Aditya Mogadala
Fusion Models for Improved Visual Captioning
Oct 28, 2020


Abstract:Visual captioning aims to generate textual descriptions given images. Traditionally, the captioning models are trained on human annotated datasets such as Flickr30k and MS-COCO, which are limited in size and diversity. This limitation hinders the generalization capabilities of these models while also rendering them to often make mistakes. Language models can, however, be trained on vast amounts of freely available unlabelled data and have recently emerged as successful language encoders and coherent text generators. Meanwhile, several unimodal and multimodal fusion techniques have been proven to work well for natural language generation and automatic speech recognition. Building on these recent developments, and with an aim of improving the quality of generated captions, the contribution of our work in this paper is two-fold: First, we propose a generic multimodal model fusion framework for caption generation as well as emendation where we utilize different fusion strategies to integrate a pretrained Auxiliary Language Model (AuxLM) within the traditional encoder-decoder visual captioning frameworks. Next, we employ the same fusion strategies to integrate a pretrained Masked Language Model (MLM), namely BERT, with a visual captioning model, viz. Show, Attend, and Tell, for emending both syntactic and semantic errors in captions. Our caption emendation experiments on three benchmark image captioning datasets, viz. Flickr8k, Flickr30k, and MSCOCO, show improvements over the baseline, indicating the usefulness of our proposed multimodal fusion strategies. Further, we perform a preliminary qualitative analysis on the emended captions and identify error categories based on the type of corrections.
Integrating Image Captioning with Rule-based Entity Masking
Jul 22, 2020



Abstract:Given an image, generating its natural language description (i.e., caption) is a well studied problem. Approaches proposed to address this problem usually rely on image features that are difficult to interpret. Particularly, these image features are subdivided into global and local features, where global features are extracted from the global representation of the image, while local features are extracted from the objects detected locally in an image. Although, local features extract rich visual information from the image, existing models generate captions in a blackbox manner and humans have difficulty interpreting which local objects the caption is aimed to represent. Hence in this paper, we propose a novel framework for the image captioning with an explicit object (e.g., knowledge graph entity) selection process while still maintaining its end-to-end training ability. The model first explicitly selects which local entities to include in the caption according to a human-interpretable mask, then generate proper captions by attending to selected entities. Experiments conducted on the MSCOCO dataset demonstrate that our method achieves good performance in terms of the caption quality and diversity with a more interpretable generating process than previous counterparts.
Sparse Graph to Sequence Learning for Vision Conditioned Long Textual Sequence Generation
Jul 12, 2020



Abstract:Generating longer textual sequences when conditioned on the visual information is an interesting problem to explore. The challenge here proliferate over the standard vision conditioned sentence-level generation (e.g., image or video captioning) as it requires to produce a brief and coherent story describing the visual content. In this paper, we mask this Vision-to-Sequence as Graph-to-Sequence learning problem and approach it with the Transformer architecture. To be specific, we introduce Sparse Graph-to-Sequence Transformer (SGST) for encoding the graph and decoding a sequence. The encoder aims to directly encode graph-level semantics, while the decoder is used to generate longer sequences. Experiments conducted with the benchmark image paragraph dataset show that our proposed achieve 13.3% improvement on the CIDEr evaluation measure when comparing to the previous state-of-the-art approach.
Image Manipulation with Natural Language using Two-sidedAttentive Conditional Generative Adversarial Network
Dec 16, 2019



Abstract:Altering the content of an image with photo editing tools is a tedious task for an inexperienced user. Especially, when modifying the visual attributes of a specific object in an image without affecting other constituents such as background etc. To simplify the process of image manipulation and to provide more control to users, it is better to utilize a simpler interface like natural language. Therefore, in this paper, we address the challenge of manipulating images using natural language description. We propose the Two-sidEd Attentive conditional Generative Adversarial Network (TEA-cGAN) to generate semantically manipulated images while preserving other contents such as background intact. TEA-cGAN uses fine-grained attention both in the generator and discriminator of Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) based framework at different scales. Experimental results show that TEA-cGAN which generates 128x128 and 256x256 resolution images outperforms existing methods on CUB and Oxford-102 datasets both quantitatively and qualitatively.
Trends in Integration of Vision and Language Research: A Survey of Tasks, Datasets, and Methods
Jul 22, 2019



Abstract:Integration of vision and language tasks has seen a significant growth in the recent times due to surge of interest from multi-disciplinary communities such as deep learning, computer vision, and natural language processing. In this survey, we focus on ten different vision and language integration tasks in terms of their problem formulation, methods, existing datasets, evaluation measures, and comparison of results achieved with the corresponding state-of-the-art methods. This goes beyond earlier surveys which are either task-specific or concentrate only on one type of visual content i.e., image or video. We then conclude the survey by discussing some possible future directions for integration of vision and language research.
Linking Tweets with Monolingual and Cross-Lingual News using Transformed Word Embeddings
Oct 25, 2017



Abstract:Social media platforms have grown into an important medium to spread information about an event published by the traditional media, such as news articles. Grouping such diverse sources of information that discuss the same topic in varied perspectives provide new insights. But the gap in word usage between informal social media content such as tweets and diligently written content (e.g. news articles) make such assembling difficult. In this paper, we propose a transformation framework to bridge the word usage gap between tweets and online news articles across languages by leveraging their word embeddings. Using our framework, word embeddings extracted from tweets and news articles are aligned closer to each other across languages, thus facilitating the identification of similarity between news articles and tweets. Experimental results show a notable improvement over baselines for monolingual tweets and news articles comparison, while new findings are reported for cross-lingual comparison.
Describing Natural Images Containing Novel Objects with Knowledge Guided Assitance
Oct 17, 2017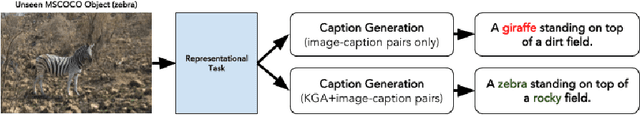
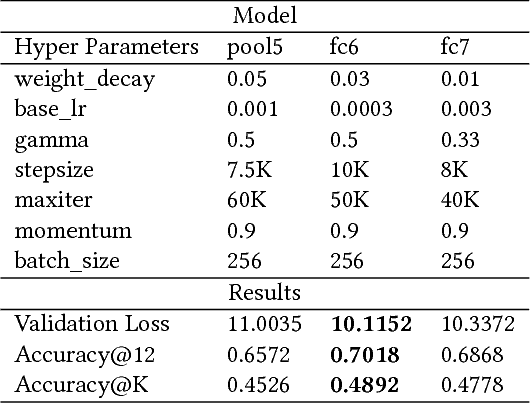
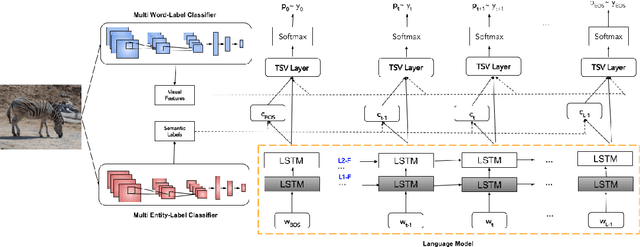
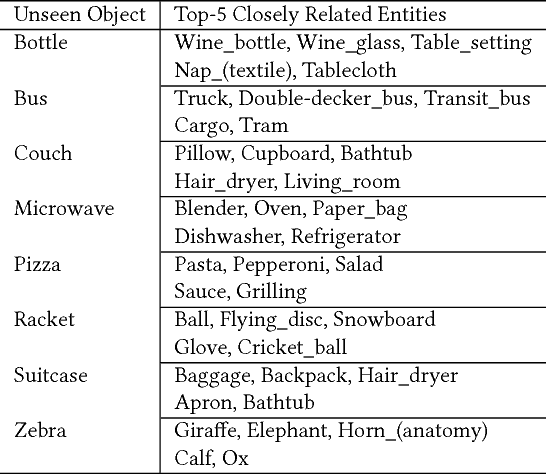
Abstract:Images in the wild encapsulate rich knowledge about varied abstract concepts and cannot be sufficiently described with models built only using image-caption pairs containing selected objects. We propose to handle such a task with the guidance of a knowledge base that incorporate many abstract concepts. Our method is a two-step process where we first build a multi-entity-label image recognition model to predict abstract concepts as image labels and then leverage them in the second step as an external semantic attention and constrained inference in the caption generation model for describing images that depict unseen/novel objects. Evaluations show that our models outperform most of the prior work for out-of-domain captioning on MSCOCO and are useful for integration of knowledge and vision in general.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge