Yun Xin Teoh
Segmentation of Knee Bones for Osteoarthritis Assessment: A Comparative Analysis of Supervised, Few-Shot, and Zero-Shot Learning Approaches
Mar 13, 2024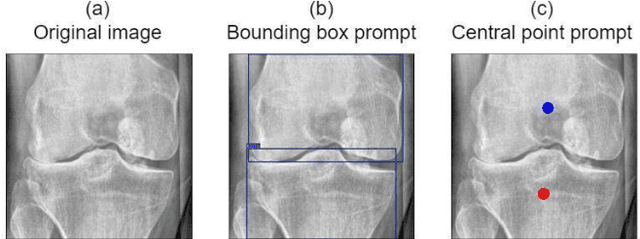
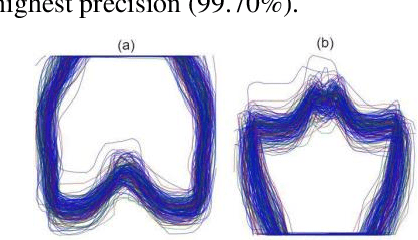
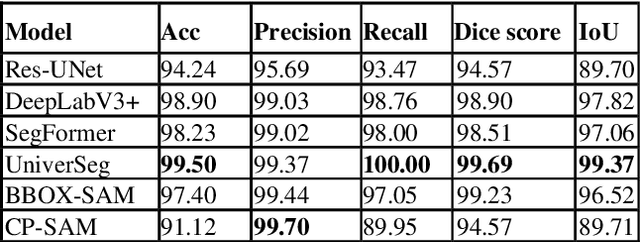
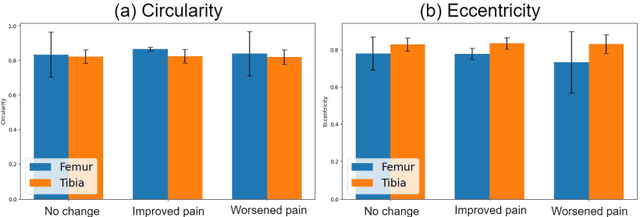
Abstract:Knee osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that induces chronic pain and disability. Bone morphological analysis is a promising tool to understand the mechanical aspect of this disorder. This study proposes a 2D bone morphological analysis using manually segmented bones to explore morphological features related to distinct pain conditions. Furthermore, six semantic segmentation algorithms are assessed for extracting femur and tibia bones from X-ray images. Our analysis reveals that the morphology of the femur undergoes significant changes in instances where pain worsens. Conversely, improvements in pain may not manifest pronounced alterations in bone shape. The few-shot-learning-based algorithm, UniverSeg, demonstrated superior segmentation results with Dice scores of 99.69% for femur and 99.60% for tibia. Regarding pain condition classification, the zero-shot-learning-based algorithm, CP-SAM, achieved the highest accuracy at 66% among all models. UniverSeg is recommended for automatic knee bone segmentation, while SAM models show potential with prompt encoder modifications for optimized outcomes. These findings highlight the effectiveness of few-shot learning for semantic segmentation and the potential of zero-shot learning in enhancing classification models for knee osteoarthritis diagnosis.
Deciphering knee osteoarthritis diagnostic features with explainable artificial intelligence: A systematic review
Aug 18, 2023Abstract:Existing artificial intelligence (AI) models for diagnosing knee osteoarthritis (OA) have faced criticism for their lack of transparency and interpretability, despite achieving medical-expert-like performance. This opacity makes them challenging to trust in clinical practice. Recently, explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) has emerged as a specialized technique that can provide confidence in the model's prediction by revealing how the prediction is derived, thus promoting the use of AI systems in healthcare. This paper presents the first survey of XAI techniques used for knee OA diagnosis. The XAI techniques are discussed from two perspectives: data interpretability and model interpretability. The aim of this paper is to provide valuable insights into XAI's potential towards a more reliable knee OA diagnosis approach and encourage its adoption in clinical practice.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge