Walid El Maouaki
RobQFL: Robust Quantum Federated Learning in Adversarial Environment
Sep 05, 2025Abstract:Quantum Federated Learning (QFL) merges privacy-preserving federation with quantum computing gains, yet its resilience to adversarial noise is unknown. We first show that QFL is as fragile as centralized quantum learning. We propose Robust Quantum Federated Learning (RobQFL), embedding adversarial training directly into the federated loop. RobQFL exposes tunable axes: client coverage $\gamma$ (0-100\%), perturbation scheduling (fixed-$\varepsilon$ vs $\varepsilon$-mixes), and optimization (fine-tune vs scratch), and distils the resulting $\gamma \times \varepsilon$ surface into two metrics: Accuracy-Robustness Area and Robustness Volume. On 15-client simulations with MNIST and Fashion-MNIST, IID and Non-IID conditions, training only 20-50\% clients adversarially boosts $\varepsilon \leq 0.1$ accuracy $\sim$15 pp at $< 2$ pp clean-accuracy cost; fine-tuning adds 3-5 pp. With $\geq$75\% coverage, a moderate $\varepsilon$-mix is optimal, while high-$\varepsilon$ schedules help only at 100\% coverage. Label-sorted non-IID splits halve robustness, underscoring data heterogeneity as a dominant risk.
QFAL: Quantum Federated Adversarial Learning
Feb 28, 2025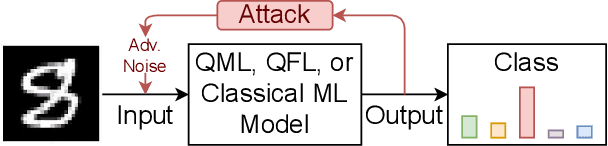
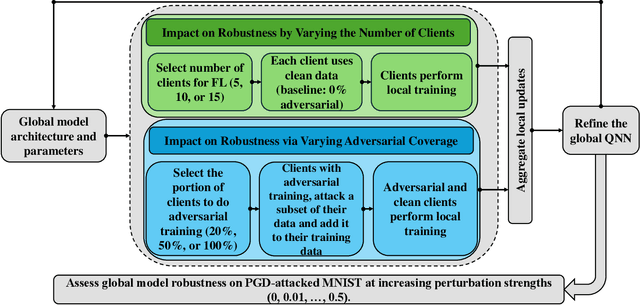
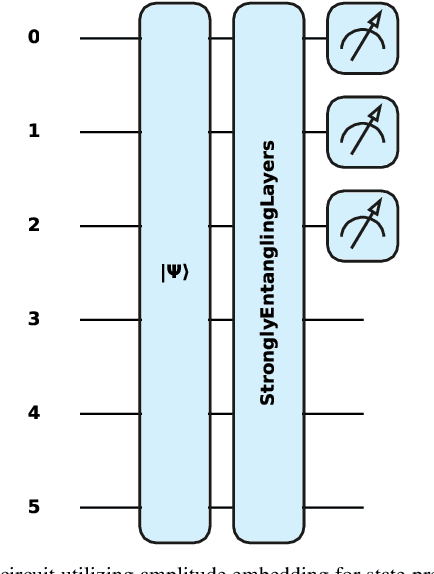
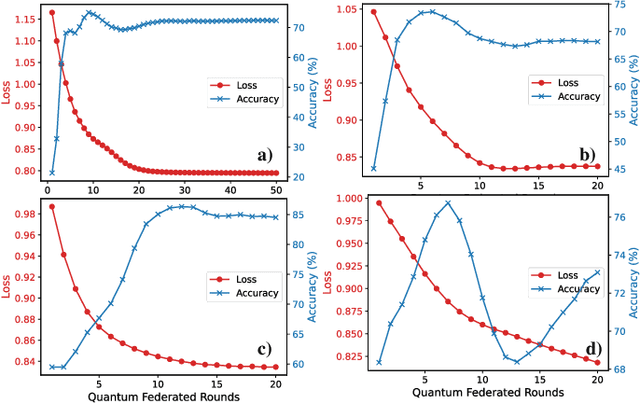
Abstract:Quantum federated learning (QFL) merges the privacy advantages of federated systems with the computational potential of quantum neural networks (QNNs), yet its vulnerability to adversarial attacks remains poorly understood. This work pioneers the integration of adversarial training into QFL, proposing a robust framework, quantum federated adversarial learning (QFAL), where clients collaboratively defend against perturbations by combining local adversarial example generation with federated averaging (FedAvg). We systematically evaluate the interplay between three critical factors: client count (5, 10, 15), adversarial training coverage (0-100%), and adversarial attack perturbation strength (epsilon = 0.01-0.5), using the MNIST dataset. Our experimental results show that while fewer clients often yield higher clean-data accuracy, larger federations can more effectively balance accuracy and robustness when partially adversarially trained. Notably, even limited adversarial coverage (e.g., 20%-50%) can significantly improve resilience to moderate perturbations, though at the cost of reduced baseline performance. Conversely, full adversarial training (100%) may regain high clean accuracy but is vulnerable under stronger attacks. These findings underscore an inherent trade-off between robust and standard objectives, which is further complicated by quantum-specific factors. We conclude that a carefully chosen combination of client count and adversarial coverage is critical for mitigating adversarial vulnerabilities in QFL. Moreover, we highlight opportunities for future research, including adaptive adversarial training schedules, more diverse quantum encoding schemes, and personalized defense strategies to further enhance the robustness-accuracy trade-off in real-world quantum federated environments.
Quantum Support Vector Machine for Prostate Cancer Detection: A Performance Analysis
Mar 12, 2024



Abstract:This study addresses the urgent need for improved prostate cancer detection methods by harnessing the power of advanced technological solutions. We introduce the application of Quantum Support Vector Machine (QSVM) to this critical healthcare challenge, showcasing an enhancement in diagnostic performance over the classical Support Vector Machine (SVM) approach. Our study not only outlines the remarkable improvements in diagnostic performance made by QSVM over the classic SVM technique, but it delves into the advancements brought about by the quantum feature map architecture, which has been carefully identified and evaluated, ensuring it aligns seamlessly with the unique characteristics of our prostate cancer dataset. This architecture succeded in creating a distinct feature space, enabling the detection of complex, non-linear patterns in the data. The findings reveal not only a comparable accuracy with classical SVM ($92\%$) but also a $7.14\%$ increase in sensitivity and a notably high F1-Score ($93.33\%$). This study's important combination of quantum computing in medical diagnostics marks a pivotal step forward in cancer detection, offering promising implications for the future of healthcare technology.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge