Abhinaba Roy
Aligning Generative Music AI with Human Preferences: Methods and Challenges
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in generative AI for music have achieved remarkable fidelity and stylistic diversity, yet these systems often fail to align with nuanced human preferences due to the specific loss functions they use. This paper advocates for the systematic application of preference alignment techniques to music generation, addressing the fundamental gap between computational optimization and human musical appreciation. Drawing on recent breakthroughs including MusicRL's large-scale preference learning, multi-preference alignment frameworks like diffusion-based preference optimization in DiffRhythm+, and inference-time optimization techniques like Text2midi-InferAlign, we discuss how these techniques can address music's unique challenges: temporal coherence, harmonic consistency, and subjective quality assessment. We identify key research challenges including scalability to long-form compositions, reliability amongst others in preference modelling. Looking forward, we envision preference-aligned music generation enabling transformative applications in interactive composition tools and personalized music services. This work calls for sustained interdisciplinary research combining advances in machine learning, music-theory to create music AI systems that truly serve human creative and experiential needs.
SonicVerse: Multi-Task Learning for Music Feature-Informed Captioning
Jun 18, 2025Abstract:Detailed captions that accurately reflect the characteristics of a music piece can enrich music databases and drive forward research in music AI. This paper introduces a multi-task music captioning model, SonicVerse, that integrates caption generation with auxiliary music feature detection tasks such as key detection, vocals detection, and more, so as to directly capture both low-level acoustic details as well as high-level musical attributes. The key contribution is a projection-based architecture that transforms audio input into language tokens, while simultaneously detecting music features through dedicated auxiliary heads. The outputs of these heads are also projected into language tokens, to enhance the captioning input. This framework not only produces rich, descriptive captions for short music fragments but also directly enables the generation of detailed time-informed descriptions for longer music pieces, by chaining the outputs using a large-language model. To train the model, we extended the MusicBench dataset by annotating it with music features using MIRFLEX, a modular music feature extractor, resulting in paired audio, captions and music feature data. Experimental results show that incorporating features in this way improves the quality and detail of the generated captions.
* 14 pages, 2 figures, Accepted to AIMC 2025
MelodySim: Measuring Melody-aware Music Similarity for Plagiarism Detection
May 27, 2025Abstract:We propose MelodySim, a melody-aware music similarity model and dataset for plagiarism detection. First, we introduce a novel method to construct a dataset with focus on melodic similarity. By augmenting Slakh2100; an existing MIDI dataset, we generate variations of each piece while preserving the melody through modifications such as note splitting, arpeggiation, minor track dropout (excluding bass), and re-instrumentation. A user study confirms that positive pairs indeed contain similar melodies, with other musical tracks significantly changed. Second, we develop a segment-wise melodic-similarity detection model that uses a MERT encoder and applies a triplet neural network to capture melodic similarity. The resultant decision matrix highlights where plagiarism might occur. Our model achieves high accuracy on the MelodySim test set.
Text2midi-InferAlign: Improving Symbolic Music Generation with Inference-Time Alignment
May 19, 2025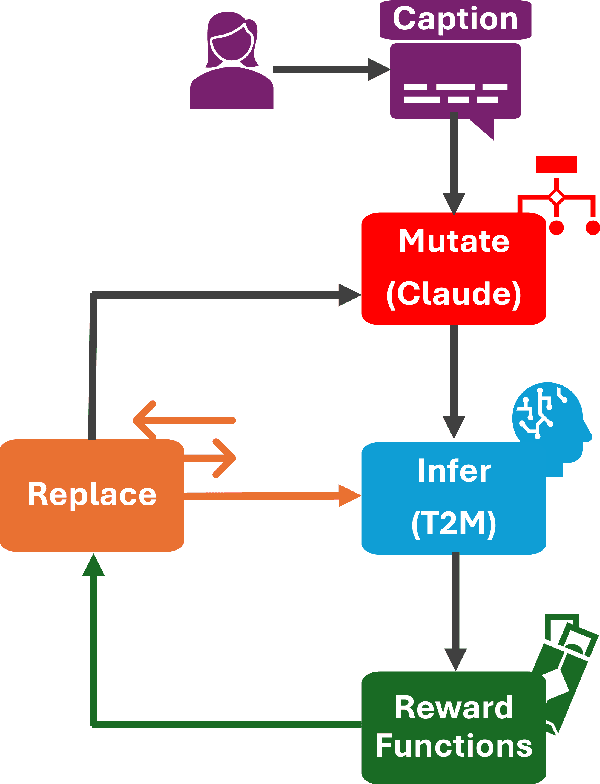
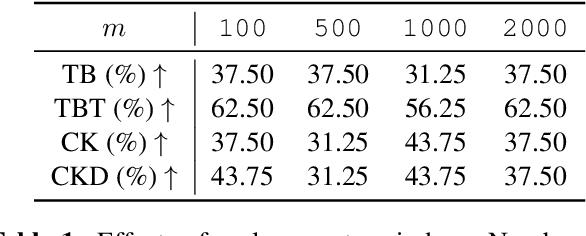
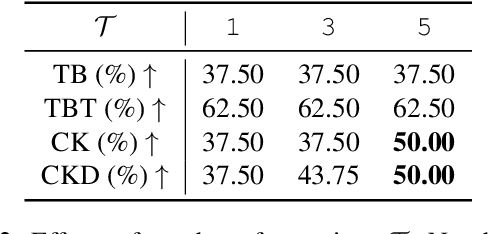
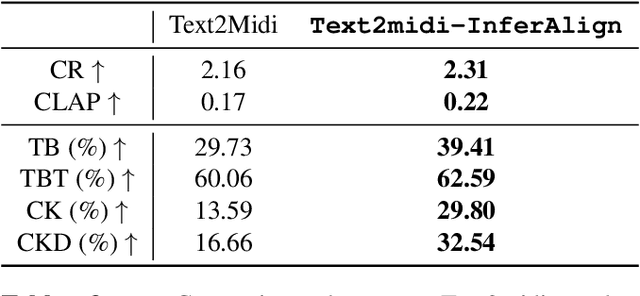
Abstract:We present Text2midi-InferAlign, a novel technique for improving symbolic music generation at inference time. Our method leverages text-to-audio alignment and music structural alignment rewards during inference to encourage the generated music to be consistent with the input caption. Specifically, we introduce two objectives scores: a text-audio consistency score that measures rhythmic alignment between the generated music and the original text caption, and a harmonic consistency score that penalizes generated music containing notes inconsistent with the key. By optimizing these alignment-based objectives during the generation process, our model produces symbolic music that is more closely tied to the input captions, thereby improving the overall quality and coherence of the generated compositions. Our approach can extend any existing autoregressive model without requiring further training or fine-tuning. We evaluate our work on top of Text2midi - an existing text-to-midi generation model, demonstrating significant improvements in both objective and subjective evaluation metrics.
JamendoMaxCaps: A Large Scale Music-caption Dataset with Imputed Metadata
Feb 11, 2025Abstract:We introduce JamendoMaxCaps, a large-scale music-caption dataset featuring over 200,000 freely licensed instrumental tracks from the renowned Jamendo platform. The dataset includes captions generated by a state-of-the-art captioning model, enhanced with imputed metadata. We also introduce a retrieval system that leverages both musical features and metadata to identify similar songs, which are then used to fill in missing metadata using a local large language model (LLLM). This approach allows us to provide a more comprehensive and informative dataset for researchers working on music-language understanding tasks. We validate this approach quantitatively with five different measurements. By making the JamendoMaxCaps dataset publicly available, we provide a high-quality resource to advance research in music-language understanding tasks such as music retrieval, multimodal representation learning, and generative music models.
Text2midi: Generating Symbolic Music from Captions
Dec 21, 2024Abstract:This paper introduces text2midi, an end-to-end model to generate MIDI files from textual descriptions. Leveraging the growing popularity of multimodal generative approaches, text2midi capitalizes on the extensive availability of textual data and the success of large language models (LLMs). Our end-to-end system harnesses the power of LLMs to generate symbolic music in the form of MIDI files. Specifically, we utilize a pretrained LLM encoder to process captions, which then condition an autoregressive transformer decoder to produce MIDI sequences that accurately reflect the provided descriptions. This intuitive and user-friendly method significantly streamlines the music creation process by allowing users to generate music pieces using text prompts. We conduct comprehensive empirical evaluations, incorporating both automated and human studies, that show our model generates MIDI files of high quality that are indeed controllable by text captions that may include music theory terms such as chords, keys, and tempo. We release the code and music samples on our demo page (https://github.com/AMAAI-Lab/Text2midi) for users to interact with text2midi.
MIRFLEX: Music Information Retrieval Feature Library for Extraction
Nov 01, 2024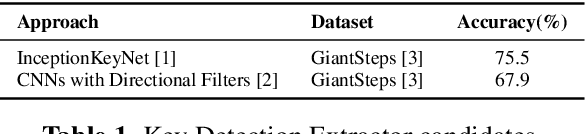
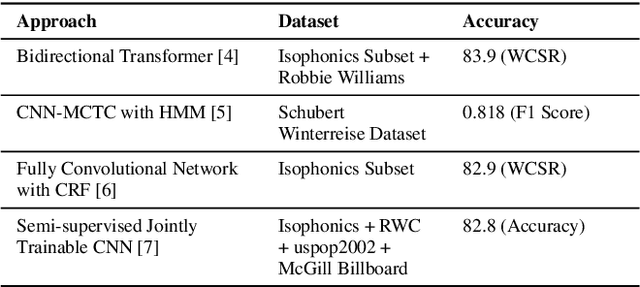
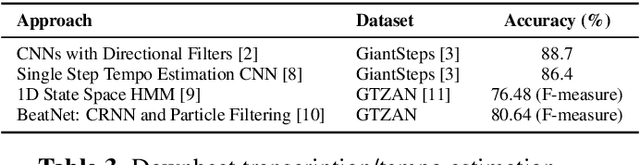
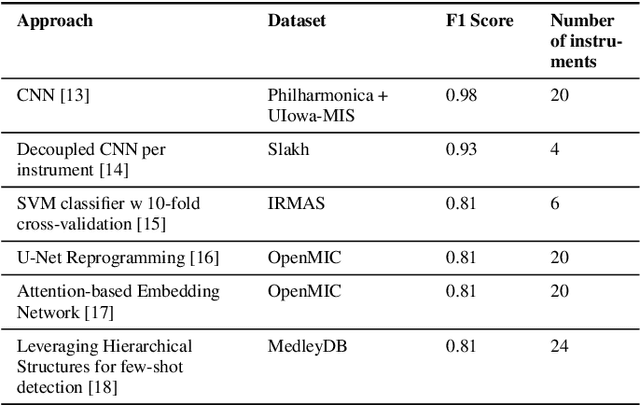
Abstract:This paper introduces an extendable modular system that compiles a range of music feature extraction models to aid music information retrieval research. The features include musical elements like key, downbeats, and genre, as well as audio characteristics like instrument recognition, vocals/instrumental classification, and vocals gender detection. The integrated models are state-of-the-art or latest open-source. The features can be extracted as latent or post-processed labels, enabling integration into music applications such as generative music, recommendation, and playlist generation. The modular design allows easy integration of newly developed systems, making it a good benchmarking and comparison tool. This versatile toolkit supports the research community in developing innovative solutions by providing concrete musical features.
Leveraging LLM Embeddings for Cross Dataset Label Alignment and Zero Shot Music Emotion Prediction
Oct 15, 2024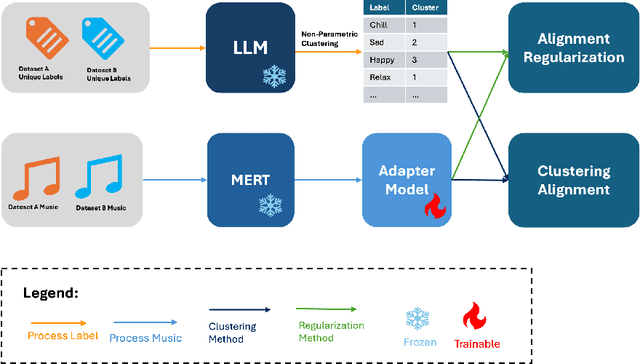
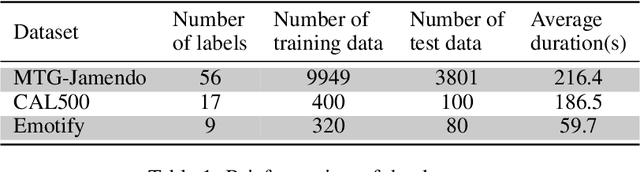
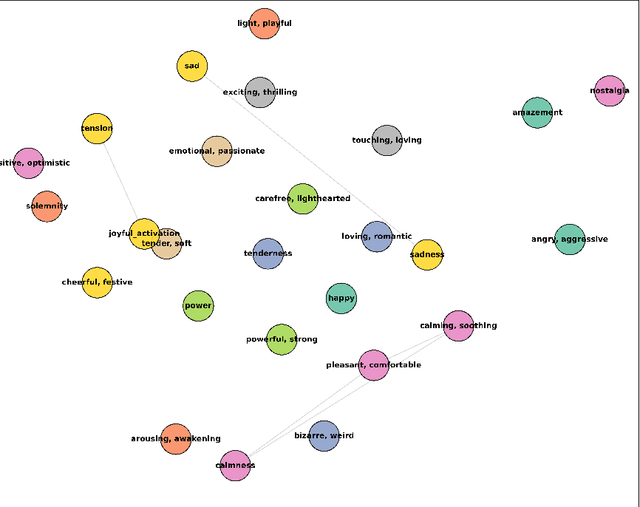
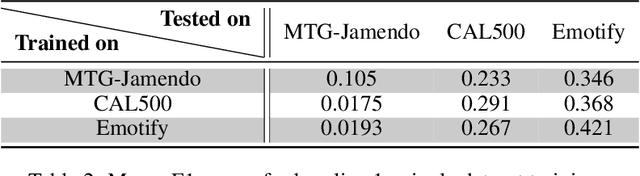
Abstract:In this work, we present a novel method for music emotion recognition that leverages Large Language Model (LLM) embeddings for label alignment across multiple datasets and zero-shot prediction on novel categories. First, we compute LLM embeddings for emotion labels and apply non-parametric clustering to group similar labels, across multiple datasets containing disjoint labels. We use these cluster centers to map music features (MERT) to the LLM embedding space. To further enhance the model, we introduce an alignment regularization that enables dissociation of MERT embeddings from different clusters. This further enhances the model's ability to better adaptation to unseen datasets. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach by performing zero-shot inference on a new dataset, showcasing its ability to generalize to unseen labels without additional training.
MidiCaps -- A large-scale MIDI dataset with text captions
Jun 04, 2024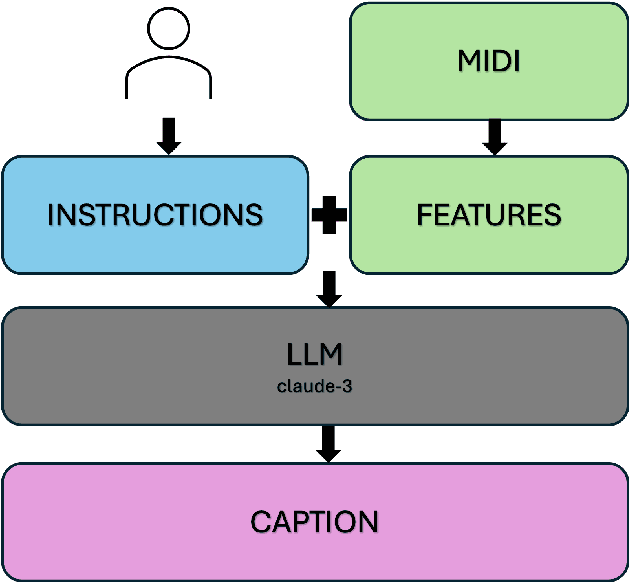
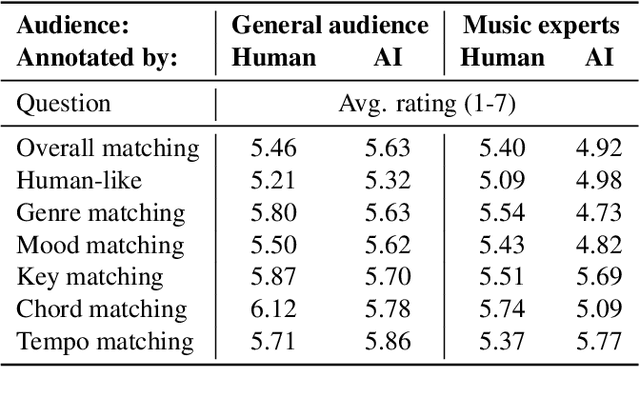
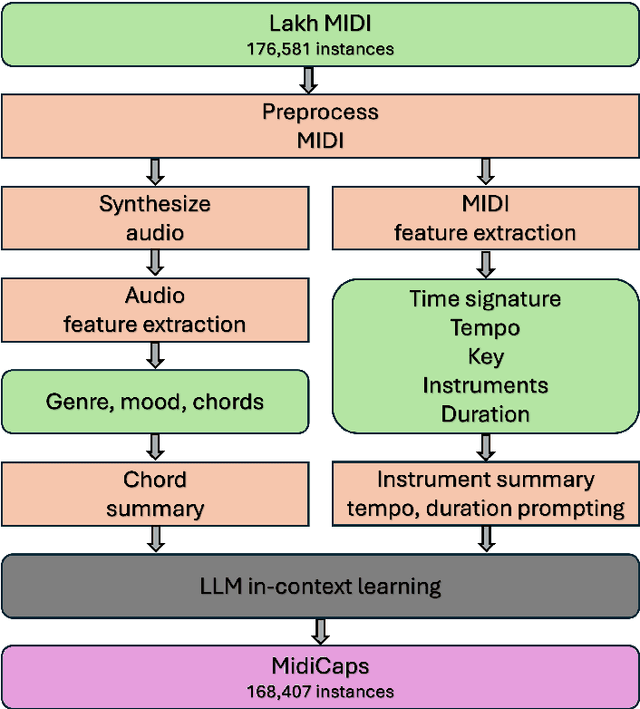
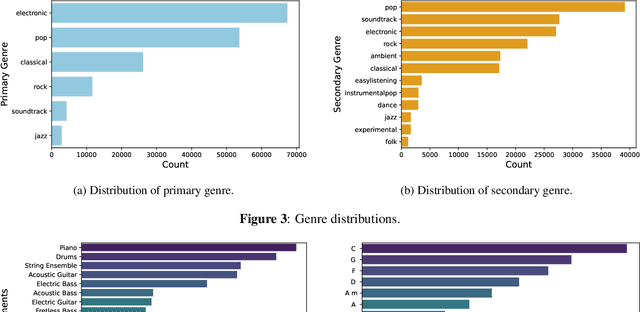
Abstract:Generative models guided by text prompts are increasingly becoming more popular. However, no text-to-MIDI models currently exist, mostly due to the lack of a captioned MIDI dataset. This work aims to enable research that combines LLMs with symbolic music by presenting the first large-scale MIDI dataset with text captions that is openly available: MidiCaps. MIDI (Musical Instrument Digital Interface) files are a widely used format for encoding musical information. Their structured format captures the nuances of musical composition and has practical applications by music producers, composers, musicologists, as well as performers. Inspired by recent advancements in captioning techniques applied to various domains, we present a large-scale curated dataset of over 168k MIDI files accompanied by textual descriptions. Each MIDI caption succinctly describes the musical content, encompassing tempo, chord progression, time signature, instruments present, genre and mood; thereby facilitating multi-modal exploration and analysis. The dataset contains a mix of various genres, styles, and complexities, offering a rich source for training and evaluating models for tasks such as music information retrieval, music understanding and cross-modal translation. We provide detailed statistics about the dataset and have assessed the quality of the captions in an extensive listening study. We anticipate that this resource will stimulate further research in the intersection of music and natural language processing, fostering advancements in both fields.
Improving Zero Shot Learning Baselines with Commonsense Knowledge
Dec 11, 2020

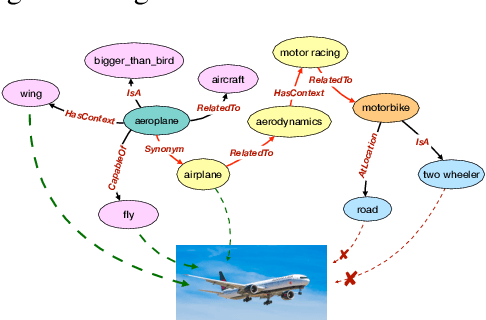
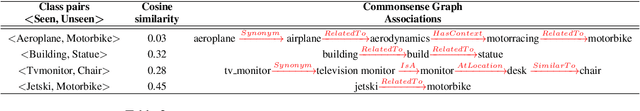
Abstract:Zero shot learning -- the problem of training and testing on a completely disjoint set of classes -- relies greatly on its ability to transfer knowledge from train classes to test classes. Traditionally semantic embeddings consisting of human defined attributes (HA) or distributed word embeddings (DWE) are used to facilitate this transfer by improving the association between visual and semantic embeddings. In this paper, we take advantage of explicit relations between nodes defined in ConceptNet, a commonsense knowledge graph, to generate commonsense embeddings of the class labels by using a graph convolution network-based autoencoder. Our experiments performed on three standard benchmark datasets surpass the strong baselines when we fuse our commonsense embeddings with existing semantic embeddings i.e. HA and DWE.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge