Ant Colony
Papers and Code
HEATACO: Heatmap-Guided Ant Colony Decoding for Large-Scale Travelling Salesman Problems
Jan 26, 2026Heatmap-based non-autoregressive solvers for large-scale Travelling Salesman Problems output dense edge-probability scores, yet final performance largely hinges on the decoder that must satisfy degree-2 constraints and form a single Hamiltonian tour. Greedy commitment can cascade into irreparable mistakes at large $N$, whereas MCTS-guided local search is accurate but compute-heavy and highly engineered. We instead treat the heatmap as a soft edge prior and cast decoding as probabilistic tour construction under feasibility constraints, where the key is to correct local mis-rankings via inexpensive global coordination. Based on this view, we introduce HeatACO, a plug-and-play Max-Min Ant System decoder whose transition policy is softly biased by the heatmap while pheromone updates provide lightweight, instance-specific feedback to resolve global conflicts; optional 2-opt/3-opt post-processing further improves tour quality. On TSP500/1K/10K, using heatmaps produced by four pretrained predictors, HeatACO+2opt achieves gaps down to 0.11%/0.23%/1.15% with seconds-to-minutes CPU decoding for fixed heatmaps, offering a better quality--time trade-off than greedy decoding and published MCTS-based decoders. Finally, we find the gains track heatmap reliability: under distribution shift, miscalibration and confidence collapse bound decoding improvements, suggesting heatmap generalisation is a primary lever for further progress.
Reinforcement Learning-Based Energy-Aware Coverage Path Planning for Precision Agriculture
Jan 23, 2026Coverage Path Planning (CPP) is a fundamental capability for agricultural robots; however, existing solutions often overlook energy constraints, resulting in incomplete operations in large-scale or resource-limited environments. This paper proposes an energy-aware CPP framework grounded in Soft Actor-Critic (SAC) reinforcement learning, designed for grid-based environments with obstacles and charging stations. To enable robust and adaptive decision-making under energy limitations, the framework integrates Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) for spatial feature extraction and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks for temporal dynamics. A dedicated reward function is designed to jointly optimize coverage efficiency, energy consumption, and return-to-base constraints. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed approach consistently achieves over 90% coverage while ensuring energy safety, outperforming traditional heuristic algorithms such as Rapidly-exploring Random Tree (RRT), Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO), and Ant Colony Optimization (ACO) baselines by 13.4-19.5% in coverage and reducing constraint violations by 59.9-88.3%. These findings validate the proposed SAC-based framework as an effective and scalable solution for energy-constrained CPP in agricultural robotics.
* Accepted by RACS '25: International Conference on Research in Adaptive and Convergent Systems, November 16-19, 2025, Ho Chi Minh, Vietnam. 10 pages, 5 figures
A full process algebraic representation of Ant Colony Optimization
Jan 20, 2026We present a process algebra capable of specifying parallelized Ant Colony Optimization algorithms in full detail: PA$^2$CO. After explaining the basis of three different ACO algorithms (Ant System, MAX-MIN Ant System, and Ant Colony System), we formally define PA$^2$CO and use it for representing several types of implementations with different parallel schemes. In particular fine-grained and coarse-grained specifications, each one taking advantage of parallel executions at different levels of system granularity, are formalized.
Generalization and Completeness of Stochastic Local Search Algorithms
Jan 20, 2026We generalize Stochastic Local Search (SLS) heuristics into a unique formal model. This model has two key components: a common structure designed to be as large as possible and a parametric structure intended to be as small as possible. Each heuristic is obtained by instantiating the parametric part in a different way. Particular instances for Genetic Algorithms (GA), Ant Colony Optimization (ACO), and Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) are presented. Then, we use our model to prove the Turing-completeness of SLS algorithms in general. The proof uses our framework to construct a GA able to simulate any Turing machine. This Turing-completeness implies that determining any non-trivial property concerning the relationship between the inputs and the computed outputs is undecidable for GA and, by extension, for the general set of SLS methods (although not necessarily for each particular method). Similar proofs are more informally presented for PSO and ACO.
Pheromone-Focused Ant Colony Optimization algorithm for path planning
Jan 12, 2026Ant Colony Optimization (ACO) is a prominent swarm intelligence algorithm extensively applied to path planning. However, traditional ACO methods often exhibit shortcomings, such as blind search behavior and slow convergence within complex environments. To address these challenges, this paper proposes the Pheromone-Focused Ant Colony Optimization (PFACO) algorithm, which introduces three key strategies to enhance the problem-solving ability of the ant colony. First, the initial pheromone distribution is concentrated in more promising regions based on the Euclidean distances of nodes to the start and end points, balancing the trade-off between exploration and exploitation. Second, promising solutions are reinforced during colony iterations to intensify pheromone deposition along high-quality paths, accelerating convergence while maintaining solution diversity. Third, a forward-looking mechanism is implemented to penalize redundant path turns, promoting smoother and more efficient solutions. These strategies collectively produce the focused pheromones to guide the ant colony's search, which enhances the global optimization capabilities of the PFACO algorithm, significantly improving convergence speed and solution quality across diverse optimization problems. The experimental results demonstrate that PFACO consistently outperforms comparative ACO algorithms in terms of convergence speed and solution quality.
Structural Induced Exploration for Balanced and Scalable Multi-Robot Path Planning
Dec 25, 2025Multi-robot path planning is a fundamental yet challenging problem due to its combinatorial complexity and the need to balance global efficiency with fair task allocation among robots. Traditional swarm intelligence methods, although effective on small instances, often converge prematurely and struggle to scale to complex environments. In this work, we present a structure-induced exploration framework that integrates structural priors into the search process of the ant colony optimization (ACO). The approach leverages the spatial distribution of the task to induce a structural prior at initialization, thereby constraining the search space. The pheromone update rule is then designed to emphasize structurally meaningful connections and incorporates a load-aware objective to reconcile the total travel distance with individual robot workload. An explicit overlap suppression strategy further ensures that tasks remain distinct and balanced across the team. The proposed framework was validated on diverse benchmark scenarios covering a wide range of instance sizes and robot team configurations. The results demonstrate consistent improvements in route compactness, stability, and workload distribution compared to representative metaheuristic baselines. Beyond performance gains, the method also provides a scalable and interpretable framework that can be readily applied to logistics, surveillance, and search-and-rescue applications where reliable large-scale coordination is essential.
Random-Key Metaheuristic and Linearization for the Quadratic Multiple Constraints Variable-Sized Bin Packing Problem
Nov 15, 2025This paper addresses the Quadratic Multiple Constraints Variable-Sized Bin Packing Problem (QMC-VSBPP), a challenging combinatorial optimization problem that generalizes the classical bin packing by incorporating multiple capacity dimensions, heterogeneous bin types, and quadratic interaction costs between items. We propose two complementary methods that advance the current state-of-the-art. First, a linearized mathematical formulation is introduced to eliminate quadratic terms, enabling the use of exact solvers such as Gurobi to compute strong lower bounds - reported here for the first time for this problem. Second, we develop RKO-ACO, a continuous-domain Ant Colony Optimization algorithm within the Random-Key Optimization framework, enhanced with adaptive Q-learning parameter control and efficient local search. Extensive computational experiments on benchmark instances show that the proposed linearized model produces significantly tighter lower bounds than the original quadratic formulation, while RKO-ACO consistently matches or improves upon all best-known solutions in the literature, establishing new upper bounds for large-scale instances. These results provide new reference values for future studies and demonstrate the effectiveness of evolutionary and random-key metaheuristic approaches for solving complex quadratic packing problems. Source code and data available at https://github.com/nataliaalves03/RKO-ACO
A Unified Stochastic Mechanism Underlying Collective Behavior in Ants, Physical Systems, and Robotic Swarms
Nov 08, 2025Biological swarms, such as ant colonies, achieve collective goals through decentralized and stochastic individual behaviors. Similarly, physical systems composed of gases, liquids, and solids exhibit random particle motion governed by entropy maximization, yet do not achieve collective objectives. Despite this analogy, no unified framework exists to explain the stochastic behavior in both biological and physical systems. Here, we present empirical evidence from \textit{Formica polyctena} ants that reveals a shared statistical mechanism underlying both systems: maximization under different energy function constraints. We further demonstrate that robotic swarms governed by this principle can exhibit scalable, decentralized cooperation, mimicking physical phase-like behaviors with minimal individual computation. These findings established a unified stochastic model linking biological, physical, and robotic swarms, offering a scalable principle for designing robust and intelligent swarm robotics.
Exploration-Exploitation-Evaluation (EEE): A Framework for Metaheuristic Algorithms in Combinatorial Optimization
Oct 06, 2025
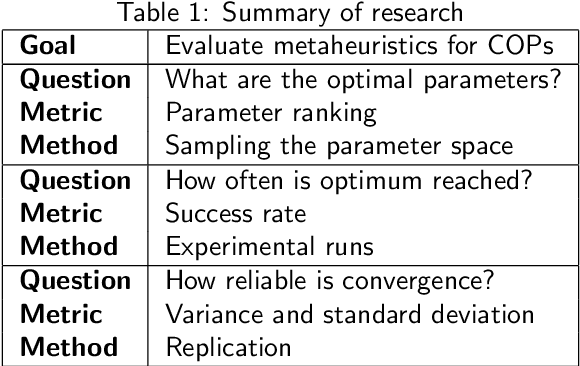


We introduce a framework for applying metaheuristic algorithms, such as ant colony optimization (ACO), to combinatorial optimization problems (COPs) like the traveling salesman problem (TSP). The framework consists of three sequential stages: broad exploration of the parameter space, exploitation of top-performing parameters, and uncertainty quantification (UQ) to assess the reliability of results. As a case study, we apply ACO to the TSPLIB berlin52 dataset, which has a known optimal tour length of 7542. Using our framework, we calculate that the probability of ACO finding the global optimum is approximately 1/40 in a single run and improves to 1/5 when aggregated over ten runs.
LLM-Powered Swarms: A New Frontier or a Conceptual Stretch?
Jun 17, 2025Swarm intelligence traditionally refers to systems of simple, decentralized agents whose local interactions lead to emergent, collective behavior. Recently, the term 'swarm' has been extended to describe AI systems like OpenAI's Swarm, where large language models (LLMs) act as collaborative agents. This paper contrasts traditional swarm algorithms with LLM-driven swarms exploring how decentralization, scalability, and emergence are redefined in modern artificial intelligence (AI). We implement and compare both paradigms using Boids and Ant Colony Optimization (ACO), evaluating latency, resource usage, and behavioral accuracy. The suitability of both cloud-based and local LLMs is assessed for the agent-based use in swarms. Although LLMs offer powerful reasoning and abstraction capabilities, they introduce new constraints in computation and coordination that challenge traditional notions of swarm design. This study highlights the opportunities and limitations of integrating LLMs into swarm systems and discusses the evolving definition of 'swarm' in modern AI research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge