Sharvi Endait
Chain-of-Sanitized-Thoughts: Plugging PII Leakage in CoT of Large Reasoning Models
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) improve performance, reliability, and interpretability by generating explicit chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning, but this transparency introduces a serious privacy risk: intermediate reasoning often leaks personally identifiable information (PII) even when final answers are sanitized. We study how to induce privacy-first reasoning, where models reason without exposing sensitive information, using deployable interventions rather than post-hoc redaction. We introduce PII-CoT-Bench, a supervised dataset with privacy-aware CoT annotations, and a category-balanced evaluation benchmark covering realistic and adversarial leakage scenarios. Our results reveal a capability-dependent trend: state-of-the-art models benefit most from prompt-based controls, whereas weaker models require fine-tuning to achieve meaningful leakage reduction. Across models and categories, both approaches substantially reduce PII exposure with minimal degradation in utility, demonstrating that private reasoning can be achieved without sacrificing performance. Overall, we show that private CoT reasoning can be achieved with minimal utility loss, providing practical guidance for building privacy-preserving reasoning systems.
IndicSQuAD: A Comprehensive Multilingual Question Answering Dataset for Indic Languages
May 06, 2025Abstract:The rapid progress in question-answering (QA) systems has predominantly benefited high-resource languages, leaving Indic languages largely underrepresented despite their vast native speaker base. In this paper, we present IndicSQuAD, a comprehensive multi-lingual extractive QA dataset covering nine major Indic languages, systematically derived from the SQuAD dataset. Building on previous work with MahaSQuAD for Marathi, our approach adapts and extends translation techniques to maintain high linguistic fidelity and accurate answer-span alignment across diverse languages. IndicSQuAD comprises extensive training, validation, and test sets for each language, providing a robust foundation for model development. We evaluate baseline performances using language-specific monolingual BERT models and the multilingual MuRIL-BERT. The results indicate some challenges inherent in low-resource settings. Moreover, our experiments suggest potential directions for future work, including expanding to additional languages, developing domain-specific datasets, and incorporating multimodal data. The dataset and models are publicly shared at https://github.com/l3cube-pune/indic-nlp
MahaSQuAD: Bridging Linguistic Divides in Marathi Question-Answering
Apr 20, 2024



Abstract:Question-answering systems have revolutionized information retrieval, but linguistic and cultural boundaries limit their widespread accessibility. This research endeavors to bridge the gap of the absence of efficient QnA datasets in low-resource languages by translating the English Question Answering Dataset (SQuAD) using a robust data curation approach. We introduce MahaSQuAD, the first-ever full SQuAD dataset for the Indic language Marathi, consisting of 118,516 training, 11,873 validation, and 11,803 test samples. We also present a gold test set of manually verified 500 examples. Challenges in maintaining context and handling linguistic nuances are addressed, ensuring accurate translations. Moreover, as a QnA dataset cannot be simply converted into any low-resource language using translation, we need a robust method to map the answer translation to its span in the translated passage. Hence, to address this challenge, we also present a generic approach for translating SQuAD into any low-resource language. Thus, we offer a scalable approach to bridge linguistic and cultural gaps present in low-resource languages, in the realm of question-answering systems. The datasets and models are shared publicly at https://github.com/l3cube-pune/MarathiNLP .
Multilingual Evaluation of Semantic Textual Relatedness
Apr 13, 2024



Abstract:The explosive growth of online content demands robust Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques that can capture nuanced meanings and cultural context across diverse languages. Semantic Textual Relatedness (STR) goes beyond superficial word overlap, considering linguistic elements and non-linguistic factors like topic, sentiment, and perspective. Despite its pivotal role, prior NLP research has predominantly focused on English, limiting its applicability across languages. Addressing this gap, our paper dives into capturing deeper connections between sentences beyond simple word overlap. Going beyond English-centric NLP research, we explore STR in Marathi, Hindi, Spanish, and English, unlocking the potential for information retrieval, machine translation, and more. Leveraging the SemEval-2024 shared task, we explore various language models across three learning paradigms: supervised, unsupervised, and cross-lingual. Our comprehensive methodology gains promising results, demonstrating the effectiveness of our approach. This work aims to not only showcase our achievements but also inspire further research in multilingual STR, particularly for low-resourced languages.
Handling and extracting key entities from customer conversations using Speech recognition and Named Entity recognition
Nov 28, 2022
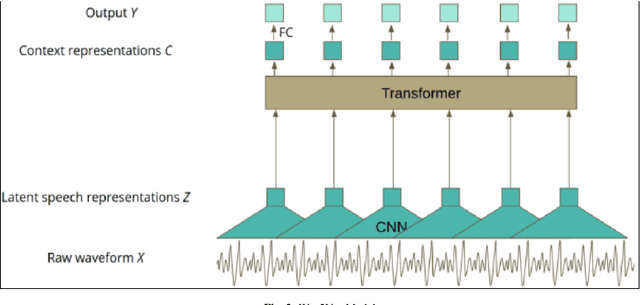

Abstract:In this modern era of technology with e-commerce developing at a rapid pace, it is very important to understand customer requirements and details from a business conversation. It is very crucial for customer retention and satisfaction. Extracting key insights from these conversations is very important when it comes to developing their product or solving their issue. Understanding customer feedback, responses, and important details of the product are essential and it would be done using Named entity recognition (NER). For extracting the entities we would be converting the conversations to text using the optimal speech-to-text model. The model would be a two-stage network in which the conversation is converted to text. Then, suitable entities are extracted using robust techniques using a NER BERT transformer model. This will aid in the enrichment of customer experience when there is an issue which is faced by them. If a customer faces a problem he will call and register his complaint. The model will then extract the key features from this conversation which will be necessary to look into the problem. These features would include details like the order number, and the exact problem. All these would be extracted directly from the conversation and this would reduce the effort of going through the conversation again.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge