Muhammad Kashif
Quantum vs. Classical Machine Learning: A Benchmark Study for Financial Prediction
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:In this paper, we present a reproducible benchmarking framework that systematically compares QML models with architecture-matched classical counterparts across three financial tasks: (i) directional return prediction on U.S. and Turkish equities, (ii) live-trading simulation with Quantum LSTMs versus classical LSTMs on the S\&P 500, and (iii) realized volatility forecasting using Quantum Support Vector Regression. By standardizing data splits, features, and evaluation metrics, our study provides a fair assessment of when current-generation QML models can match or exceed classical methods. Our results reveal that quantum approaches show performance gains when data structure and circuit design are well aligned. In directional classification, hybrid quantum neural networks surpass the parameter-matched ANN by \textbf{+3.8 AUC} and \textbf{+3.4 accuracy points} on \texttt{AAPL} stock and by \textbf{+4.9 AUC} and \textbf{+3.6 accuracy points} on Turkish stock \texttt{KCHOL}. In live trading, the QLSTM achieves higher risk-adjusted returns in \textbf{two of four} S\&P~500 regimes. For volatility forecasting, an angle-encoded QSVR attains the \textbf{lowest QLIKE} on \texttt{KCHOL} and remains within $\sim$0.02-0.04 QLIKE of the best classical kernels on \texttt{S\&P~500} and \texttt{AAPL}. Our benchmarking framework clearly identifies the scenarios where current QML architectures offer tangible improvements and where established classical methods continue to dominate.
FAQNAS: FLOPs-aware Hybrid Quantum Neural Architecture Search using Genetic Algorithm
Nov 13, 2025


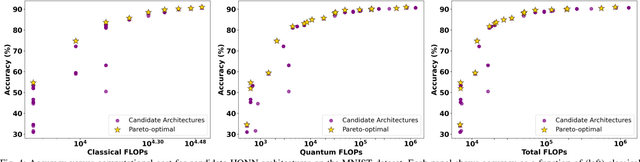
Abstract:Hybrid Quantum Neural Networks (HQNNs), which combine parameterized quantum circuits with classical neural layers, are emerging as promising models in the noisy intermediate-scale quantum (NISQ) era. While quantum circuits are not naturally measured in floating point operations (FLOPs), most HQNNs (in NISQ era) are still trained on classical simulators where FLOPs directly dictate runtime and scalability. Hence, FLOPs represent a practical and viable metric to measure the computational complexity of HQNNs. In this work, we introduce FAQNAS, a FLOPs-aware neural architecture search (NAS) framework that formulates HQNN design as a multi-objective optimization problem balancing accuracy and FLOPs. Unlike traditional approaches, FAQNAS explicitly incorporates FLOPs into the optimization objective, enabling the discovery of architectures that achieve strong performance while minimizing computational cost. Experiments on five benchmark datasets (MNIST, Digits, Wine, Breast Cancer, and Iris) show that quantum FLOPs dominate accuracy improvements, while classical FLOPs remain largely fixed. Pareto-optimal solutions reveal that competitive accuracy can often be achieved with significantly reduced computational cost compared to FLOPs-agnostic baselines. Our results establish FLOPs-awareness as a practical criterion for HQNN design in the NISQ era and as a scalable principle for future HQNN systems.
PennyLang: Pioneering LLM-Based Quantum Code Generation with a Novel PennyLane-Centric Dataset
Mar 04, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) offer remarkable capabilities in code generation, natural language processing, and domain-specific reasoning. Their potential in aiding quantum software development remains underexplored, particularly for the PennyLane framework-a leading platform for hybrid quantum-classical computing. To address this gap, we introduce a novel, high-quality dataset comprising 3,347 PennyLane-specific code samples of quantum circuits and their contextual descriptions, specifically curated to train/fine-tune LLM-based quantum code assistance. Our key contributions are threefold: (1) the automatic creation and open-source release of a comprehensive PennyLane dataset leveraging quantum computing textbooks, official documentation, and open-source repositories; (2) the development of a systematic methodology for data refinement, annotation, and formatting to optimize LLM training efficiency; and (3) a thorough evaluation, based on a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) framework, demonstrating the effectiveness of our dataset in streamlining PennyLane code generation and improving quantum development workflows. Compared to existing efforts that predominantly focus on Qiskit, our dataset significantly broadens the spectrum of quantum frameworks covered in AI-driven code assistance. By bridging this gap and providing reproducible dataset-creation methodologies, we aim to advance the field of AI-assisted quantum programming, making quantum computing more accessible to both newcomers and experienced developers.
ResQuNNs:Towards Enabling Deep Learning in Quantum Convolution Neural Networks
Feb 14, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we present a novel framework for enhancing the performance of Quanvolutional Neural Networks (QuNNs) by introducing trainable quanvolutional layers and addressing the critical challenges associated with them. Traditional quanvolutional layers, although beneficial for feature extraction, have largely been static, offering limited adaptability. Unlike state-of-the-art, our research overcomes this limitation by enabling training within these layers, significantly increasing the flexibility and potential of QuNNs. However, the introduction of multiple trainable quanvolutional layers induces complexities in gradient-based optimization, primarily due to the difficulty in accessing gradients across these layers. To resolve this, we propose a novel architecture, Residual Quanvolutional Neural Networks (ResQuNNs), leveraging the concept of residual learning, which facilitates the flow of gradients by adding skip connections between layers. By inserting residual blocks between quanvolutional layers, we ensure enhanced gradient access throughout the network, leading to improved training performance. Moreover, we provide empirical evidence on the strategic placement of these residual blocks within QuNNs. Through extensive experimentation, we identify an efficient configuration of residual blocks, which enables gradients across all the layers in the network that eventually results in efficient training. Our findings suggest that the precise location of residual blocks plays a crucial role in maximizing the performance gains in QuNNs. Our results mark a substantial step forward in the evolution of quantum deep learning, offering new avenues for both theoretical development and practical quantum computing applications.
District Wise Price Forecasting of Wheat in Pakistan using Deep Learning
Mar 05, 2021



Abstract:Wheat is the main agricultural crop of Pakistan and is a staple food requirement of almost every Pakistani household making it the main strategic commodity of the country whose availability and affordability is the government's main priority. Wheat food availability can be vastly affected by multiple factors included but not limited to the production, consumption, financial crisis, inflation, or volatile market. The government ensures food security by particular policy and monitory arrangements, which keeps up purchase parity for the poor. Such arrangements can be made more effective if a dynamic analysis is carried out to estimate the future yield based on certain current factors. Future planning of commodity pricing is achievable by forecasting their future price anticipated by the current circumstances. This paper presents a wheat price forecasting methodology, which uses the price, weather, production, and consumption trends for wheat prices taken over the past few years and analyzes them with the help of advance neural networks architecture Long Short Term Memory (LSTM) networks. The proposed methodology presented significantly improved results versus other conventional machine learning and statistical time series analysis methods.
Urdu Handwritten Text Recognition Using ResNet18
Feb 19, 2021



Abstract:Handwritten text recognition is an active research area in the field of deep learning and artificial intelligence to convert handwritten text into machine-understandable. A lot of work has been done for other languages, especially for English, but work for the Urdu language is very minimal due to the cursive nature of Urdu characters. The need for Urdu HCR systems is increasing because of the advancement of technology. In this paper, we propose a ResNet18 model for handwritten text recognition using Urdu Nastaliq Handwritten Dataset (UNHD) which contains 3,12000 words written by 500 candidates.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge