Increasing a microscope's effective field of view via overlapped imaging and machine learning
Paper and Code
Oct 10, 2021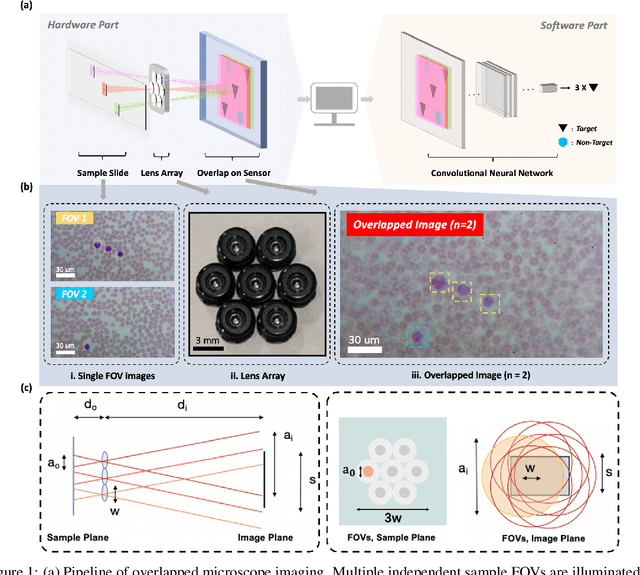
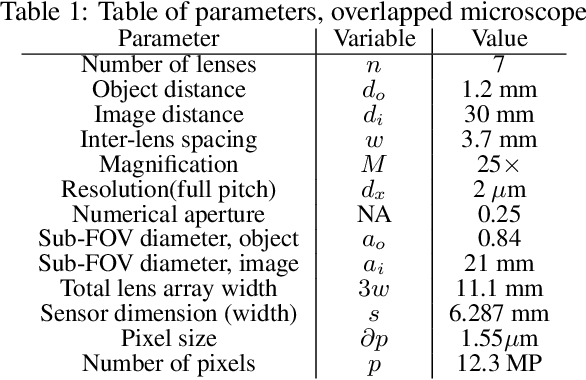
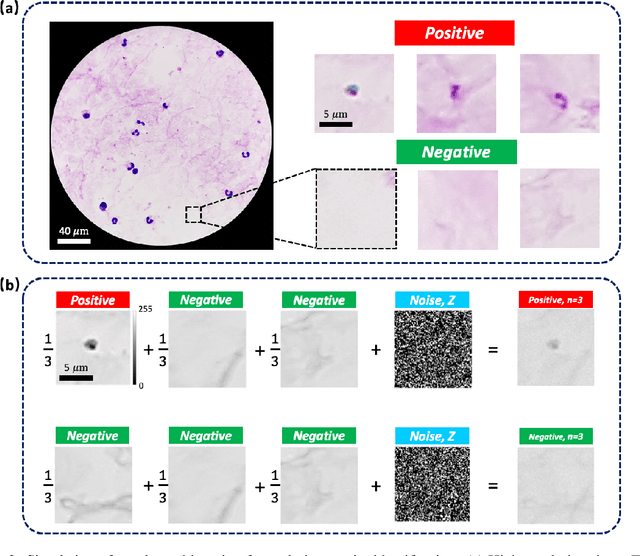
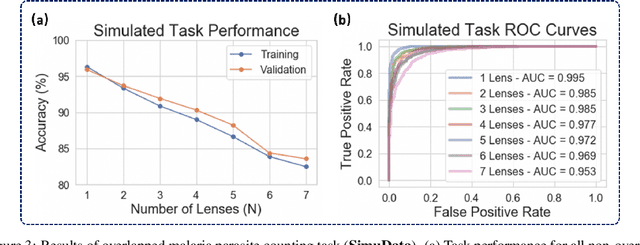
This work demonstrates a multi-lens microscopic imaging system that overlaps multiple independent fields of view on a single sensor for high-efficiency automated specimen analysis. Automatic detection, classification and counting of various morphological features of interest is now a crucial component of both biomedical research and disease diagnosis. While convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have dramatically improved the accuracy of counting cells and sub-cellular features from acquired digital image data, the overall throughput is still typically hindered by the limited space-bandwidth product (SBP) of conventional microscopes. Here, we show both in simulation and experiment that overlapped imaging and co-designed analysis software can achieve accurate detection of diagnostically-relevant features for several applications, including counting of white blood cells and the malaria parasite, leading to multi-fold increase in detection and processing throughput with minimal reduction in accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge