Alice Othmani
A Novel Stochastic Transformer-based Approach for Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Detection using Audio Recording of Clinical Interviews
Mar 28, 2024Abstract:Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a mental disorder that can be developed after witnessing or experiencing extremely traumatic events. PTSD can affect anyone, regardless of ethnicity, or culture. An estimated one in every eleven people will experience PTSD during their lifetime. The Clinician-Administered PTSD Scale (CAPS) and the PTSD Check List for Civilians (PCL-C) interviews are gold standards in the diagnosis of PTSD. These questionnaires can be fooled by the subject's responses. This work proposes a deep learning-based approach that achieves state-of-the-art performances for PTSD detection using audio recordings during clinical interviews. Our approach is based on MFCC low-level features extracted from audio recordings of clinical interviews, followed by deep high-level learning using a Stochastic Transformer. Our proposed approach achieves state-of-the-art performances with an RMSE of 2.92 on the eDAIC dataset thanks to the stochastic depth, stochastic deep learning layers, and stochastic activation function.
Segmentation of Knee Bones for Osteoarthritis Assessment: A Comparative Analysis of Supervised, Few-Shot, and Zero-Shot Learning Approaches
Mar 13, 2024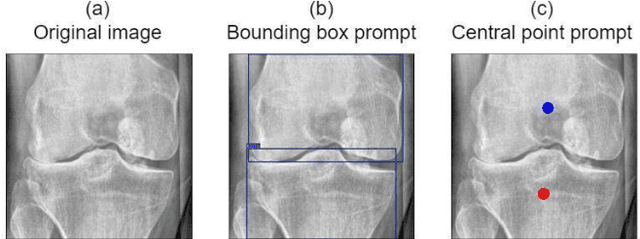
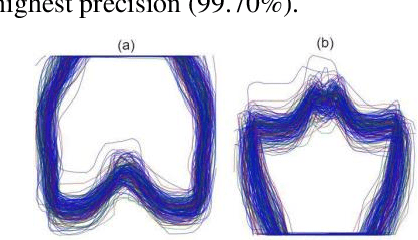
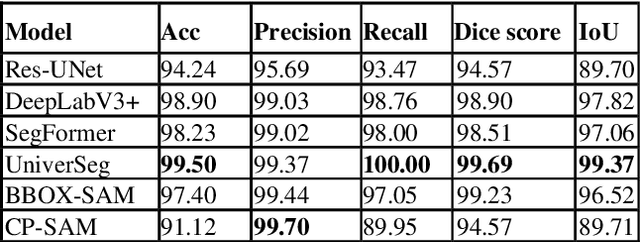
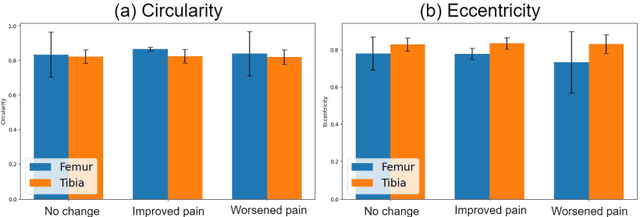
Abstract:Knee osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that induces chronic pain and disability. Bone morphological analysis is a promising tool to understand the mechanical aspect of this disorder. This study proposes a 2D bone morphological analysis using manually segmented bones to explore morphological features related to distinct pain conditions. Furthermore, six semantic segmentation algorithms are assessed for extracting femur and tibia bones from X-ray images. Our analysis reveals that the morphology of the femur undergoes significant changes in instances where pain worsens. Conversely, improvements in pain may not manifest pronounced alterations in bone shape. The few-shot-learning-based algorithm, UniverSeg, demonstrated superior segmentation results with Dice scores of 99.69% for femur and 99.60% for tibia. Regarding pain condition classification, the zero-shot-learning-based algorithm, CP-SAM, achieved the highest accuracy at 66% among all models. UniverSeg is recommended for automatic knee bone segmentation, while SAM models show potential with prompt encoder modifications for optimized outcomes. These findings highlight the effectiveness of few-shot learning for semantic segmentation and the potential of zero-shot learning in enhancing classification models for knee osteoarthritis diagnosis.
Deciphering knee osteoarthritis diagnostic features with explainable artificial intelligence: A systematic review
Aug 18, 2023Abstract:Existing artificial intelligence (AI) models for diagnosing knee osteoarthritis (OA) have faced criticism for their lack of transparency and interpretability, despite achieving medical-expert-like performance. This opacity makes them challenging to trust in clinical practice. Recently, explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) has emerged as a specialized technique that can provide confidence in the model's prediction by revealing how the prediction is derived, thus promoting the use of AI systems in healthcare. This paper presents the first survey of XAI techniques used for knee OA diagnosis. The XAI techniques are discussed from two perspectives: data interpretability and model interpretability. The aim of this paper is to provide valuable insights into XAI's potential towards a more reliable knee OA diagnosis approach and encourage its adoption in clinical practice.
Using U-Net Network for Efficient Brain Tumor Segmentation in MRI Images
Nov 03, 2022
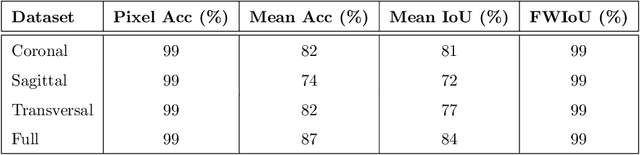
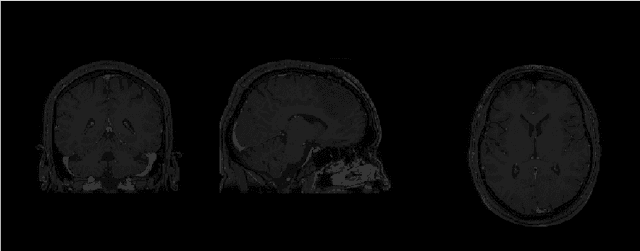
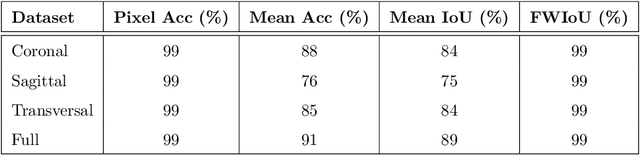
Abstract:Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is the most commonly used non-intrusive technique for medical image acquisition. Brain tumor segmentation is the process of algorithmically identifying tumors in brain MRI scans. While many approaches have been proposed in the literature for brain tumor segmentation, this paper proposes a lightweight implementation of U-Net. Apart from providing real-time segmentation of MRI scans, the proposed architecture does not need large amount of data to train the proposed lightweight U-Net. Moreover, no additional data augmentation step is required. The lightweight U-Net shows very promising results on BITE dataset and it achieves a mean intersection-over-union (IoU) of 89% while outperforming the standard benchmark algorithms. Additionally, this work demonstrates an effective use of the three perspective planes, instead of the original three-dimensional volumetric images, for simplified brain tumor segmentation.
PTSD in the Wild: A Video Database for Studying Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Recognition in Unconstrained Environments
Sep 28, 2022
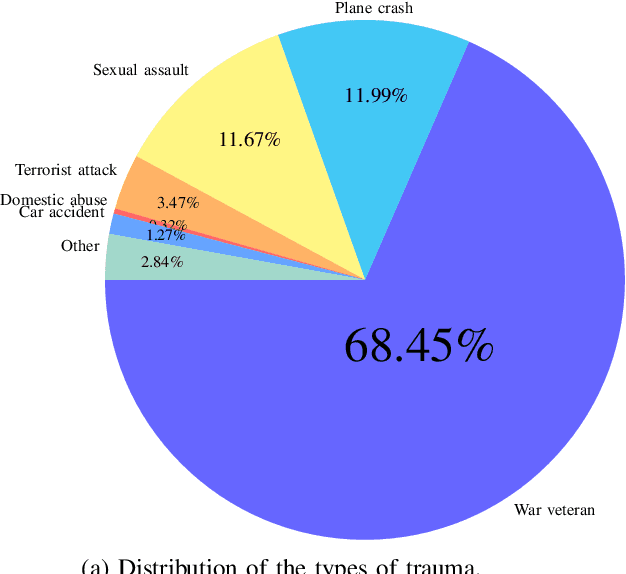
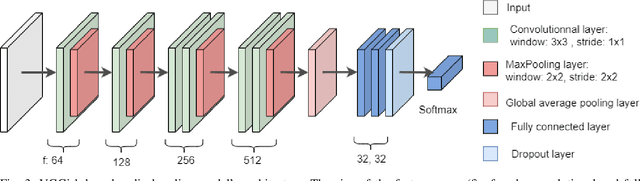
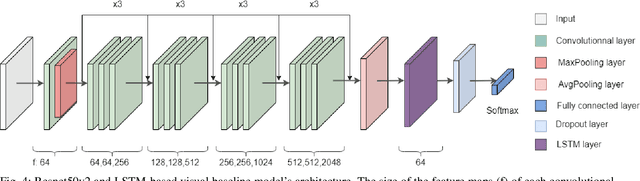
Abstract:POST-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a chronic and debilitating mental condition that is developed in response to catastrophic life events, such as military combat, sexual assault, and natural disasters. PTSD is characterized by flashbacks of past traumatic events, intrusive thoughts, nightmares, hypervigilance, and sleep disturbance, all of which affect a person's life and lead to considerable social, occupational, and interpersonal dysfunction. The diagnosis of PTSD is done by medical professionals using self-assessment questionnaire of PTSD symptoms as defined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM). In this paper, and for the first time, we collected, annotated, and prepared for public distribution a new video database for automatic PTSD diagnosis, called PTSD in the wild dataset. The database exhibits "natural" and big variability in acquisition conditions with different pose, facial expression, lighting, focus, resolution, age, gender, race, occlusions and background. In addition to describing the details of the dataset collection, we provide a benchmark for evaluating computer vision and machine learning based approaches on PTSD in the wild dataset. In addition, we propose and we evaluate a deep learning based approach for PTSD detection in respect to the given benchmark. The proposed approach shows very promising results. Interested researcher can download a copy of PTSD-in-the wild dataset from: http://www.lissi.fr/PTSD-Dataset/
Towards a General Deep Feature Extractor for Facial Expression Recognition
Jan 19, 2022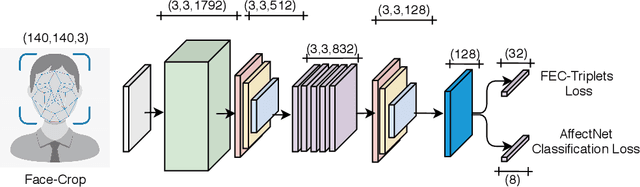
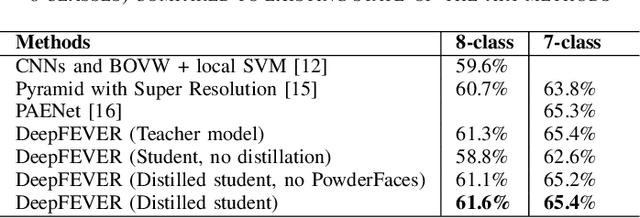


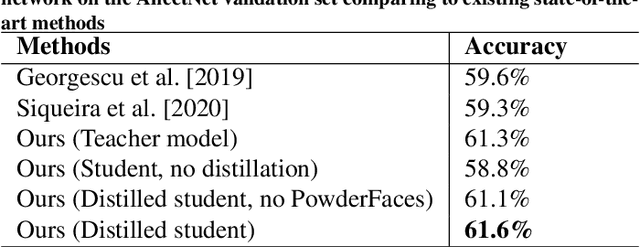
Abstract:The human face conveys a significant amount of information. Through facial expressions, the face is able to communicate numerous sentiments without the need for verbalisation. Visual emotion recognition has been extensively studied. Recently several end-to-end trained deep neural networks have been proposed for this task. However, such models often lack generalisation ability across datasets. In this paper, we propose the Deep Facial Expression Vector ExtractoR (DeepFEVER), a new deep learning-based approach that learns a visual feature extractor general enough to be applied to any other facial emotion recognition task or dataset. DeepFEVER outperforms state-of-the-art results on the AffectNet and Google Facial Expression Comparison datasets. DeepFEVER's extracted features also generalise extremely well to other datasets -- even those unseen during training -- namely, the Real-World Affective Faces (RAF) dataset.
* Published in: 2021 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP). arXiv admin note: text overlap with arXiv:2103.09154
Leveraging Recent Advances in Deep Learning for Audio-Visual Emotion Recognition
Mar 16, 2021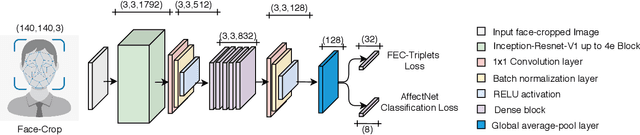
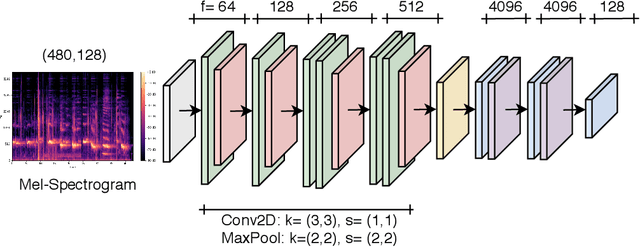
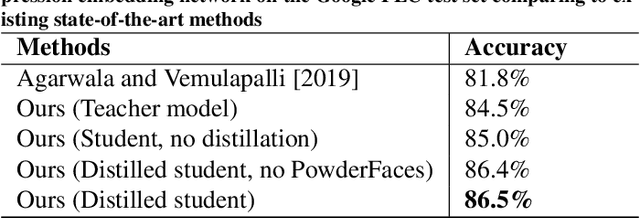
Abstract:Emotional expressions are the behaviors that communicate our emotional state or attitude to others. They are expressed through verbal and non-verbal communication. Complex human behavior can be understood by studying physical features from multiple modalities; mainly facial, vocal and physical gestures. Recently, spontaneous multi-modal emotion recognition has been extensively studied for human behavior analysis. In this paper, we propose a new deep learning-based approach for audio-visual emotion recognition. Our approach leverages recent advances in deep learning like knowledge distillation and high-performing deep architectures. The deep feature representations of the audio and visual modalities are fused based on a model-level fusion strategy. A recurrent neural network is then used to capture the temporal dynamics. Our proposed approach substantially outperforms state-of-the-art approaches in predicting valence on the RECOLA dataset. Moreover, our proposed visual facial expression feature extraction network outperforms state-of-the-art results on the AffectNet and Google Facial Expression Comparison datasets.
Neural Networks based approaches for Major Depressive Disorder and Bipolar Disorder Diagnosis using EEG signals: A review
Sep 28, 2020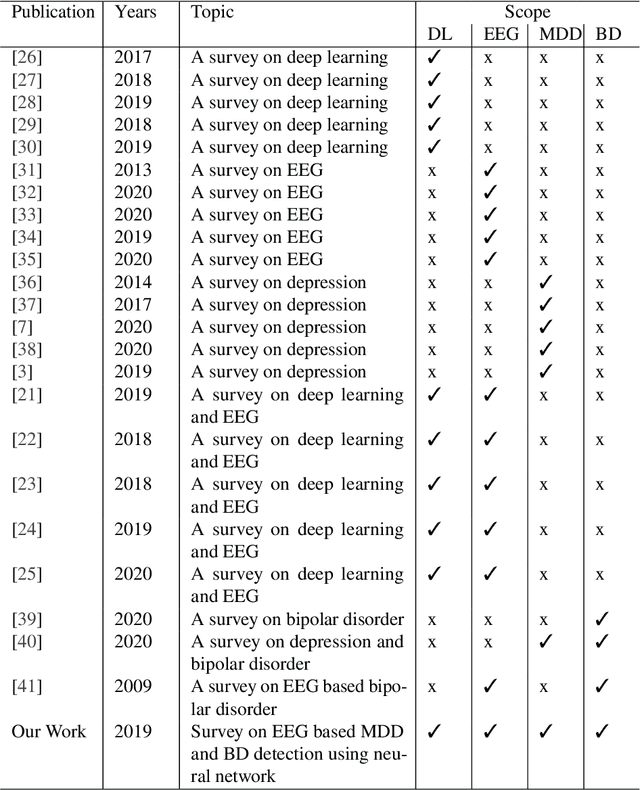
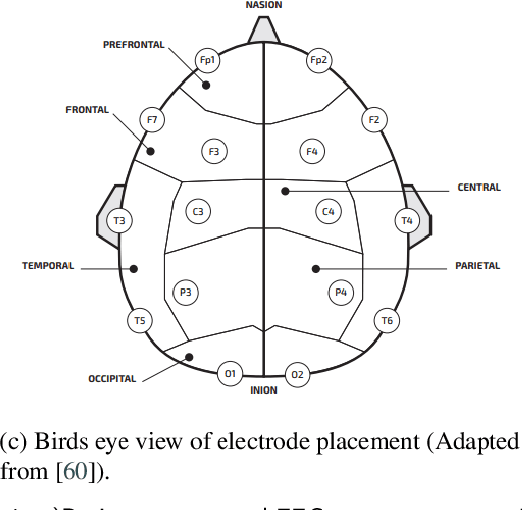
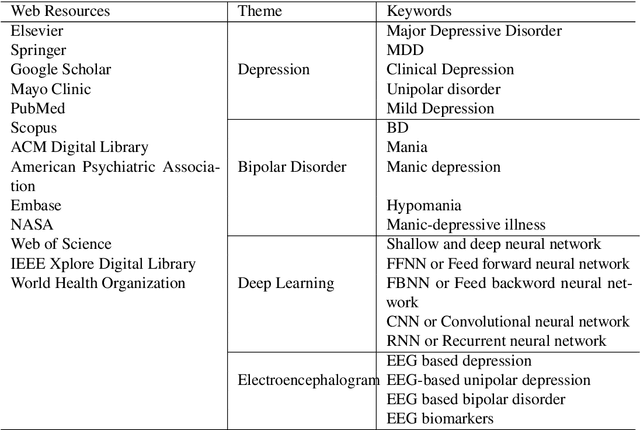
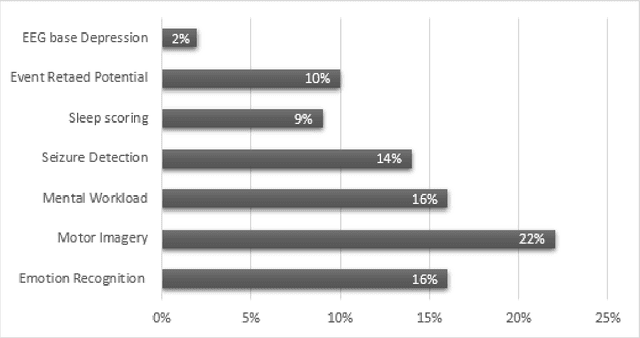
Abstract:Mental disorders represent critical public health challenges as they are leading contributors to the global burden of disease and intensely influence social and financial welfare of individuals. The present comprehensive review concentrate on the two mental disorders: Major depressive Disorder (MDD) and Bipolar Disorder (BD) with noteworthy publications during the last ten years. There's a big need nowadays for phenotypic characterization of psychiatric disorders with biomarkers. Electroencephalography (EEG) signals could offer a rich signature for MDD and BD and then they could improve understanding of pathophysiological mechanisms underling these mental disorders. In this work, we focus on the literature works adopting neural networks fed by EEG signals. Among those studies using EEG and neural networks, we have discussed a variety of EEG based protocols, biomarkers and public datasets for depression and bipolar disorder detection. We conclude with a discussion and valuable recommendations that will help to improve the reliability of developed models and for more accurate and more deterministic computational intelligence based systems in psychiatry. This review will prove to be a structured and valuable initial point for the researchers working on depression and bipolar disorders recognition by using EEG signals.
Deep Multi-Facial Patches Aggregation Network For Facial Expression Recognition
Feb 20, 2020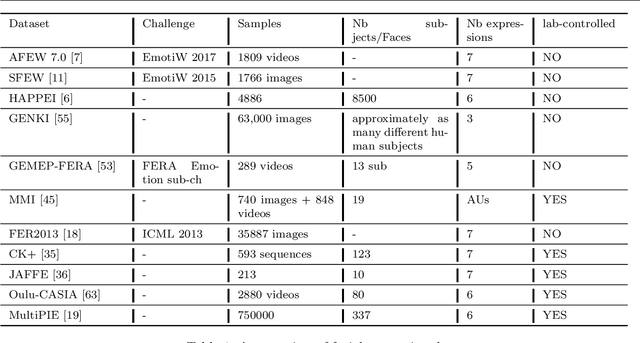
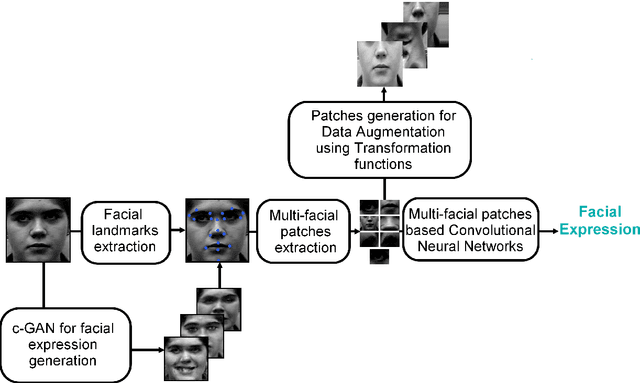
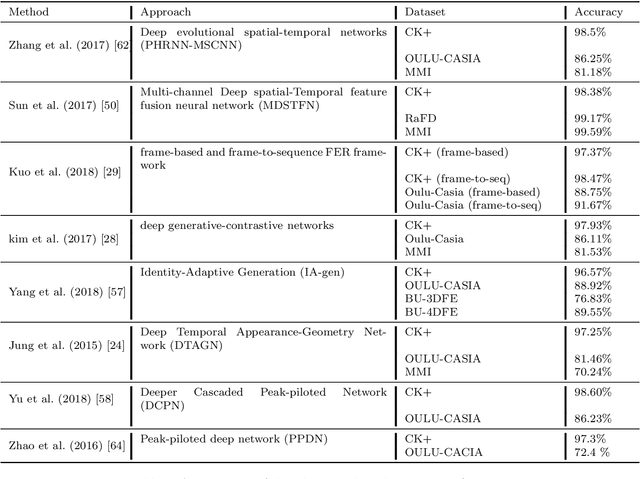
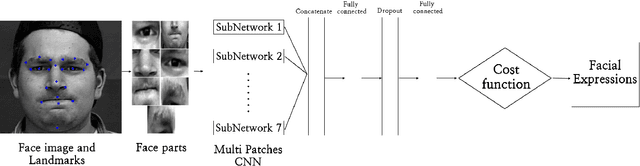
Abstract:In this paper, we propose an approach for Facial Expressions Recognition (FER) based on a deep multi-facial patches aggregation network. Deep features are learned from facial patches using deep sub-networks and aggregated within one deep architecture for expression classification . Several problems may affect the performance of deep-learning based FER approaches, in particular, the small size of existing FER datasets which might not be sufficient to train large deep learning networks. Moreover, it is extremely time-consuming to collect and annotate a large number of facial images. To account for this, we propose two data augmentation techniques for facial expression generation to expand FER labeled training datasets. We evaluate the proposed framework on three FER datasets. Results show that the proposed approach achieves state-of-art FER deep learning approaches performance when the model is trained and tested on images from the same dataset. Moreover, the proposed data augmentation techniques improve the expression recognition rate, and thus can be a solution for training deep learning FER models using small datasets. The accuracy degrades significantly when testing for dataset bias.
Deep Multi-Facial patches Aggregation Network for Expression Classification from Face Images
Sep 23, 2019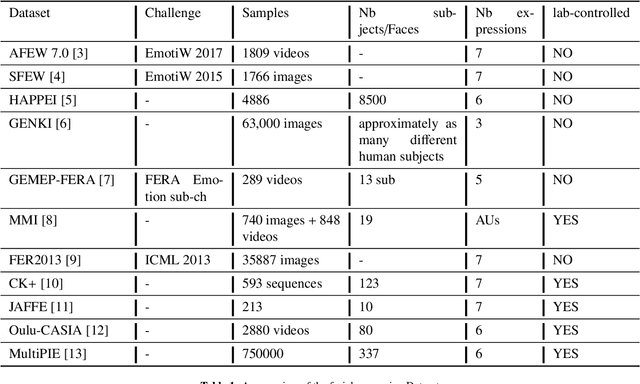
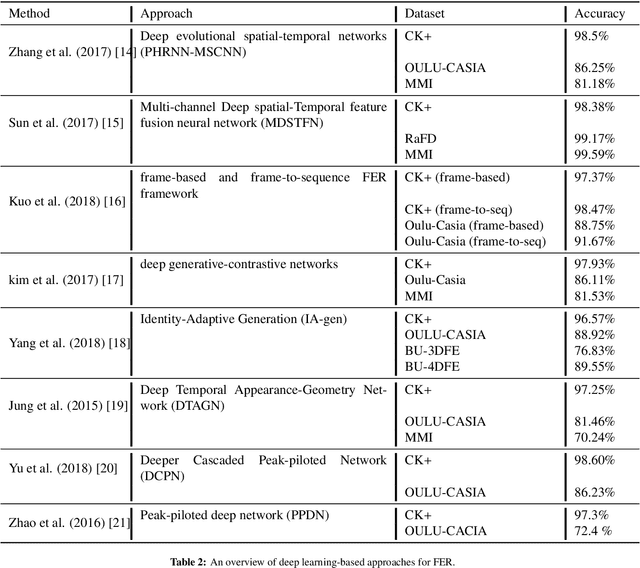
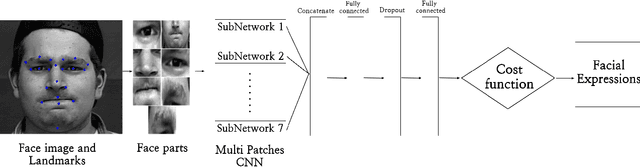
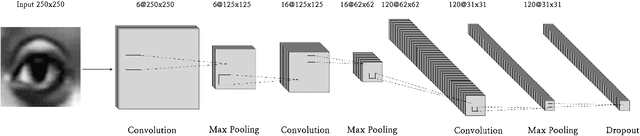
Abstract:Emotional Intelligence in Human-Computer Interaction has attracted increasing attention from researchers in multidisciplinary research fields including psychology, computer vision, neuroscience, artificial intelligence, and related disciplines. Human prone to naturally interact with computers face-to-face. Human Expressions is an important key to better link human and computers. Thus, designing interfaces able to understand human expressions and emotions can improve Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) for better communication. In this paper, we investigate HCI via a deep multi-facial patches aggregation network for Face Expression Recognition (FER). Deep features are extracted from facial parts and aggregated for expression classification. Several problems may affect the performance of the proposed framework like the small size of FER datasets and the high number of parameters to learn. For That, two data augmentation techniques are proposed for facial expression generation to expand the labeled training. The proposed framework is evaluated on the extended Cohn-Konade dataset (CK+) and promising results are achieved.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge