Alberto Marchisio
FAQNAS: FLOPs-aware Hybrid Quantum Neural Architecture Search using Genetic Algorithm
Nov 13, 2025


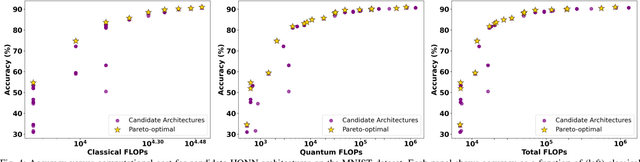
Abstract:Hybrid Quantum Neural Networks (HQNNs), which combine parameterized quantum circuits with classical neural layers, are emerging as promising models in the noisy intermediate-scale quantum (NISQ) era. While quantum circuits are not naturally measured in floating point operations (FLOPs), most HQNNs (in NISQ era) are still trained on classical simulators where FLOPs directly dictate runtime and scalability. Hence, FLOPs represent a practical and viable metric to measure the computational complexity of HQNNs. In this work, we introduce FAQNAS, a FLOPs-aware neural architecture search (NAS) framework that formulates HQNN design as a multi-objective optimization problem balancing accuracy and FLOPs. Unlike traditional approaches, FAQNAS explicitly incorporates FLOPs into the optimization objective, enabling the discovery of architectures that achieve strong performance while minimizing computational cost. Experiments on five benchmark datasets (MNIST, Digits, Wine, Breast Cancer, and Iris) show that quantum FLOPs dominate accuracy improvements, while classical FLOPs remain largely fixed. Pareto-optimal solutions reveal that competitive accuracy can often be achieved with significantly reduced computational cost compared to FLOPs-agnostic baselines. Our results establish FLOPs-awareness as a practical criterion for HQNN design in the NISQ era and as a scalable principle for future HQNN systems.
RobQFL: Robust Quantum Federated Learning in Adversarial Environment
Sep 05, 2025Abstract:Quantum Federated Learning (QFL) merges privacy-preserving federation with quantum computing gains, yet its resilience to adversarial noise is unknown. We first show that QFL is as fragile as centralized quantum learning. We propose Robust Quantum Federated Learning (RobQFL), embedding adversarial training directly into the federated loop. RobQFL exposes tunable axes: client coverage $\gamma$ (0-100\%), perturbation scheduling (fixed-$\varepsilon$ vs $\varepsilon$-mixes), and optimization (fine-tune vs scratch), and distils the resulting $\gamma \times \varepsilon$ surface into two metrics: Accuracy-Robustness Area and Robustness Volume. On 15-client simulations with MNIST and Fashion-MNIST, IID and Non-IID conditions, training only 20-50\% clients adversarially boosts $\varepsilon \leq 0.1$ accuracy $\sim$15 pp at $< 2$ pp clean-accuracy cost; fine-tuning adds 3-5 pp. With $\geq$75\% coverage, a moderate $\varepsilon$-mix is optimal, while high-$\varepsilon$ schedules help only at 100\% coverage. Label-sorted non-IID splits halve robustness, underscoring data heterogeneity as a dominant risk.
PennyLang: Pioneering LLM-Based Quantum Code Generation with a Novel PennyLane-Centric Dataset
Mar 04, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) offer remarkable capabilities in code generation, natural language processing, and domain-specific reasoning. Their potential in aiding quantum software development remains underexplored, particularly for the PennyLane framework-a leading platform for hybrid quantum-classical computing. To address this gap, we introduce a novel, high-quality dataset comprising 3,347 PennyLane-specific code samples of quantum circuits and their contextual descriptions, specifically curated to train/fine-tune LLM-based quantum code assistance. Our key contributions are threefold: (1) the automatic creation and open-source release of a comprehensive PennyLane dataset leveraging quantum computing textbooks, official documentation, and open-source repositories; (2) the development of a systematic methodology for data refinement, annotation, and formatting to optimize LLM training efficiency; and (3) a thorough evaluation, based on a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) framework, demonstrating the effectiveness of our dataset in streamlining PennyLane code generation and improving quantum development workflows. Compared to existing efforts that predominantly focus on Qiskit, our dataset significantly broadens the spectrum of quantum frameworks covered in AI-driven code assistance. By bridging this gap and providing reproducible dataset-creation methodologies, we aim to advance the field of AI-assisted quantum programming, making quantum computing more accessible to both newcomers and experienced developers.
QFAL: Quantum Federated Adversarial Learning
Feb 28, 2025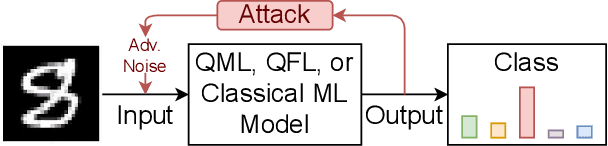
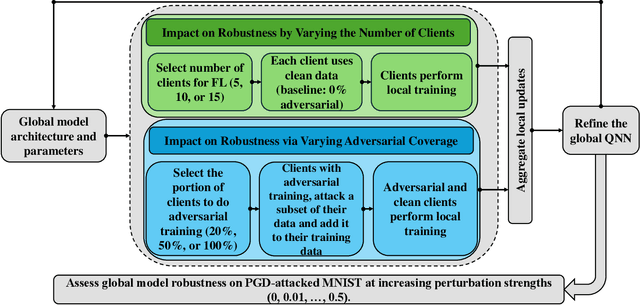
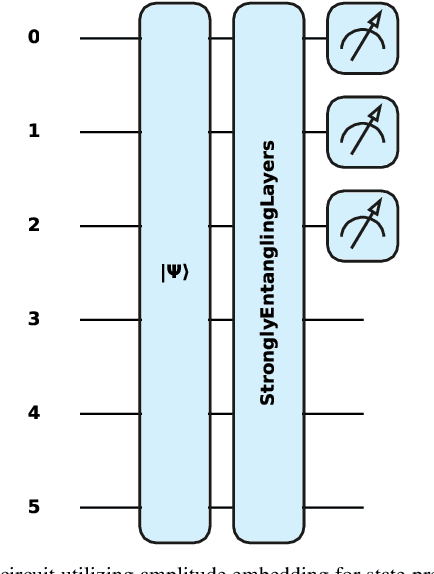
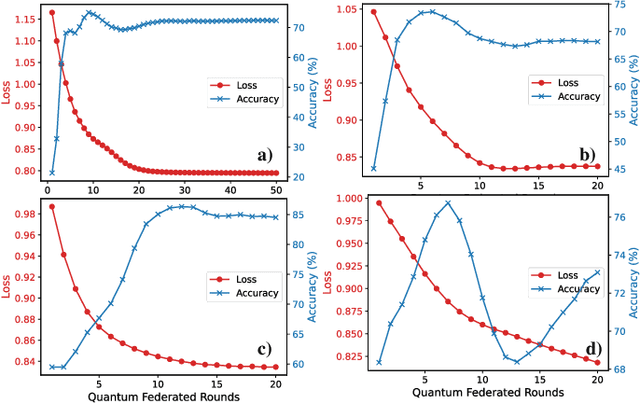
Abstract:Quantum federated learning (QFL) merges the privacy advantages of federated systems with the computational potential of quantum neural networks (QNNs), yet its vulnerability to adversarial attacks remains poorly understood. This work pioneers the integration of adversarial training into QFL, proposing a robust framework, quantum federated adversarial learning (QFAL), where clients collaboratively defend against perturbations by combining local adversarial example generation with federated averaging (FedAvg). We systematically evaluate the interplay between three critical factors: client count (5, 10, 15), adversarial training coverage (0-100%), and adversarial attack perturbation strength (epsilon = 0.01-0.5), using the MNIST dataset. Our experimental results show that while fewer clients often yield higher clean-data accuracy, larger federations can more effectively balance accuracy and robustness when partially adversarially trained. Notably, even limited adversarial coverage (e.g., 20%-50%) can significantly improve resilience to moderate perturbations, though at the cost of reduced baseline performance. Conversely, full adversarial training (100%) may regain high clean accuracy but is vulnerable under stronger attacks. These findings underscore an inherent trade-off between robust and standard objectives, which is further complicated by quantum-specific factors. We conclude that a carefully chosen combination of client count and adversarial coverage is critical for mitigating adversarial vulnerabilities in QFL. Moreover, we highlight opportunities for future research, including adaptive adversarial training schedules, more diverse quantum encoding schemes, and personalized defense strategies to further enhance the robustness-accuracy trade-off in real-world quantum federated environments.
MoENAS: Mixture-of-Expert based Neural Architecture Search for jointly Accurate, Fair, and Robust Edge Deep Neural Networks
Feb 11, 2025Abstract:There has been a surge in optimizing edge Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) for accuracy and efficiency using traditional optimization techniques such as pruning, and more recently, employing automatic design methodologies. However, the focus of these design techniques has often overlooked critical metrics such as fairness, robustness, and generalization. As a result, when evaluating SOTA edge DNNs' performance in image classification using the FACET dataset, we found that they exhibit significant accuracy disparities (14.09%) across 10 different skin tones, alongside issues of non-robustness and poor generalizability. In response to these observations, we introduce Mixture-of-Experts-based Neural Architecture Search (MoENAS), an automatic design technique that navigates through a space of mixture of experts to discover accurate, fair, robust, and general edge DNNs. MoENAS improves the accuracy by 4.02% compared to SOTA edge DNNs and reduces the skin tone accuracy disparities from 14.09% to 5.60%, while enhancing robustness by 3.80% and minimizing overfitting to 0.21%, all while keeping model size close to state-of-the-art models average size (+0.4M). With these improvements, MoENAS establishes a new benchmark for edge DNN design, paving the way for the development of more inclusive and robust edge DNNs.
LEP-QNN: Loan Eligibility Prediction Using Quantum Neural Networks
Dec 04, 2024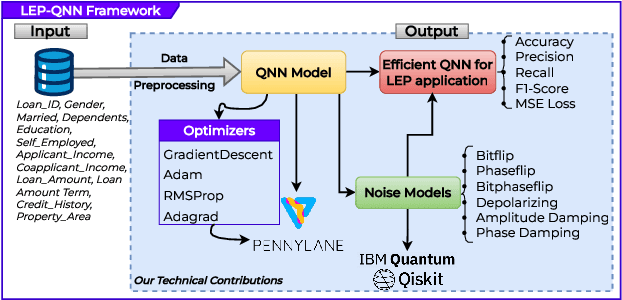
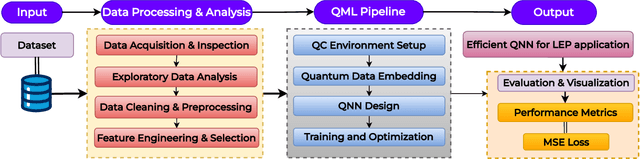
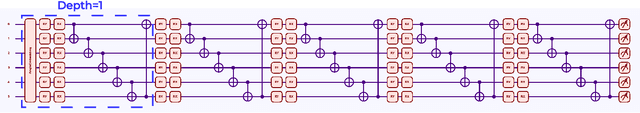
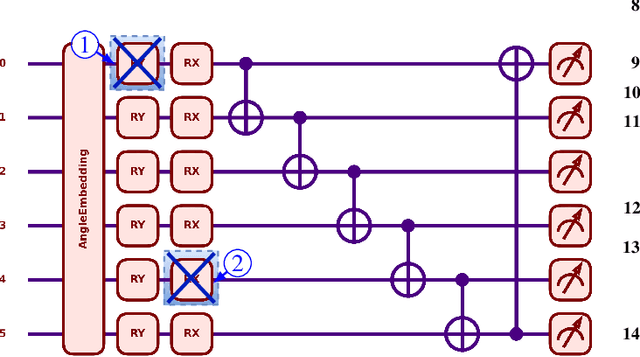
Abstract:Predicting loan eligibility with high accuracy remains a significant challenge in the finance sector. Accurate predictions enable financial institutions to make informed decisions, mitigate risks, and effectively adapt services to meet customer needs. However, the complexity and the high-dimensional nature of financial data have always posed significant challenges to achieving this level of precision. To overcome these issues, we propose a novel approach that employs Quantum Machine Learning (QML) for Loan Eligibility Prediction using Quantum Neural Networks (LEP-QNN).Our innovative approach achieves an accuracy of 98% in predicting loan eligibility from a single, comprehensive dataset. This performance boost is attributed to the strategic implementation of a dropout mechanism within the quantum circuit, aimed at minimizing overfitting and thereby improving the model's predictive reliability. In addition, our exploration of various optimizers leads to identifying the most efficient setup for our LEP-QNN framework, optimizing its performance. We also rigorously evaluate the resilience of LEP-QNN under different quantum noise scenarios, ensuring its robustness and dependability for quantum computing environments. This research showcases the potential of QML in financial predictions and establishes a foundational guide for advancing QML technologies, marking a step towards developing advanced, quantum-driven financial decision-making tools.
QADQN: Quantum Attention Deep Q-Network for Financial Market Prediction
Aug 06, 2024Abstract:Financial market prediction and optimal trading strategy development remain challenging due to market complexity and volatility. Our research in quantum finance and reinforcement learning for decision-making demonstrates the approach of quantum-classical hybrid algorithms to tackling real-world financial challenges. In this respect, we corroborate the concept with rigorous backtesting and validate the framework's performance under realistic market conditions, by including fixed transaction cost per trade. This paper introduces a Quantum Attention Deep Q-Network (QADQN) approach to address these challenges through quantum-enhanced reinforcement learning. Our QADQN architecture uses a variational quantum circuit inside a traditional deep Q-learning framework to take advantage of possible quantum advantages in decision-making. We gauge the QADQN agent's performance on historical data from major market indices, including the S&P 500. We evaluate the agent's learning process by examining its reward accumulation and the effectiveness of its experience replay mechanism. Our empirical results demonstrate the QADQN's superior performance, achieving better risk-adjusted returns with Sortino ratios of 1.28 and 1.19 for non-overlapping and overlapping test periods respectively, indicating effective downside risk management.
FastSpiker: Enabling Fast Training for Spiking Neural Networks on Event-based Data through Learning Rate Enhancements for Autonomous Embedded Systems
Jul 07, 2024Abstract:Autonomous embedded systems (e.g., robots) typically necessitate intelligent computation with low power/energy processing for completing their tasks. Such requirements can be fulfilled by embodied neuromorphic intelligence with spiking neural networks (SNNs) because of their high learning quality (e.g., accuracy) and sparse computation. Here, the employment of event-based data is preferred to ensure seamless connectivity between input and processing parts. However, state-of-the-art SNNs still face a long training time to achieve high accuracy, thereby incurring high energy consumption and producing a high rate of carbon emission. Toward this, we propose FastSpiker, a novel methodology that enables fast SNN training on event-based data through learning rate enhancements targeting autonomous embedded systems. In FastSpiker, we first investigate the impact of different learning rate policies and their values, then select the ones that quickly offer high accuracy. Afterward, we explore different settings for the selected learning rate policies to find the appropriate policies through a statistical-based decision. Experimental results show that our FastSpiker offers up to 10.5x faster training time and up to 88.39% lower carbon emission to achieve higher or comparable accuracy to the state-of-the-art on the event-based automotive dataset (i.e., NCARS). In this manner, our FastSpiker methodology paves the way for green and sustainable computing in realizing embodied neuromorphic intelligence for autonomous embedded systems.
SNN4Agents: A Framework for Developing Energy-Efficient Embodied Spiking Neural Networks for Autonomous Agents
Apr 14, 2024Abstract:Recent trends have shown that autonomous agents, such as Autonomous Ground Vehicles (AGVs), Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), and mobile robots, effectively improve human productivity in solving diverse tasks. However, since these agents are typically powered by portable batteries, they require extremely low power/energy consumption to operate in a long lifespan. To solve this challenge, neuromorphic computing has emerged as a promising solution, where bio-inspired Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) use spikes from event-based cameras or data conversion pre-processing to perform sparse computations efficiently. However, the studies of SNN deployments for autonomous agents are still at an early stage. Hence, the optimization stages for enabling efficient embodied SNN deployments for autonomous agents have not been defined systematically. Toward this, we propose a novel framework called SNN4Agents that consists of a set of optimization techniques for designing energy-efficient embodied SNNs targeting autonomous agent applications. Our SNN4Agents employs weight quantization, timestep reduction, and attention window reduction to jointly improve the energy efficiency, reduce the memory footprint, optimize the processing latency, while maintaining high accuracy. In the evaluation, we investigate use cases of event-based car recognition, and explore the trade-offs among accuracy, latency, memory, and energy consumption. The experimental results show that our proposed framework can maintain high accuracy (i.e., 84.12% accuracy) with 68.75% memory saving, 3.58x speed-up, and 4.03x energy efficiency improvement as compared to the state-of-the-art work for NCARS dataset, thereby enabling energy-efficient embodied SNN deployments for autonomous agents.
A Methodology to Study the Impact of Spiking Neural Network Parameters considering Event-Based Automotive Data
Apr 05, 2024Abstract:Autonomous Driving (AD) systems are considered as the future of human mobility and transportation. Solving computer vision tasks such as image classification and object detection/segmentation, with high accuracy and low power/energy consumption, is highly needed to realize AD systems in real life. These requirements can potentially be satisfied by Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs). However, the state-of-the-art works in SNN-based AD systems still focus on proposing network models that can achieve high accuracy, and they have not systematically studied the roles of SNN parameters when used for learning event-based automotive data. Therefore, we still lack understanding of how to effectively develop SNN models for AD systems. Toward this, we propose a novel methodology to systematically study and analyze the impact of SNN parameters considering event-based automotive data, then leverage this analysis for enhancing SNN developments. To do this, we first explore different settings of SNN parameters that directly affect the learning mechanism (i.e., batch size, learning rate, neuron threshold potential, and weight decay), then analyze the accuracy results. Afterward, we propose techniques that jointly improve SNN accuracy and reduce training time. Experimental results show that our methodology can improve the SNN models for AD systems than the state-of-the-art, as it achieves higher accuracy (i.e., 86%) for the NCARS dataset, and it can also achieve iso-accuracy (i.e., ~85% with standard deviation less than 0.5%) while speeding up the training time by 1.9x. In this manner, our research work provides a set of guidelines for SNN parameter enhancements, thereby enabling the practical developments of SNN-based AD systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge