Alexander Rodríguez
Modular Deep-Learning-Based Early Warning System for Deadly Heatwave Prediction
Dec 09, 2025Abstract:Severe heatwaves in urban areas significantly threaten public health, calling for establishing early warning strategies. Despite predicting occurrence of heatwaves and attributing historical mortality, predicting an incoming deadly heatwave remains a challenge due to the difficulty in defining and estimating heat-related mortality. Furthermore, establishing an early warning system imposes additional requirements, including data availability, spatial and temporal robustness, and decision costs. To address these challenges, we propose DeepTherm, a modular early warning system for deadly heatwave prediction without requiring heat-related mortality history. By highlighting the flexibility of deep learning, DeepTherm employs a dual-prediction pipeline, disentangling baseline mortality in the absence of heatwaves and other irregular events from all-cause mortality. We evaluated DeepTherm on real-world data across Spain. Results demonstrate consistent, robust, and accurate performance across diverse regions, time periods, and population groups while allowing trade-off between missed alarms and false alarms.
Neural Conformal Control for Time Series Forecasting
Dec 24, 2024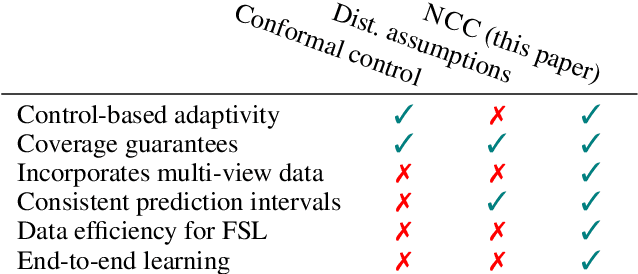


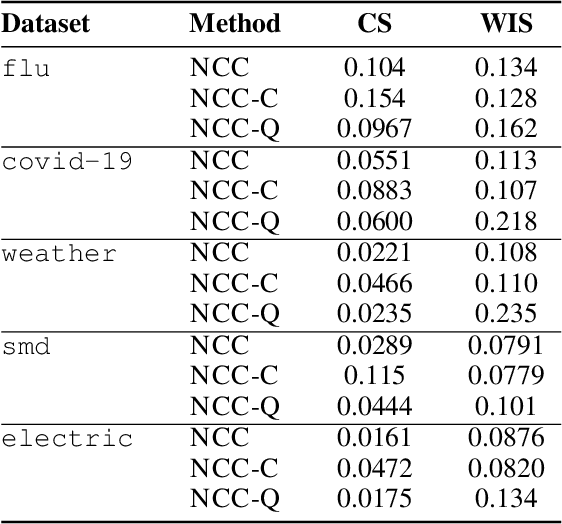
Abstract:We introduce a neural network conformal prediction method for time series that enhances adaptivity in non-stationary environments. Our approach acts as a neural controller designed to achieve desired target coverage, leveraging auxiliary multi-view data with neural network encoders in an end-to-end manner to further enhance adaptivity. Additionally, our model is designed to enhance the consistency of prediction intervals in different quantiles by integrating monotonicity constraints and leverages data from related tasks to boost few-shot learning performance. Using real-world datasets from epidemics, electric demand, weather, and others, we empirically demonstrate significant improvements in coverage and probabilistic accuracy, and find that our method is the only one that combines good calibration with consistency in prediction intervals.
When Rigidity Hurts: Soft Consistency Regularization for Probabilistic Hierarchical Time Series Forecasting
Oct 19, 2023Abstract:Probabilistic hierarchical time-series forecasting is an important variant of time-series forecasting, where the goal is to model and forecast multivariate time-series that have underlying hierarchical relations. Most methods focus on point predictions and do not provide well-calibrated probabilistic forecasts distributions. Recent state-of-art probabilistic forecasting methods also impose hierarchical relations on point predictions and samples of distribution which does not account for coherency of forecast distributions. Previous works also silently assume that datasets are always consistent with given hierarchical relations and do not adapt to real-world datasets that show deviation from this assumption. We close both these gap and propose PROFHiT, which is a fully probabilistic hierarchical forecasting model that jointly models forecast distribution of entire hierarchy. PROFHiT uses a flexible probabilistic Bayesian approach and introduces a novel Distributional Coherency regularization to learn from hierarchical relations for entire forecast distribution that enables robust and calibrated forecasts as well as adapt to datasets of varying hierarchical consistency. On evaluating PROFHiT over wide range of datasets, we observed 41-88% better performance in accuracy and significantly better calibration. Due to modeling the coherency over full distribution, we observed that PROFHiT can robustly provide reliable forecasts even if up to 10% of input time-series data is missing where other methods' performance severely degrade by over 70%.
Differentiable Agent-based Epidemiology
Jul 20, 2022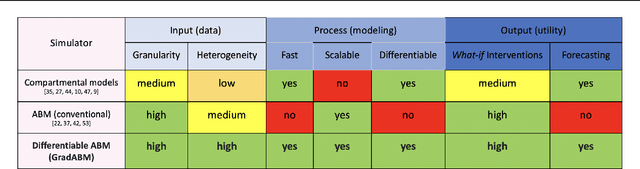
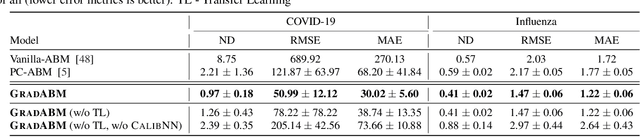
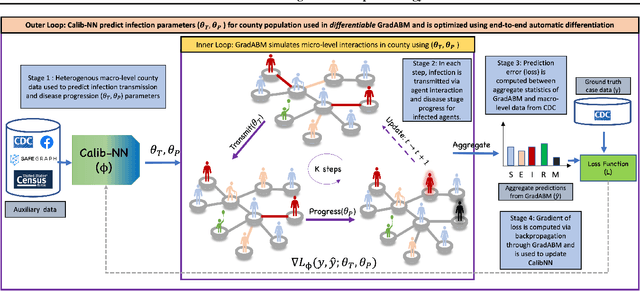
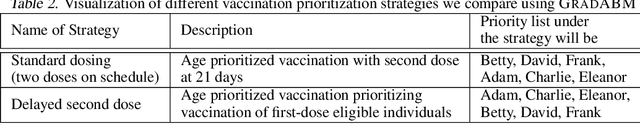
Abstract:Mechanistic simulators are an indispensable tool for epidemiology to explore the behavior of complex, dynamic infections under varying conditions and navigate uncertain environments. ODE-based models are the dominant paradigm that enable fast simulations and are tractable to gradient-based optimization, but make simplifying assumptions about population homogeneity. Agent-based models (ABMs) are an increasingly popular alternative paradigm that can represent the heterogeneity of contact interactions with granular detail and agency of individual behavior. However, conventional ABM frameworks are not differentiable and present challenges in scalability; due to which it is non-trivial to connect them to auxiliary data sources easily. In this paper we introduce GradABM which is a new scalable, fast and differentiable design for ABMs. GradABM runs simulations in few seconds on commodity hardware and enables fast forward and differentiable inverse simulations. This makes it amenable to be merged with deep neural networks and seamlessly integrate heterogeneous data sources to help with calibration, forecasting and policy evaluation. We demonstrate the efficacy of GradABM via extensive experiments with real COVID-19 and influenza datasets. We are optimistic this work will bring ABM and AI communities closer together.
Data-Centric Epidemic Forecasting: A Survey
Jul 20, 2022



Abstract:The COVID-19 pandemic has brought forth the importance of epidemic forecasting for decision makers in multiple domains, ranging from public health to the economy as a whole. While forecasting epidemic progression is frequently conceptualized as being analogous to weather forecasting, however it has some key differences and remains a non-trivial task. The spread of diseases is subject to multiple confounding factors spanning human behavior, pathogen dynamics, weather and environmental conditions. Research interest has been fueled by the increased availability of rich data sources capturing previously unobservable facets and also due to initiatives from government public health and funding agencies. This has resulted, in particular, in a spate of work on 'data-centered' solutions which have shown potential in enhancing our forecasting capabilities by leveraging non-traditional data sources as well as recent innovations in AI and machine learning. This survey delves into various data-driven methodological and practical advancements and introduces a conceptual framework to navigate through them. First, we enumerate the large number of epidemiological datasets and novel data streams that are relevant to epidemic forecasting, capturing various factors like symptomatic online surveys, retail and commerce, mobility, genomics data and more. Next, we discuss methods and modeling paradigms focusing on the recent data-driven statistical and deep-learning based methods as well as on the novel class of hybrid models that combine domain knowledge of mechanistic models with the effectiveness and flexibility of statistical approaches. We also discuss experiences and challenges that arise in real-world deployment of these forecasting systems including decision-making informed by forecasts. Finally, we highlight some challenges and open problems found across the forecasting pipeline.
PROFHIT: Probabilistic Robust Forecasting for Hierarchical Time-series
Jun 20, 2022



Abstract:Probabilistic hierarchical time-series forecasting is an important variant of time-series forecasting, where the goal is to model and forecast multivariate time-series that have underlying hierarchical relations. Most methods focus on point predictions and do not provide well-calibrated probabilistic forecasts distributions. Recent state-of-art probabilistic forecasting methods also impose hierarchical relations on point predictions and samples of distribution which does not account for coherency of forecast distributions. Previous works also silently assume that datasets are always consistent with given hierarchical relations and do not adapt to real-world datasets that show deviation from this assumption. We close both these gaps and propose PROFHIT, which is a fully probabilistic hierarchical forecasting model that jointly models forecast distribution of entire hierarchy. PROFHIT uses a flexible probabilistic Bayesian approach and introduces a novel Distributional Coherency regularization to learn from hierarchical relations for entire forecast distribution that enables robust and calibrated forecasts as well as adapt to datasets of varying hierarchical consistency. On evaluating PROFHIT over wide range of datasets, we observed 41-88% better performance in accuracy and calibration. Due to modeling the coherency over full distribution, we observed that PROFHIT can robustly provide reliable forecasts even if up to 10% of input time-series data is missing where other methods' performance severely degrade by over 70%.
EINNs: Epidemiologically-Informed Neural Networks
Feb 21, 2022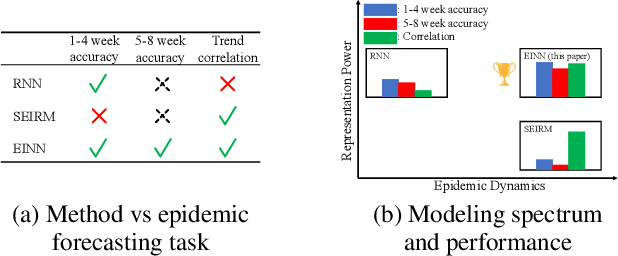
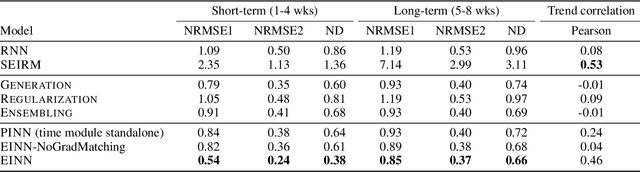
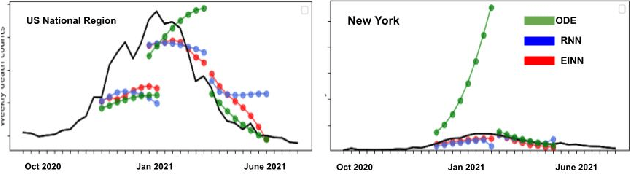
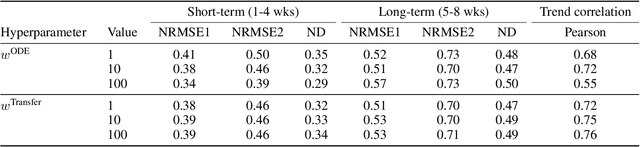
Abstract:We introduce a new class of physics-informed neural networks-EINN-crafted for epidemic forecasting. We investigate how to leverage both the theoretical flexibility provided by mechanistic models as well as the data-driven expressability afforded by AI models, to ingest heterogeneous information. Although neural forecasting models has been successful in multiple tasks, long-term predictions and anticipating trend changes remain open challenges. Epidemiological ODE models contain mechanisms that can guide us in these two tasks; however, they have limited capability of ingesting data sources and modeling composite signals. Thus we propose to supervise neural networks with epidemic mechanistic models while simultaneously learning their hidden dynamics. Our method EINN allows neural models have the flexibility to learn the disease spread dynamics and use auxiliary features in a general framework. In contrast with previous work, we not assume the observability of complete dynamics and do not need to numerically solve the ODE equations during training. Our thorough experiments showcase the clear benefits of our approach with other non-trivial alternatives.
CAMul: Calibrated and Accurate Multi-view Time-Series Forecasting
Sep 15, 2021



Abstract:Probabilistic time-series forecasting enables reliable decision making across many domains. Most forecasting problems have diverse sources of data containing multiple modalities and structures. Leveraging information as well as uncertainty from these data sources for well-calibrated and accurate forecasts is an important challenging problem. Most previous work on multi-modal learning and forecasting simply aggregate intermediate representations from each data view by simple methods of summation or concatenation and do not explicitly model uncertainty for each data-view. We propose a general probabilistic multi-view forecasting framework CAMul, that can learn representations and uncertainty from diverse data sources. It integrates the knowledge and uncertainty from each data view in a dynamic context-specific manner assigning more importance to useful views to model a well-calibrated forecast distribution. We use CAMul for multiple domains with varied sources and modalities and show that CAMul outperforms other state-of-art probabilistic forecasting models by over 25\% in accuracy and calibration.
Back2Future: Leveraging Backfill Dynamics for Improving Real-time Predictions in Future
Jun 08, 2021



Abstract:In real-time forecasting in public health, data collection is a non-trivial and demanding task. Often after initially released, it undergoes several revisions later (maybe due to human or technical constraints) - as a result, it may take weeks until the data reaches to a stable value. This so-called 'backfill' phenomenon and its effect on model performance has been barely studied in the prior literature. In this paper, we introduce the multi-variate backfill problem using COVID-19 as the motivating example. We construct a detailed dataset composed of relevant signals over the past year of the pandemic. We then systematically characterize several patterns in backfill dynamics and leverage our observations for formulating a novel problem and neural framework Back2Future that aims to refines a given model's predictions in real-time. Our extensive experiments demonstrate that our method refines the performance of top models for COVID-19 forecasting, in contrast to non-trivial baselines, yielding 18% improvement over baselines, enabling us obtain a new SOTA performance. In addition, we show that our model improves model evaluation too; hence policy-makers can better understand the true accuracy of forecasting models in real-time.
When in Doubt: Neural Non-Parametric Uncertainty Quantification for Epidemic Forecasting
Jun 07, 2021



Abstract:Accurate and trustworthy epidemic forecasting is an important problem that has impact on public health planning and disease mitigation. Most existing epidemic forecasting models disregard uncertainty quantification, resulting in mis-calibrated predictions. Recent works in deep neural models for uncertainty-aware time-series forecasting also have several limitations; e.g. it is difficult to specify meaningful priors in Bayesian NNs, while methods like deep ensembling are computationally expensive in practice. In this paper, we fill this important gap. We model the forecasting task as a probabilistic generative process and propose a functional neural process model called EPIFNP, which directly models the probability density of the forecast value. EPIFNP leverages a dynamic stochastic correlation graph to model the correlations between sequences in a non-parametric way, and designs different stochastic latent variables to capture functional uncertainty from different perspectives. Our extensive experiments in a real-time flu forecasting setting show that EPIFNP significantly outperforms previous state-of-the-art models in both accuracy and calibration metrics, up to 2.5x in accuracy and 2.4x in calibration. Additionally, due to properties of its generative process,EPIFNP learns the relations between the current season and similar patterns of historical seasons,enabling interpretable forecasts. Beyond epidemic forecasting, the EPIFNP can be of independent interest for advancing principled uncertainty quantification in deep sequential models for predictive analytics
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge