Geeta Puri
Digital Lifelong Learning in the Age of AI: Trends and Insights
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Rapid innovations in AI and large language models (LLMs) have accelerated the adoption of digital learning, particularly beyond formal education. What began as an emergency response during COVID-19 has shifted from a supplementary resource to an essential pillar of education. Understanding how digital learning continues to evolve for adult and lifelong learners is therefore increasingly important. This study examines how various demographics interact with digital learning platforms, focusing on the learner motivations, the effectiveness of gamification in digital learning, and the integration of AI. Using multi survey data from 200 respondents and advanced analytics, our findings reveal a notable increase in the perceived relevance of digital learning after the pandemic, especially among young adults and women, coinciding with the rise of LLM-powered AI tools that support personalized learning. We aim to provide actionable insights for businesses, government policymakers, and educators seeking to optimize their digital learning offerings to meet evolving workforce needs.
Text2midi-InferAlign: Improving Symbolic Music Generation with Inference-Time Alignment
May 19, 2025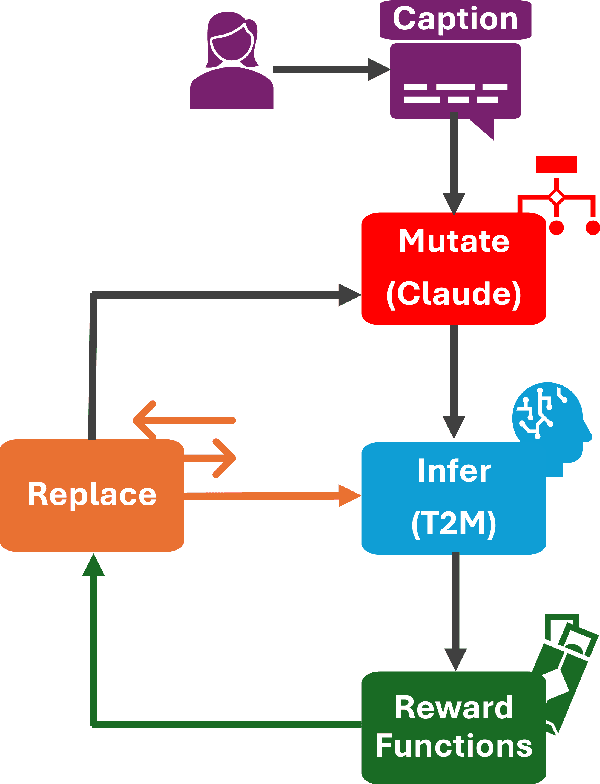
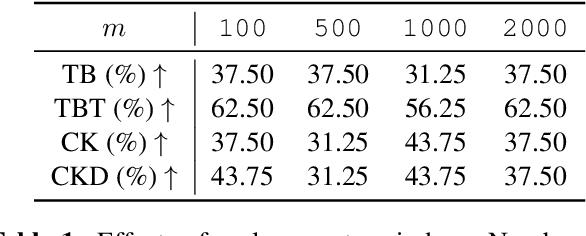
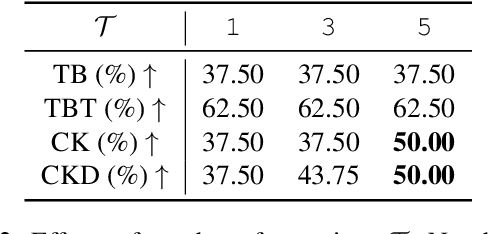
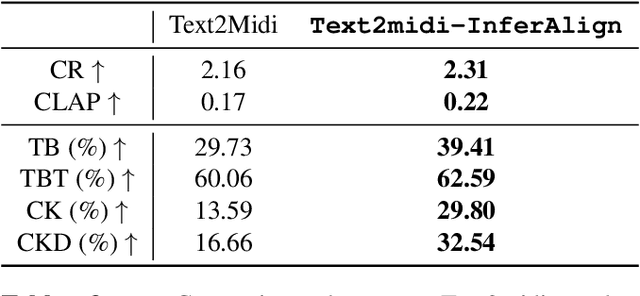
Abstract:We present Text2midi-InferAlign, a novel technique for improving symbolic music generation at inference time. Our method leverages text-to-audio alignment and music structural alignment rewards during inference to encourage the generated music to be consistent with the input caption. Specifically, we introduce two objectives scores: a text-audio consistency score that measures rhythmic alignment between the generated music and the original text caption, and a harmonic consistency score that penalizes generated music containing notes inconsistent with the key. By optimizing these alignment-based objectives during the generation process, our model produces symbolic music that is more closely tied to the input captions, thereby improving the overall quality and coherence of the generated compositions. Our approach can extend any existing autoregressive model without requiring further training or fine-tuning. We evaluate our work on top of Text2midi - an existing text-to-midi generation model, demonstrating significant improvements in both objective and subjective evaluation metrics.
Text2midi: Generating Symbolic Music from Captions
Dec 21, 2024Abstract:This paper introduces text2midi, an end-to-end model to generate MIDI files from textual descriptions. Leveraging the growing popularity of multimodal generative approaches, text2midi capitalizes on the extensive availability of textual data and the success of large language models (LLMs). Our end-to-end system harnesses the power of LLMs to generate symbolic music in the form of MIDI files. Specifically, we utilize a pretrained LLM encoder to process captions, which then condition an autoregressive transformer decoder to produce MIDI sequences that accurately reflect the provided descriptions. This intuitive and user-friendly method significantly streamlines the music creation process by allowing users to generate music pieces using text prompts. We conduct comprehensive empirical evaluations, incorporating both automated and human studies, that show our model generates MIDI files of high quality that are indeed controllable by text captions that may include music theory terms such as chords, keys, and tempo. We release the code and music samples on our demo page (https://github.com/AMAAI-Lab/Text2midi) for users to interact with text2midi.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge