Alexander Wikner
Attention-Based Ensemble Pooling for Time Series Forecasting
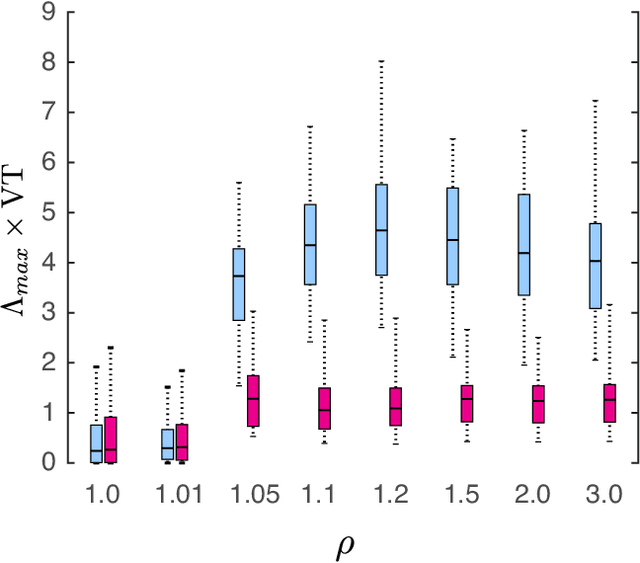
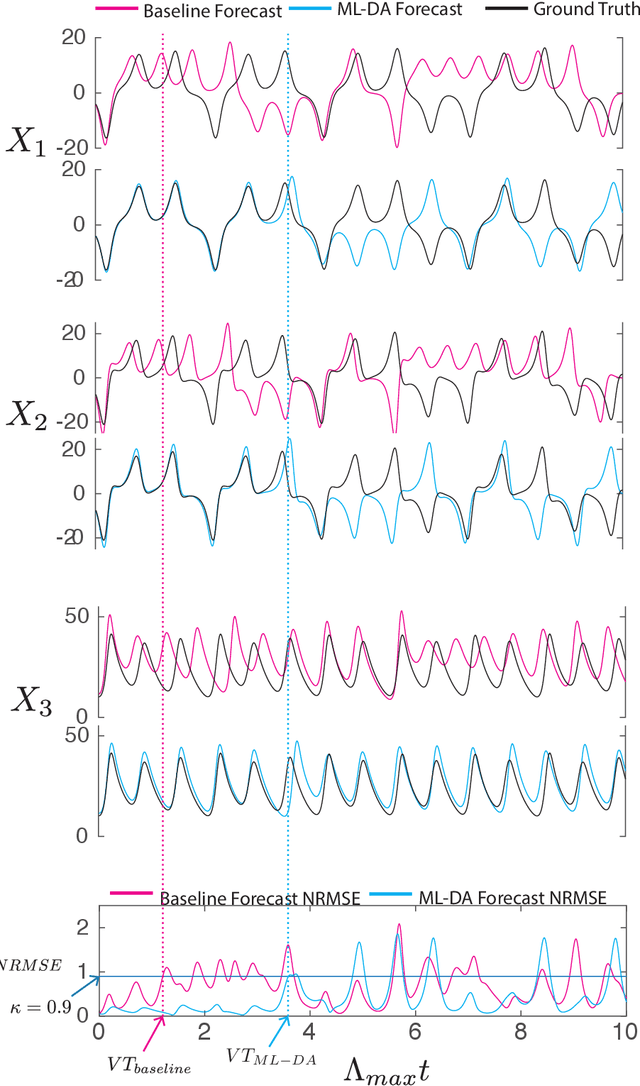
Oct 24, 2023Abstract:A common technique to reduce model bias in time-series forecasting is to use an ensemble of predictive models and pool their output into an ensemble forecast. In cases where each predictive model has different biases, however, it is not always clear exactly how each model forecast should be weighed during this pooling. We propose a method for pooling that performs a weighted average over candidate model forecasts, where the weights are learned by an attention-based ensemble pooling model. We test this method on two time-series forecasting problems: multi-step forecasting of the dynamics of the non-stationary Lorenz `63 equation, and one-step forecasting of the weekly incident deaths due to COVID-19. We find that while our model achieves excellent valid times when forecasting the non-stationary Lorenz `63 equation, it does not consistently perform better than the existing ensemble pooling when forecasting COVID-19 weekly incident deaths.
Stabilizing Machine Learning Prediction of Dynamics: Noise and Noise-inspired Regularization
Nov 09, 2022Abstract:Recent work has shown that machine learning (ML) models can be trained to accurately forecast the dynamics of unknown chaotic dynamical systems. Such ML models can be used to produce both short-term predictions of the state evolution and long-term predictions of the statistical patterns of the dynamics (``climate''). Both of these tasks can be accomplished by employing a feedback loop, whereby the model is trained to predict forward one time step, then the trained model is iterated for multiple time steps with its output used as the input. In the absence of mitigating techniques, however, this technique can result in artificially rapid error growth, leading to inaccurate predictions and/or climate instability. In this article, we systematically examine the technique of adding noise to the ML model input during training as a means to promote stability and improve prediction accuracy. Furthermore, we introduce Linearized Multi-Noise Training (LMNT), a regularization technique that deterministically approximates the effect of many small, independent noise realizations added to the model input during training. Our case study uses reservoir computing, a machine-learning method using recurrent neural networks, to predict the spatiotemporal chaotic Kuramoto-Sivashinsky equation. We find that reservoir computers trained with noise or with LMNT produce climate predictions that appear to be indefinitely stable and have a climate very similar to the true system, while reservoir computers trained without regularization are unstable. Compared with other types of regularization that yield stability in some cases, we find that both short-term and climate predictions from reservoir computers trained with noise or with LMNT are substantially more accurate. Finally, we show that the deterministic aspect of our LMNT regularization facilitates fast hyperparameter tuning when compared to training with noise.
Using Data Assimilation to Train a Hybrid Forecast System that Combines Machine-Learning and Knowledge-Based Components
Feb 15, 2021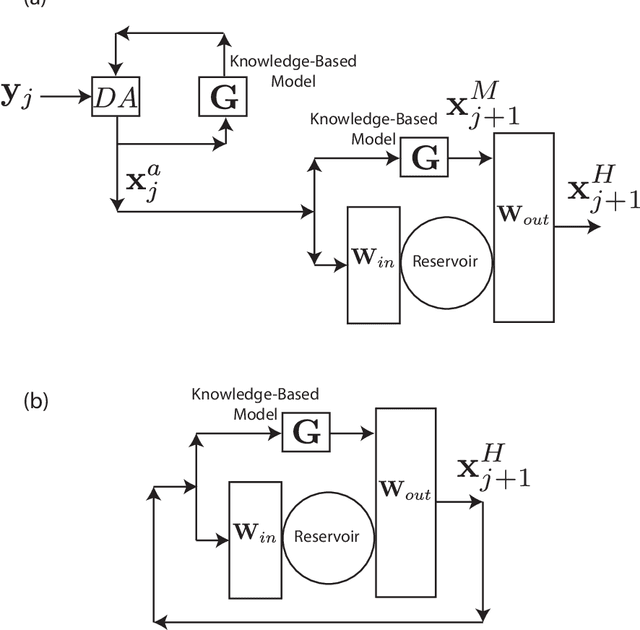
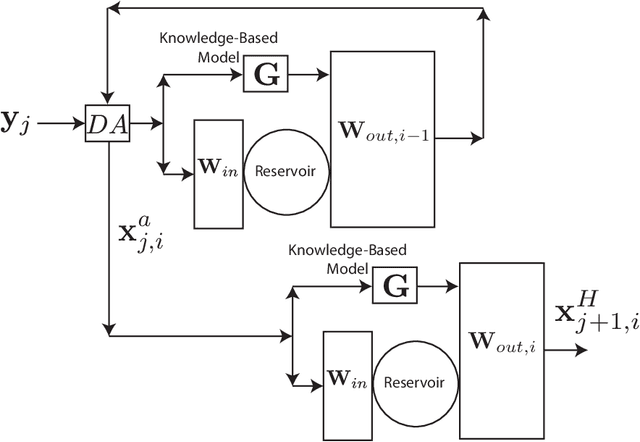
Abstract:We consider the problem of data-assisted forecasting of chaotic dynamical systems when the available data is in the form of noisy partial measurements of the past and present state of the dynamical system. Recently there have been several promising data-driven approaches to forecasting of chaotic dynamical systems using machine learning. Particularly promising among these are hybrid approaches that combine machine learning with a knowledge-based model, where a machine-learning technique is used to correct the imperfections in the knowledge-based model. Such imperfections may be due to incomplete understanding and/or limited resolution of the physical processes in the underlying dynamical system, e.g., the atmosphere or the ocean. Previously proposed data-driven forecasting approaches tend to require, for training, measurements of all the variables that are intended to be forecast. We describe a way to relax this assumption by combining data assimilation with machine learning. We demonstrate this technique using the Ensemble Transform Kalman Filter (ETKF) to assimilate synthetic data for the 3-variable Lorenz system and for the Kuramoto-Sivashinsky system, simulating model error in each case by a misspecified parameter value. We show that by using partial measurements of the state of the dynamical system, we can train a machine learning model to improve predictions made by an imperfect knowledge-based model.
Combining Machine Learning with Knowledge-Based Modeling for Scalable Forecasting and Subgrid-Scale Closure of Large, Complex, Spatiotemporal Systems
Feb 10, 2020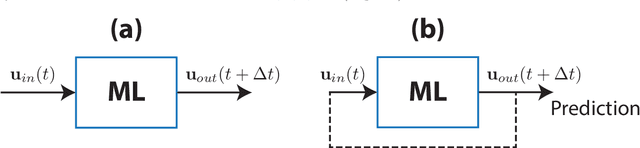
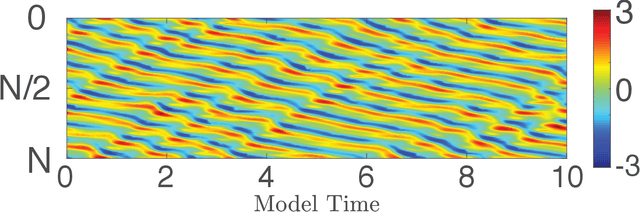
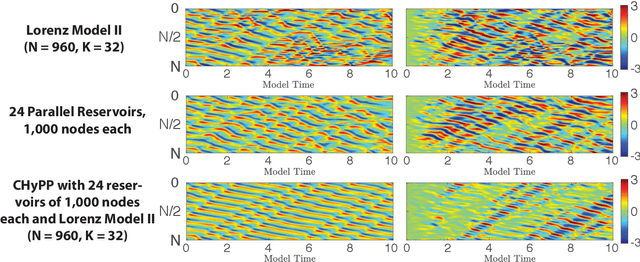
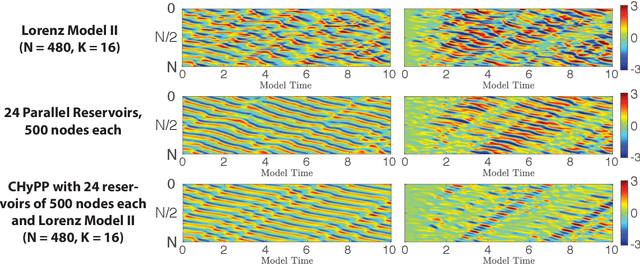
Abstract:We consider the commonly encountered situation (e.g., in weather forecasting) where the goal is to predict the time evolution of a large, spatiotemporally chaotic dynamical system when we have access to both time series data of previous system states and an imperfect model of the full system dynamics. Specifically, we attempt to utilize machine learning as the essential tool for integrating the use of past data into predictions. In order to facilitate scalability to the common scenario of interest where the spatiotemporally chaotic system is very large and complex, we propose combining two approaches:(i) a parallel machine learning prediction scheme; and (ii) a hybrid technique, for a composite prediction system composed of a knowledge-based component and a machine-learning-based component. We demonstrate that not only can this method combining (i) and (ii) be scaled to give excellent performance for very large systems, but also that the length of time series data needed to train our multiple, parallel machine learning components is dramatically less than that necessary without parallelization. Furthermore, considering cases where computational realization of the knowledge-based component does not resolve subgrid-scale processes, our scheme is able to use training data to incorporate the effect of the unresolved short-scale dynamics upon the resolved longer-scale dynamics ("subgrid-scale closure").
Hybrid Forecasting of Chaotic Processes: Using Machine Learning in Conjunction with a Knowledge-Based Model
Mar 09, 2018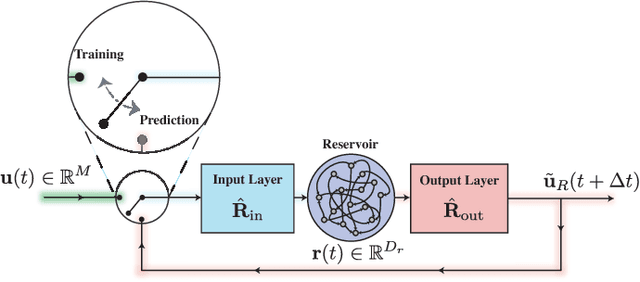
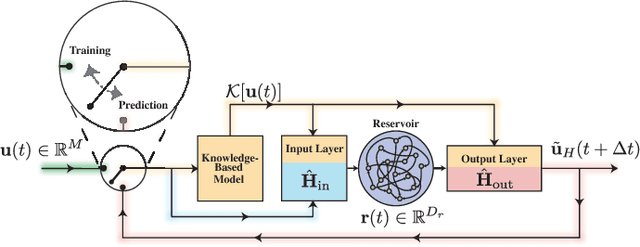
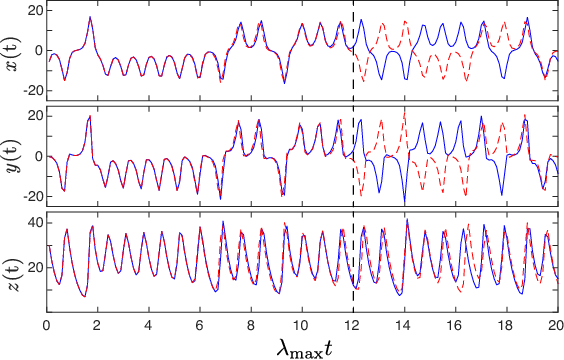
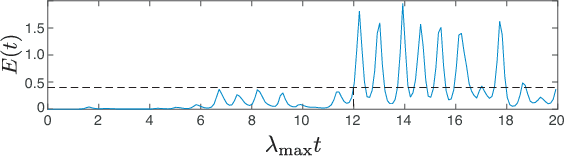
Abstract:A model-based approach to forecasting chaotic dynamical systems utilizes knowledge of the physical processes governing the dynamics to build an approximate mathematical model of the system. In contrast, machine learning techniques have demonstrated promising results for forecasting chaotic systems purely from past time series measurements of system state variables (training data), without prior knowledge of the system dynamics. The motivation for this paper is the potential of machine learning for filling in the gaps in our underlying mechanistic knowledge that cause widely-used knowledge-based models to be inaccurate. Thus we here propose a general method that leverages the advantages of these two approaches by combining a knowledge-based model and a machine learning technique to build a hybrid forecasting scheme. Potential applications for such an approach are numerous (e.g., improving weather forecasting). We demonstrate and test the utility of this approach using a particular illustrative version of a machine learning known as reservoir computing, and we apply the resulting hybrid forecaster to a low-dimensional chaotic system, as well as to a high-dimensional spatiotemporal chaotic system. These tests yield extremely promising results in that our hybrid technique is able to accurately predict for a much longer period of time than either its machine-learning component or its model-based component alone.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge