A Closer Look at Memorization in Deep Networks
Paper and Code
Jul 01, 2017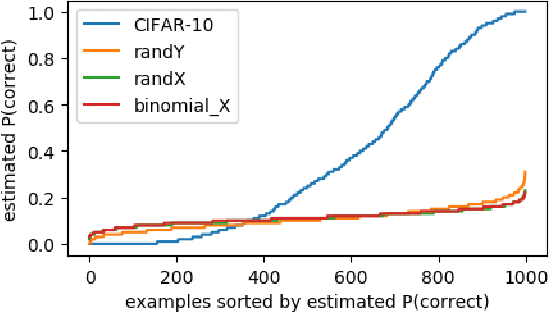
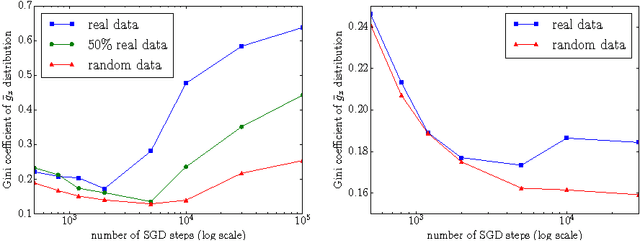
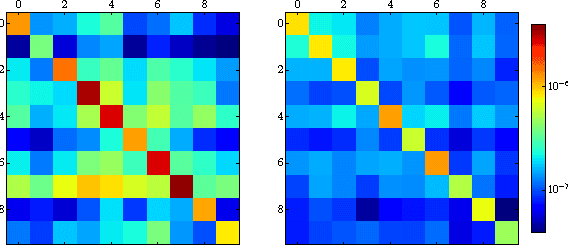
We examine the role of memorization in deep learning, drawing connections to capacity, generalization, and adversarial robustness. While deep networks are capable of memorizing noise data, our results suggest that they tend to prioritize learning simple patterns first. In our experiments, we expose qualitative differences in gradient-based optimization of deep neural networks (DNNs) on noise vs. real data. We also demonstrate that for appropriately tuned explicit regularization (e.g., dropout) we can degrade DNN training performance on noise datasets without compromising generalization on real data. Our analysis suggests that the notions of effective capacity which are dataset independent are unlikely to explain the generalization performance of deep networks when trained with gradient based methods because training data itself plays an important role in determining the degree of memorization.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge