Aditya Kulkarni
IndicSQuAD: A Comprehensive Multilingual Question Answering Dataset for Indic Languages
May 06, 2025Abstract:The rapid progress in question-answering (QA) systems has predominantly benefited high-resource languages, leaving Indic languages largely underrepresented despite their vast native speaker base. In this paper, we present IndicSQuAD, a comprehensive multi-lingual extractive QA dataset covering nine major Indic languages, systematically derived from the SQuAD dataset. Building on previous work with MahaSQuAD for Marathi, our approach adapts and extends translation techniques to maintain high linguistic fidelity and accurate answer-span alignment across diverse languages. IndicSQuAD comprises extensive training, validation, and test sets for each language, providing a robust foundation for model development. We evaluate baseline performances using language-specific monolingual BERT models and the multilingual MuRIL-BERT. The results indicate some challenges inherent in low-resource settings. Moreover, our experiments suggest potential directions for future work, including expanding to additional languages, developing domain-specific datasets, and incorporating multimodal data. The dataset and models are publicly shared at https://github.com/l3cube-pune/indic-nlp
Differentially Private Geodesic and Linear Regression
Apr 15, 2025



Abstract:In statistical applications it has become increasingly common to encounter data structures that live on non-linear spaces such as manifolds. Classical linear regression, one of the most fundamental methodologies of statistical learning, captures the relationship between an independent variable and a response variable which both are assumed to live in Euclidean space. Thus, geodesic regression emerged as an extension where the response variable lives on a Riemannian manifold. The parameters of geodesic regression, as with linear regression, capture the relationship of sensitive data and hence one should consider the privacy protection practices of said parameters. We consider releasing Differentially Private (DP) parameters of geodesic regression via the K-Norm Gradient (KNG) mechanism for Riemannian manifolds. We derive theoretical bounds for the sensitivity of the parameters showing they are tied to their respective Jacobi fields and hence the curvature of the space. This corroborates recent findings of differential privacy for the Fr\'echet mean. We demonstrate the efficacy of our methodology on the sphere, $\mbS^2\subset\mbR^3$ and, since it is general to Riemannian manifolds, the manifold of Euclidean space which simplifies geodesic regression to a case of linear regression. Our methodology is general to any Riemannian manifold and thus it is suitable for data in domains such as medical imaging and computer vision.
MahaSQuAD: Bridging Linguistic Divides in Marathi Question-Answering
Apr 20, 2024



Abstract:Question-answering systems have revolutionized information retrieval, but linguistic and cultural boundaries limit their widespread accessibility. This research endeavors to bridge the gap of the absence of efficient QnA datasets in low-resource languages by translating the English Question Answering Dataset (SQuAD) using a robust data curation approach. We introduce MahaSQuAD, the first-ever full SQuAD dataset for the Indic language Marathi, consisting of 118,516 training, 11,873 validation, and 11,803 test samples. We also present a gold test set of manually verified 500 examples. Challenges in maintaining context and handling linguistic nuances are addressed, ensuring accurate translations. Moreover, as a QnA dataset cannot be simply converted into any low-resource language using translation, we need a robust method to map the answer translation to its span in the translated passage. Hence, to address this challenge, we also present a generic approach for translating SQuAD into any low-resource language. Thus, we offer a scalable approach to bridge linguistic and cultural gaps present in low-resource languages, in the realm of question-answering systems. The datasets and models are shared publicly at https://github.com/l3cube-pune/MarathiNLP .
STEER: Semantic Turn Extension-Expansion Recognition for Voice Assistants
Oct 25, 2023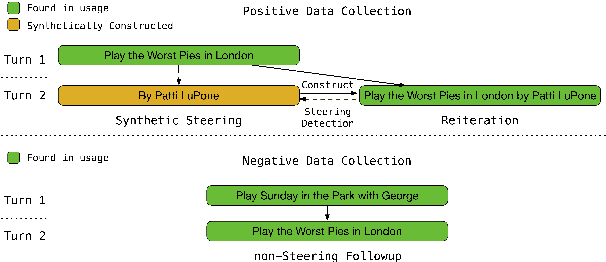
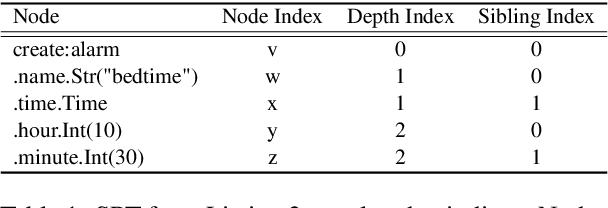
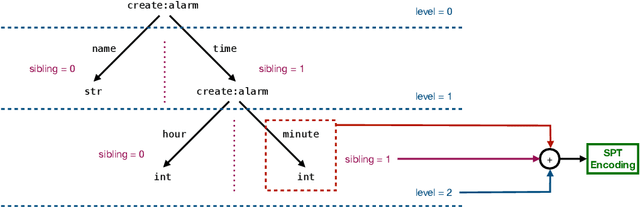
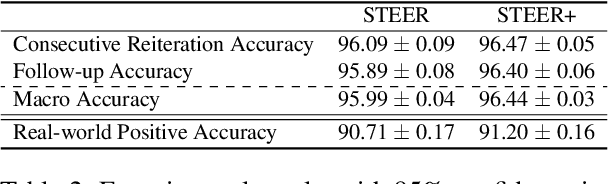
Abstract:In the context of a voice assistant system, steering refers to the phenomenon in which a user issues a follow-up command attempting to direct or clarify a previous turn. We propose STEER, a steering detection model that predicts whether a follow-up turn is a user's attempt to steer the previous command. Constructing a training dataset for steering use cases poses challenges due to the cold-start problem. To overcome this, we developed heuristic rules to sample opt-in usage data, approximating positive and negative samples without any annotation. Our experimental results show promising performance in identifying steering intent, with over 95% accuracy on our sampled data. Moreover, STEER, in conjunction with our sampling strategy, aligns effectively with real-world steering scenarios, as evidenced by its strong zero-shot performance on a human-graded evaluation set. In addition to relying solely on user transcripts as input, we introduce STEER+, an enhanced version of the model. STEER+ utilizes a semantic parse tree to provide more context on out-of-vocabulary words, such as named entities that often occur at the sentence boundary. This further improves model performance, reducing error rate in domains where entities frequently appear, such as messaging. Lastly, we present a data analysis that highlights the improvement in user experience when voice assistants support steering use cases.
Advancing Diagnostic Precision: Leveraging Machine Learning Techniques for Accurate Detection of Covid-19, Pneumonia, and Tuberculosis in Chest X-Ray Images
Oct 09, 2023Abstract:Lung diseases such as COVID-19, tuberculosis (TB), and pneumonia continue to be serious global health concerns that affect millions of people worldwide. In medical practice, chest X-ray examinations have emerged as the norm for diagnosing diseases, particularly chest infections such as COVID-19. Paramedics and scientists are working intensively to create a reliable and precise approach for early-stage COVID-19 diagnosis in order to save lives. But with a variety of symptoms, medical diagnosis of these disorders poses special difficulties. It is essential to address their identification and timely diagnosis in order to successfully treat and prevent these illnesses. In this research, a multiclass classification approach using state-of-the-art methods for deep learning and image processing is proposed. This method takes into account the robustness and efficiency of the system in order to increase diagnostic precision of chest diseases. A comparison between a brand-new convolution neural network (CNN) and several transfer learning pre-trained models including VGG19, ResNet, DenseNet, EfficientNet, and InceptionNet is recommended. Publicly available and widely used research datasets like Shenzen, Montogomery, the multiclass Kaggle dataset and the NIH dataset were used to rigorously test the model. Recall, precision, F1-score, and Area Under Curve (AUC) score are used to evaluate and compare the performance of the proposed model. An AUC value of 0.95 for COVID-19, 0.99 for TB, and 0.98 for pneumonia is obtained using the proposed network. Recall and precision ratings of 0.95, 0.98, and 0.97, respectively, likewise met high standards.
VLSI Systems for signal processing and Communications
Jun 10, 2021Abstract:The growing advances in VLSI technology and design tools have exponentially expanded the application domain of digital signal processing over the past 10 years. This survey emphasises on the architectural and performance parameters of VLSI for DSP applications such as speech processing, wireless communication, analog to digital converters, etc
Generating Synthetic Multispectral Satellite Imagery from Sentinel-2
Dec 05, 2020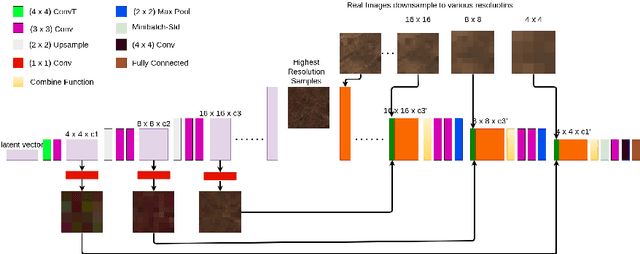
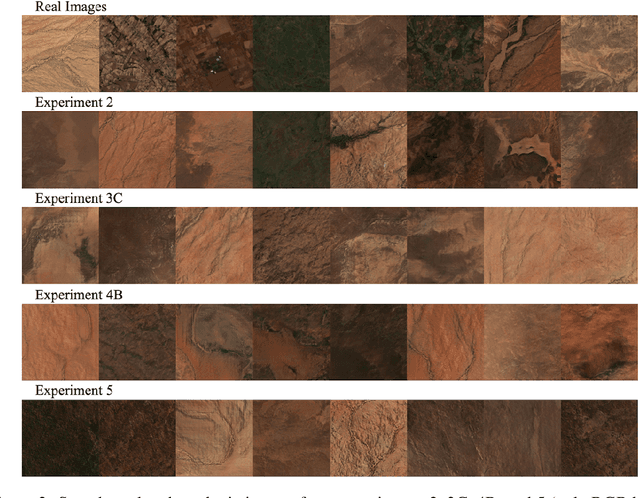
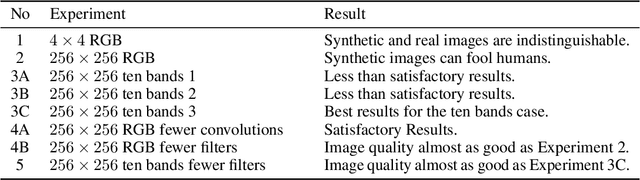

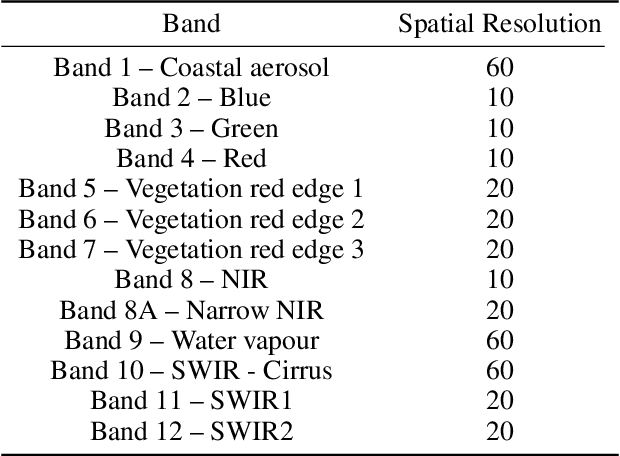
Abstract:Multi-spectral satellite imagery provides valuable data at global scale for many environmental and socio-economic applications. Building supervised machine learning models based on these imagery, however, may require ground reference labels which are not available at global scale. Here, we propose a generative model to produce multi-resolution multi-spectral imagery based on Sentinel-2 data. The resulting synthetic images are indistinguishable from real ones by humans. This technique paves the road for future work to generate labeled synthetic imagery that can be used for data augmentation in data scarce regions and applications.
Semantic Segmentation of Medium-Resolution Satellite Imagery using Conditional Generative Adversarial Networks
Dec 05, 2020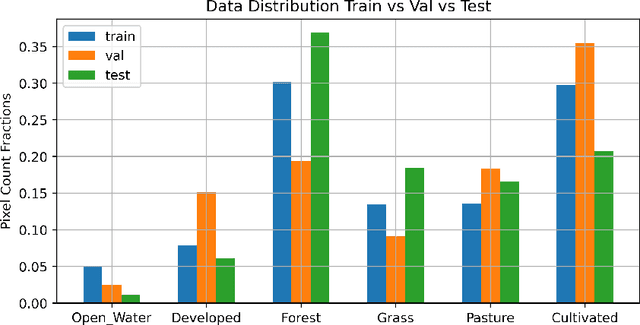
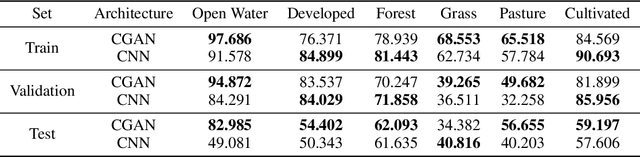

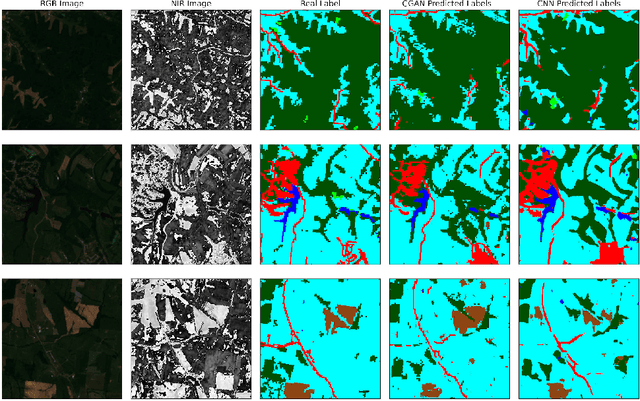
Abstract:Semantic segmentation of satellite imagery is a common approach to identify patterns and detect changes around the planet. Most of the state-of-the-art semantic segmentation models are trained in a fully supervised way using Convolutional Neural Network (CNN). The generalization property of CNN is poor for satellite imagery because the data can be very diverse in terms of landscape types, image resolutions, and scarcity of labels for different geographies and seasons. Hence, the performance of CNN doesn't translate well to images from unseen regions or seasons. Inspired by Conditional Generative Adversarial Networks (CGAN) based approach of image-to-image translation for high-resolution satellite imagery, we propose a CGAN framework for land cover classification using medium-resolution Sentinel-2 imagery. We find that the CGAN model outperforms the CNN model of similar complexity by a significant margin on an unseen imbalanced test dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge