Alissa Ostapenko
GlobalBench: A Benchmark for Global Progress in Natural Language Processing
May 24, 2023



Abstract:Despite the major advances in NLP, significant disparities in NLP system performance across languages still exist. Arguably, these are due to uneven resource allocation and sub-optimal incentives to work on less resourced languages. To track and further incentivize the global development of equitable language technology, we introduce GlobalBench. Prior multilingual benchmarks are static and have focused on a limited number of tasks and languages. In contrast, GlobalBench is an ever-expanding collection that aims to dynamically track progress on all NLP datasets in all languages. Rather than solely measuring accuracy, GlobalBench also tracks the estimated per-speaker utility and equity of technology across all languages, providing a multi-faceted view of how language technology is serving people of the world. Furthermore, GlobalBench is designed to identify the most under-served languages, and rewards research efforts directed towards those languages. At present, the most under-served languages are the ones with a relatively high population, but nonetheless overlooked by composite multilingual benchmarks (like Punjabi, Portuguese, and Wu Chinese). Currently, GlobalBench covers 966 datasets in 190 languages, and has 1,128 system submissions spanning 62 languages.
Speaker Information Can Guide Models to Better Inductive Biases: A Case Study On Predicting Code-Switching
Mar 16, 2022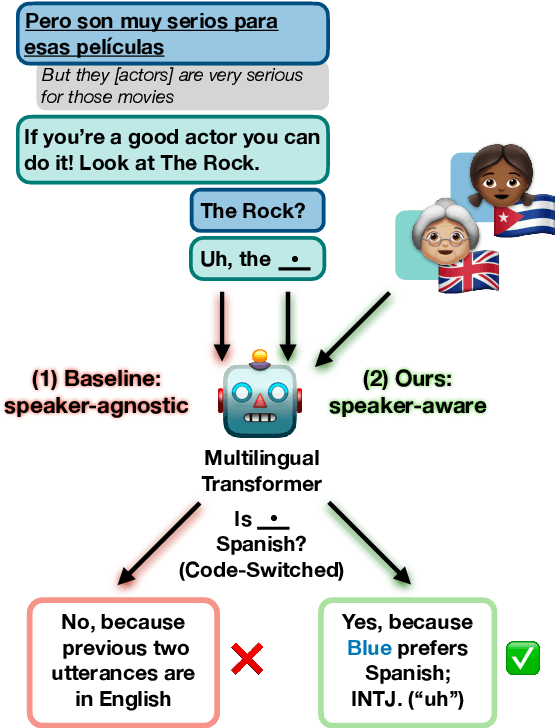

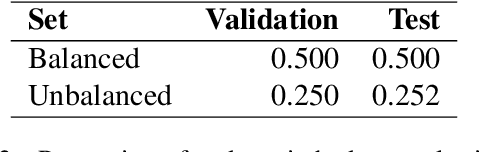
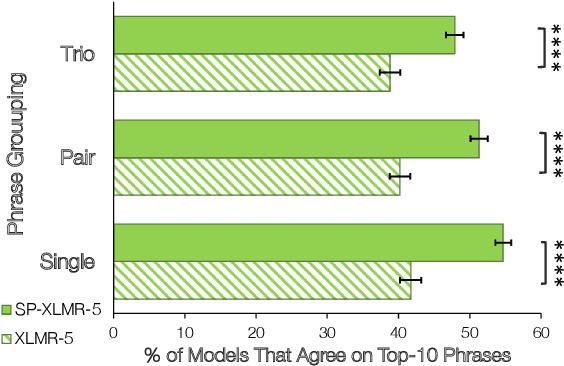
Abstract:Natural language processing (NLP) models trained on people-generated data can be unreliable because, without any constraints, they can learn from spurious correlations that are not relevant to the task. We hypothesize that enriching models with speaker information in a controlled, educated way can guide them to pick up on relevant inductive biases. For the speaker-driven task of predicting code-switching points in English--Spanish bilingual dialogues, we show that adding sociolinguistically-grounded speaker features as prepended prompts significantly improves accuracy. We find that by adding influential phrases to the input, speaker-informed models learn useful and explainable linguistic information. To our knowledge, we are the first to incorporate speaker characteristics in a neural model for code-switching, and more generally, take a step towards developing transparent, personalized models that use speaker information in a controlled way.
Rethinking End-to-End Evaluation of Decomposable Tasks: A Case Study on Spoken Language Understanding
Jun 29, 2021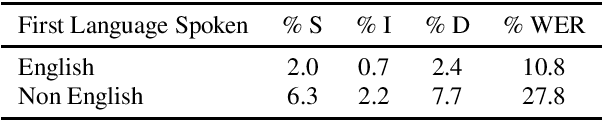
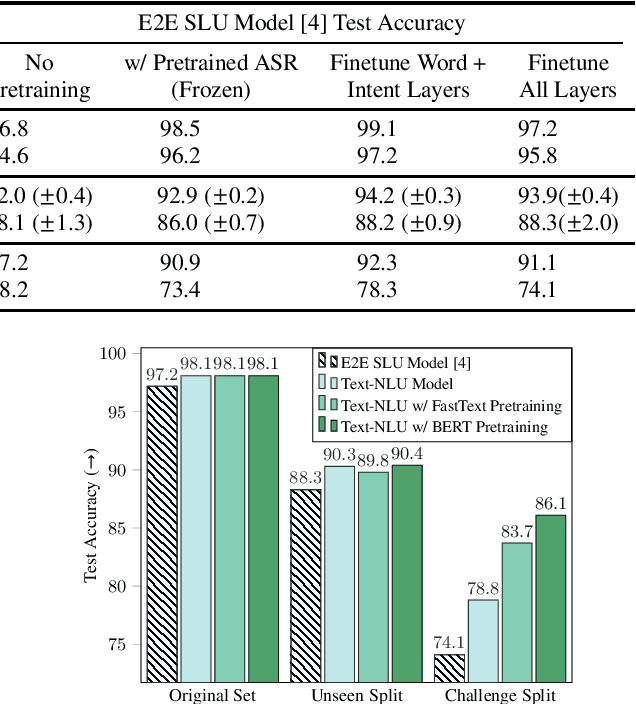
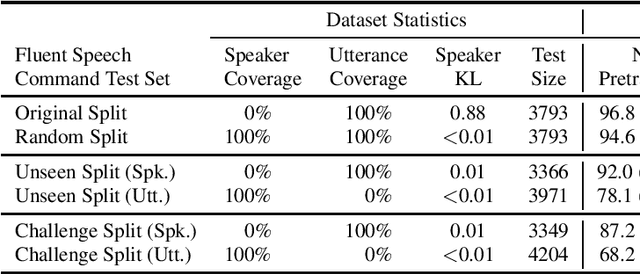

Abstract:Decomposable tasks are complex and comprise of a hierarchy of sub-tasks. Spoken intent prediction, for example, combines automatic speech recognition and natural language understanding. Existing benchmarks, however, typically hold out examples for only the surface-level sub-task. As a result, models with similar performance on these benchmarks may have unobserved performance differences on the other sub-tasks. To allow insightful comparisons between competitive end-to-end architectures, we propose a framework to construct robust test sets using coordinate ascent over sub-task specific utility functions. Given a dataset for a decomposable task, our method optimally creates a test set for each sub-task to individually assess sub-components of the end-to-end model. Using spoken language understanding as a case study, we generate new splits for the Fluent Speech Commands and Snips SmartLights datasets. Each split has two test sets: one with held-out utterances assessing natural language understanding abilities, and one with held-out speakers to test speech processing skills. Our splits identify performance gaps up to 10% between end-to-end systems that were within 1% of each other on the original test sets. These performance gaps allow more realistic and actionable comparisons between different architectures, driving future model development. We release our splits and tools for the community.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge