Zvika Ben-Haim
Google Research, Tel-Aviv, Israel
Leveraging LLM Inconsistency to Boost Pass@k Performance
May 19, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) achieve impressive abilities in numerous domains, but exhibit inconsistent performance in response to minor input changes. Rather than view this as a drawback, in this paper we introduce a novel method for leveraging models' inconsistency to boost Pass@k performance. Specifically, we present a "Variator" agent that generates k variants of a given task and submits one candidate solution for each one. Our variant generation approach is applicable to a wide range of domains as it is task agnostic and compatible with free-form inputs. We demonstrate the efficacy of our agent theoretically using a probabilistic model of the inconsistency effect, and show empirically that it outperforms the baseline on the APPS dataset. Furthermore, we establish that inconsistency persists even in frontier reasoning models across coding and cybersecurity domains, suggesting our method is likely to remain relevant for future model generations.
Flood forecasting with machine learning models in an operational framework
Nov 04, 2021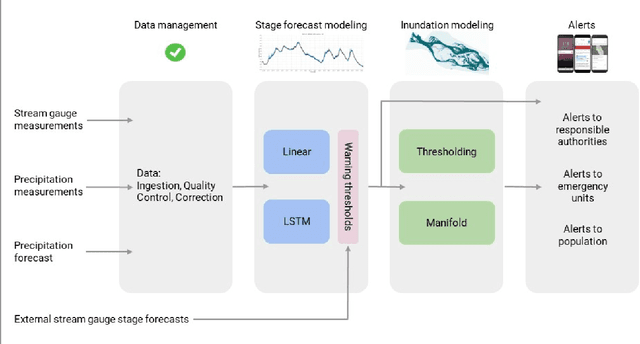
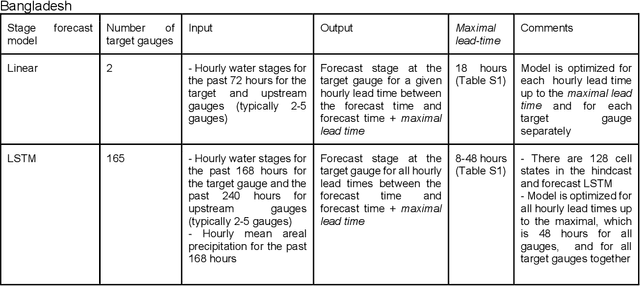
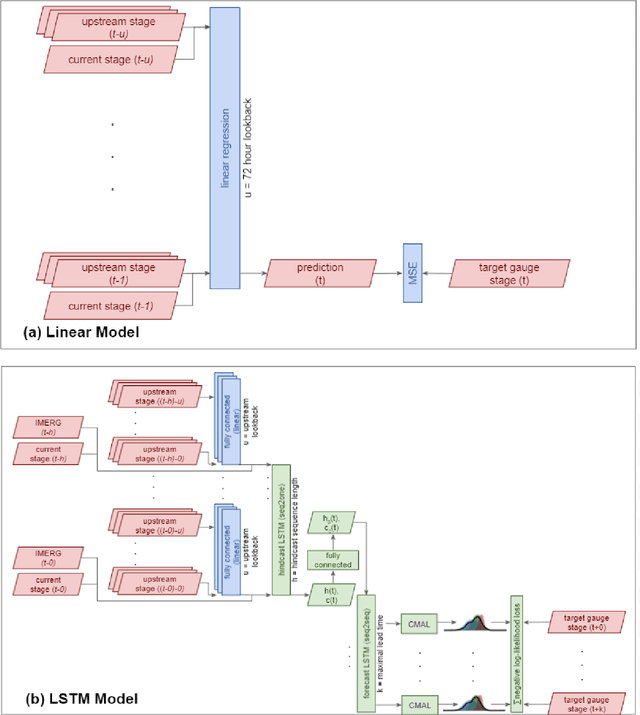
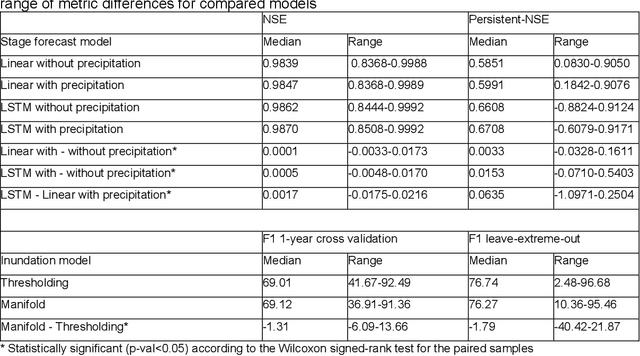
Abstract:The operational flood forecasting system by Google was developed to provide accurate real-time flood warnings to agencies and the public, with a focus on riverine floods in large, gauged rivers. It became operational in 2018 and has since expanded geographically. This forecasting system consists of four subsystems: data validation, stage forecasting, inundation modeling, and alert distribution. Machine learning is used for two of the subsystems. Stage forecasting is modeled with the Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks and the Linear models. Flood inundation is computed with the Thresholding and the Manifold models, where the former computes inundation extent and the latter computes both inundation extent and depth. The Manifold model, presented here for the first time, provides a machine-learning alternative to hydraulic modeling of flood inundation. When evaluated on historical data, all models achieve sufficiently high-performance metrics for operational use. The LSTM showed higher skills than the Linear model, while the Thresholding and Manifold models achieved similar performance metrics for modeling inundation extent. During the 2021 monsoon season, the flood warning system was operational in India and Bangladesh, covering flood-prone regions around rivers with a total area of 287,000 km2, home to more than 350M people. More than 100M flood alerts were sent to affected populations, to relevant authorities, and to emergency organizations. Current and future work on the system includes extending coverage to additional flood-prone locations, as well as improving modeling capabilities and accuracy.
Physics-Aware Downsampling with Deep Learning for Scalable Flood Modeling
Jun 14, 2021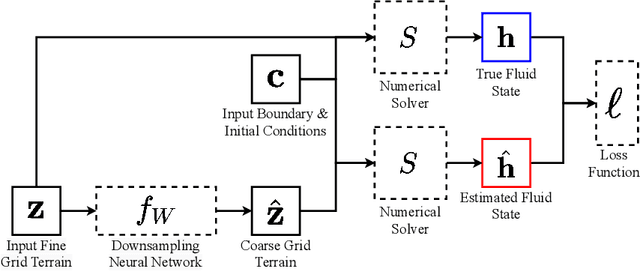
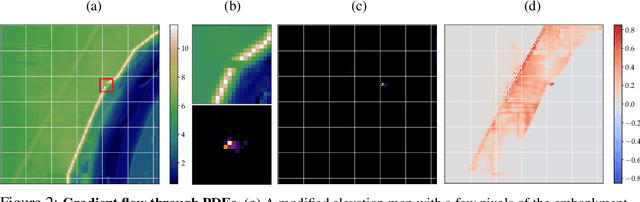
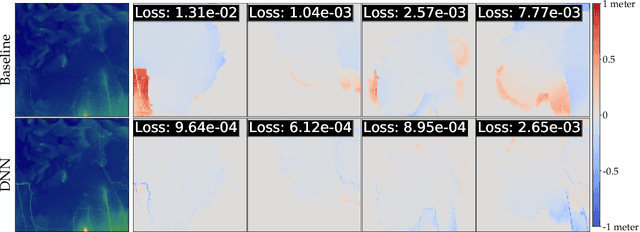

Abstract:Background: Floods are the most common natural disaster in the world, affecting the lives of hundreds of millions. Flood forecasting is therefore a vitally important endeavor, typically achieved using physical water flow simulations, which rely on accurate terrain elevation maps. However, such simulations, based on solving partial differential equations, are computationally prohibitive on a large scale. This scalability issue is commonly alleviated using a coarse grid representation of the elevation map, though this representation may distort crucial terrain details, leading to significant inaccuracies in the simulation. Contributions: We train a deep neural network to perform physics-informed downsampling of the terrain map: we optimize the coarse grid representation of the terrain maps, so that the flood prediction will match the fine grid solution. For the learning process to succeed, we configure a dataset specifically for this task. We demonstrate that with this method, it is possible to achieve a significant reduction in computational cost, while maintaining an accurate solution. A reference implementation accompanies the paper as well as documentation and code for dataset reproduction.
Inundation Modeling in Data Scarce Regions
Oct 30, 2019

Abstract:Flood forecasts are crucial for effective individual and governmental protective action. The vast majority of flood-related casualties occur in developing countries, where providing spatially accurate forecasts is a challenge due to scarcity of data and lack of funding. This paper describes an operational system providing flood extent forecast maps covering several flood-prone regions in India, with the goal of being sufficiently scalable and cost-efficient to facilitate the establishment of effective flood forecasting systems globally.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge