Alicia DeVrio
Un-Straightening Generative AI: How Queer Artists Surface and Challenge the Normativity of Generative AI Models
Mar 12, 2025Abstract:Queer people are often discussed as targets of bias, harm, or discrimination in research on generative AI. However, the specific ways that queer people engage with generative AI, and thus possible uses that support queer people, have yet to be explored. We conducted a workshop study with 13 queer artists, during which we gave participants access to GPT-4 and DALL-E 3 and facilitated group sensemaking activities. We found our participants struggled to use these models due to various normative values embedded in their designs, such as hyper-positivity and anti-sexuality. We describe various strategies our participants developed to overcome these models' limitations and how, nevertheless, our participants found value in these highly-normative technologies. Drawing on queer feminist theory, we discuss implications for the conceptualization of "state-of-the-art" models and consider how FAccT researchers might support queer alternatives.
Dehumanizing Machines: Mitigating Anthropomorphic Behaviors in Text Generation Systems
Feb 19, 2025Abstract:As text generation systems' outputs are increasingly anthropomorphic -- perceived as human-like -- scholars have also raised increasing concerns about how such outputs can lead to harmful outcomes, such as users over-relying or developing emotional dependence on these systems. How to intervene on such system outputs to mitigate anthropomorphic behaviors and their attendant harmful outcomes, however, remains understudied. With this work, we aim to provide empirical and theoretical grounding for developing such interventions. To do so, we compile an inventory of interventions grounded both in prior literature and a crowdsourced study where participants edited system outputs to make them less human-like. Drawing on this inventory, we also develop a conceptual framework to help characterize the landscape of possible interventions, articulate distinctions between different types of interventions, and provide a theoretical basis for evaluating the effectiveness of different interventions.
"I Am the One and Only, Your Cyber BFF": Understanding the Impact of GenAI Requires Understanding the Impact of Anthropomorphic AI
Oct 11, 2024Abstract:Many state-of-the-art generative AI (GenAI) systems are increasingly prone to anthropomorphic behaviors, i.e., to generating outputs that are perceived to be human-like. While this has led to scholars increasingly raising concerns about possible negative impacts such anthropomorphic AI systems can give rise to, anthropomorphism in AI development, deployment, and use remains vastly overlooked, understudied, and underspecified. In this perspective, we argue that we cannot thoroughly map the social impacts of generative AI without mapping the social impacts of anthropomorphic AI, and outline a call to action.
Understanding Practices, Challenges, and Opportunities for User-Driven Algorithm Auditing in Industry Practice
Oct 10, 2022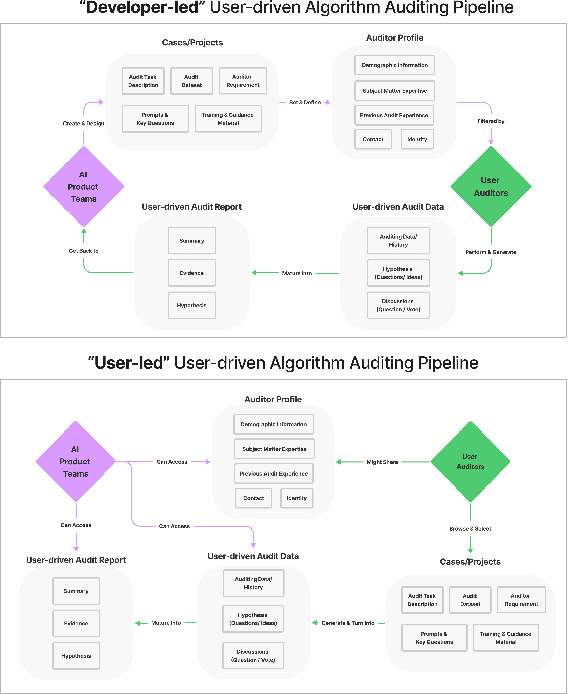
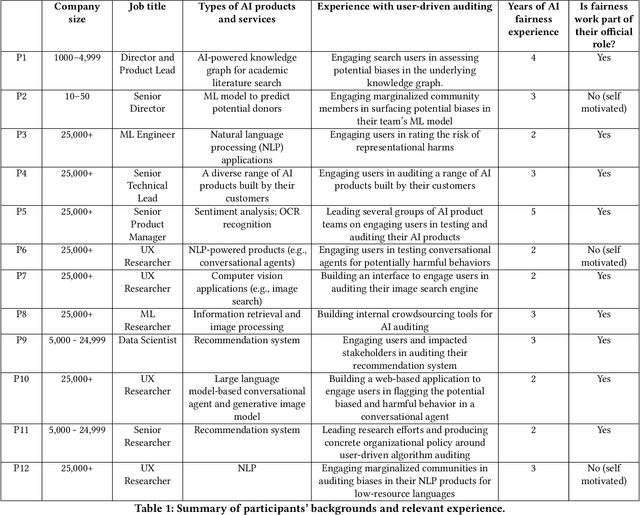
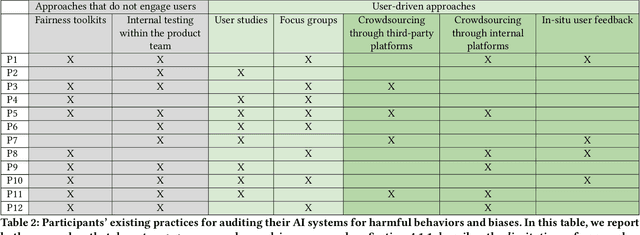
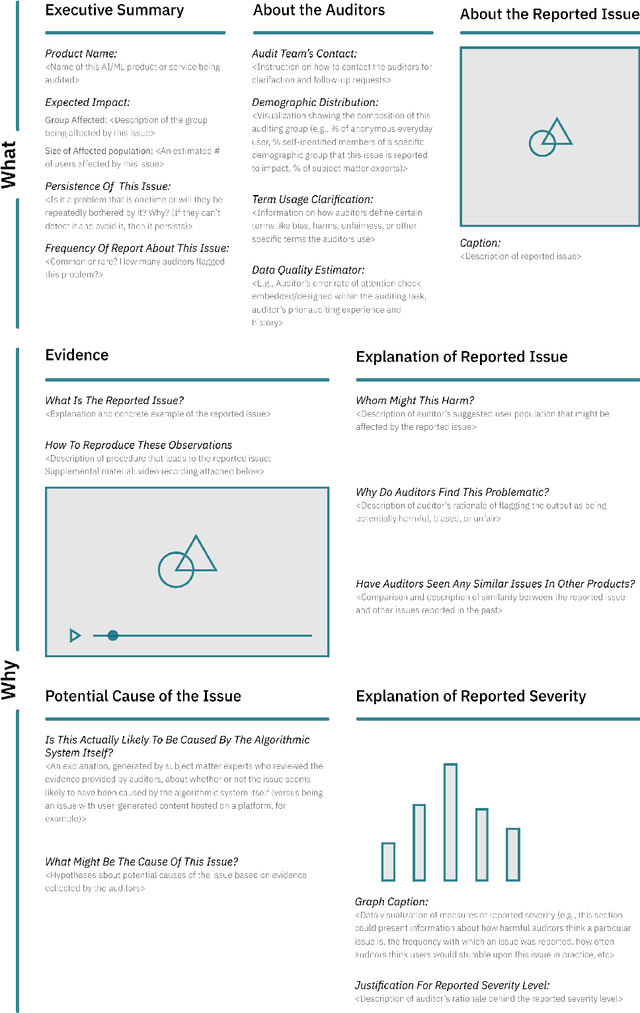
Abstract:Recent years have seen growing interest among both researchers and practitioners in user-driven approaches to algorithm auditing, which directly engage users in detecting problematic behaviors in algorithmic systems. However, we know little about industry practitioners' current practices and challenges around user-driven auditing, nor what opportunities exist for them to better leverage such approaches in practice. To investigate, we conducted a series of interviews and iterative co-design activities with practitioners who employ user-driven auditing approaches in their work. Our findings reveal several challenges practitioners face in appropriately recruiting and incentivizing user auditors, scaffolding user audits, and deriving actionable insights from user-driven audit reports. Furthermore, practitioners shared organizational obstacles to user-driven auditing, surfacing a complex relationship between practitioners and user auditors. Based on these findings, we discuss opportunities for future HCI research to help realize the potential (and mitigate risks) of user-driven auditing in industry practice.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge