Hazem Abdelkawy
MonoCInIS: Camera Independent Monocular 3D Object Detection using Instance Segmentation
Oct 01, 2021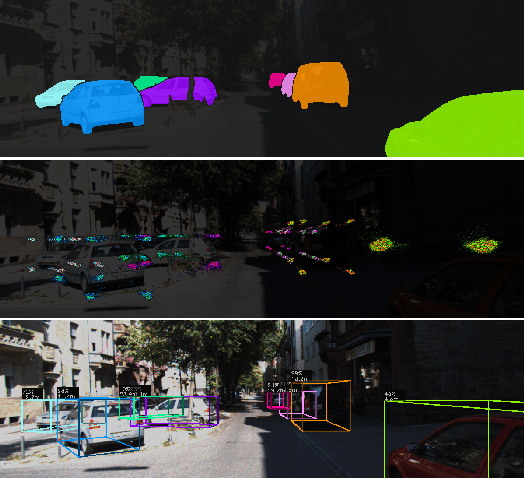
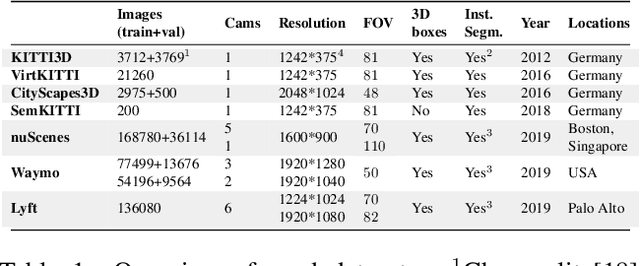
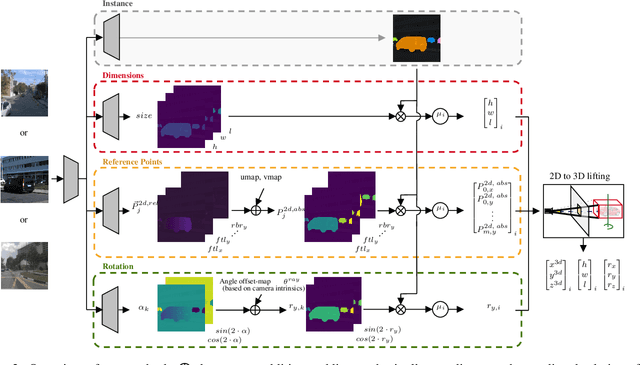
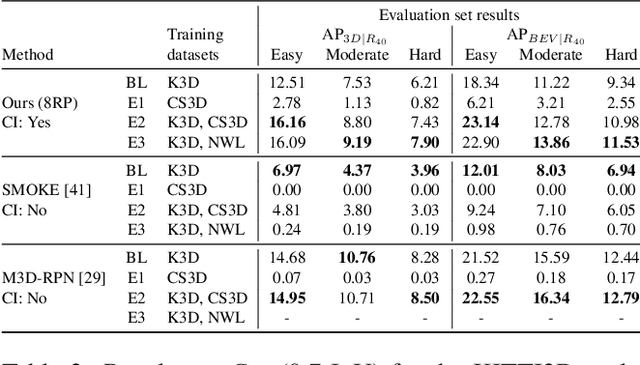
Abstract:Monocular 3D object detection has recently shown promising results, however there remain challenging problems. One of those is the lack of invariance to different camera intrinsic parameters, which can be observed across different 3D object datasets. Little effort has been made to exploit the combination of heterogeneous 3D object datasets. In contrast to general intuition, we show that more data does not automatically guarantee a better performance, but rather, methods need to have a degree of 'camera independence' in order to benefit from large and heterogeneous training data. In this paper we propose a category-level pose estimation method based on instance segmentation, using camera independent geometric reasoning to cope with the varying camera viewpoints and intrinsics of different datasets. Every pixel of an instance predicts the object dimensions, the 3D object reference points projected in 2D image space and, optionally, the local viewing angle. Camera intrinsics are only used outside of the learned network to lift the predicted 2D reference points to 3D. We surpass camera independent methods on the challenging KITTI3D benchmark and show the key benefits compared to camera dependent methods.
Leveraging Recent Advances in Deep Learning for Audio-Visual Emotion Recognition
Mar 16, 2021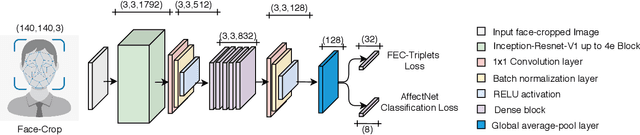
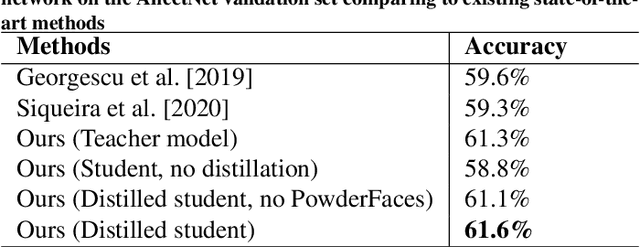
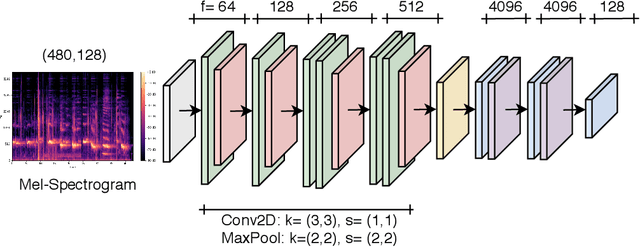
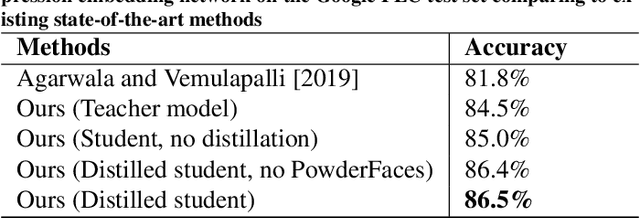
Abstract:Emotional expressions are the behaviors that communicate our emotional state or attitude to others. They are expressed through verbal and non-verbal communication. Complex human behavior can be understood by studying physical features from multiple modalities; mainly facial, vocal and physical gestures. Recently, spontaneous multi-modal emotion recognition has been extensively studied for human behavior analysis. In this paper, we propose a new deep learning-based approach for audio-visual emotion recognition. Our approach leverages recent advances in deep learning like knowledge distillation and high-performing deep architectures. The deep feature representations of the audio and visual modalities are fused based on a model-level fusion strategy. A recurrent neural network is then used to capture the temporal dynamics. Our proposed approach substantially outperforms state-of-the-art approaches in predicting valence on the RECOLA dataset. Moreover, our proposed visual facial expression feature extraction network outperforms state-of-the-art results on the AffectNet and Google Facial Expression Comparison datasets.
Deep HMResNet Model for Human Activity-Aware Robotic Systems
Oct 01, 2018



Abstract:Endowing the robotic systems with cognitive capabilities for recognizing daily activities of humans is an important challenge, which requires sophisticated and novel approaches. Most of the proposed approaches explore pattern recognition techniques which are generally based on hand-crafted features or learned features. In this paper, a novel Hierarchal Multichannel Deep Residual Network (HMResNet) model is proposed for robotic systems to recognize daily human activities in the ambient environments. The introduced model is comprised of multilevel fusion layers. The proposed Multichannel 1D Deep Residual Network model is, at the features level, combined with a Bottleneck MLP neural network to automatically extract robust features regardless of the hardware configuration and, at the decision level, is fully connected with an MLP neural network to recognize daily human activities. Empirical experiments on real-world datasets and an online demonstration are used for validating the proposed model. Results demonstrated that the proposed model outperforms the baseline models in daily human activity recognition.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge