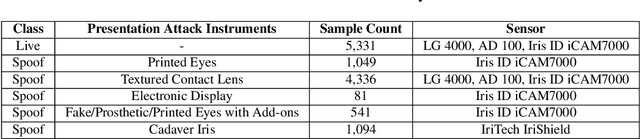
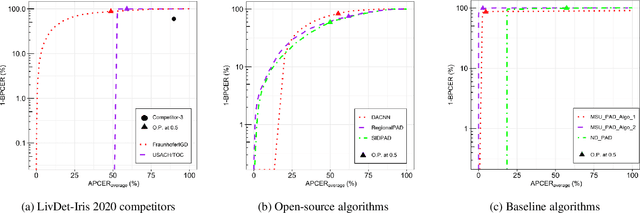
Abstract:Launched in 2013, LivDet-Iris is an international competition series open to academia and industry with the aim to assess and report advances in iris Presentation Attack Detection (PAD). This paper presents results from the fourth competition of the series: LivDet-Iris 2020. This year's competition introduced several novel elements: (a) incorporated new types of attacks (samples displayed on a screen, cadaver eyes and prosthetic eyes), (b) initiated LivDet-Iris as an on-going effort, with a testing protocol available now to everyone via the Biometrics Evaluation and Testing (BEAT)(https://www.idiap.ch/software/beat/) open-source platform to facilitate reproducibility and benchmarking of new algorithms continuously, and (c) performance comparison of the submitted entries with three baseline methods (offered by the University of Notre Dame and Michigan State University), and three open-source iris PAD methods available in the public domain. The best performing entry to the competition reported a weighted average APCER of 59.10\% and a BPCER of 0.46\% over all five attack types. This paper serves as the latest evaluation of iris PAD on a large spectrum of presentation attack instruments.
PCB Defect Detection Using Denoising Convolutional Autoencoders
Aug 28, 2020



Abstract:Printed Circuit boards (PCBs) are one of the most important stages in making electronic products. A small defect in PCBs can cause significant flaws in the final product. Hence, detecting all defects in PCBs and locating them is essential. In this paper, we propose an approach based on denoising convolutional autoencoders for detecting defective PCBs and to locate the defects. Denoising autoencoders take a corrupted image and try to recover the intact image. We trained our model with defective PCBs and forced it to repair the defective parts. Our model not only detects all kinds of defects and locates them, but it can also repair them as well. By subtracting the repaired output from the input, the defective parts are located. The experimental results indicate that our model detects the defective PCBs with high accuracy (97.5%) compare to state of the art works.
Smartphone Multi-modal Biometric Authentication: Database and Evaluation
Dec 05, 2019



Abstract:Biometric-based verification is widely employed on the smartphones for various applications, including financial transactions. In this work, we present a new multimodal biometric dataset (face, voice, and periocular) acquired using a smartphone. The new dataset is comprised of 150 subjects that are captured in six different sessions reflecting real-life scenarios of smartphone assisted authentication. One of the unique features of this dataset is that it is collected in four different geographic locations representing a diverse population and ethnicity. Additionally, we also present a multimodal Presentation Attack (PA) or spoofing dataset using a low-cost Presentation Attack Instrument (PAI) such as print and electronic display attacks. The novel acquisition protocols and the diversity of the data subjects collected from different geographic locations will allow developing a novel algorithm for either unimodal or multimodal biometrics. Further, we also report the performance evaluation of the baseline biometric verification and Presentation Attack Detection (PAD) on the newly collected dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge