Zongcheng Li
NeTO:Neural Reconstruction of Transparent Objects with Self-Occlusion Aware Refraction-Tracing
Mar 20, 2023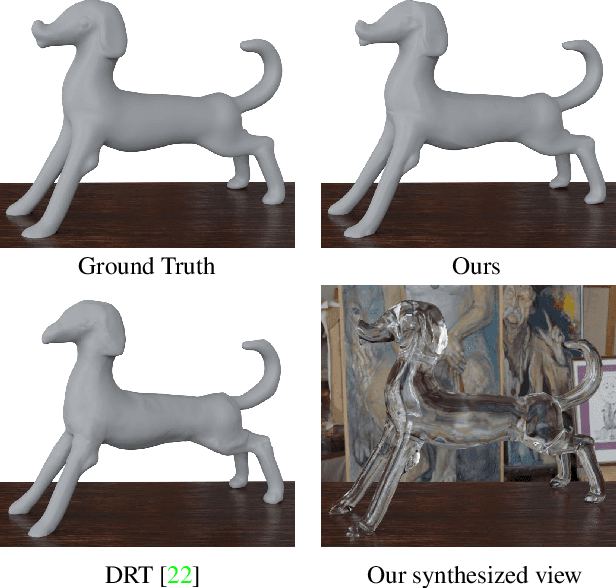
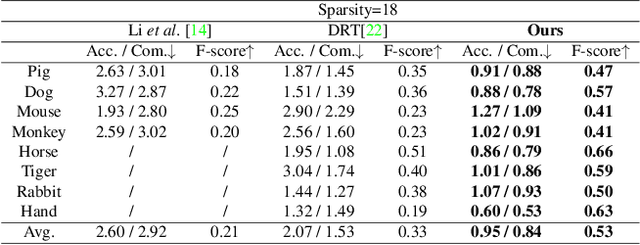
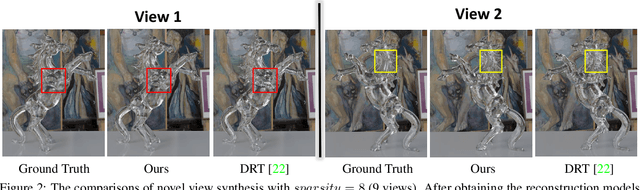
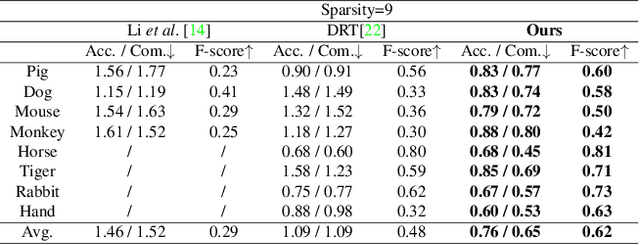
Abstract:We present a novel method, called NeTO, for capturing 3D geometry of solid transparent objects from 2D images via volume rendering. Reconstructing transparent objects is a very challenging task, which is ill-suited for general-purpose reconstruction techniques due to the specular light transport phenomena. Although existing refraction-tracing based methods, designed specially for this task, achieve impressive results, they still suffer from unstable optimization and loss of fine details, since the explicit surface representation they adopted is difficult to be optimized, and the self-occlusion problem is ignored for refraction-tracing. In this paper, we propose to leverage implicit Signed Distance Function (SDF) as surface representation, and optimize the SDF field via volume rendering with a self-occlusion aware refractive ray tracing. The implicit representation enables our method to be capable of reconstructing high-quality reconstruction even with a limited set of images, and the self-occlusion aware strategy makes it possible for our method to accurately reconstruct the self-occluded regions. Experiments show that our method achieves faithful reconstruction results and outperforms prior works by a large margin. Visit our project page at \url{https://www.xxlong.site/NeTO/}
NeuralRoom: Geometry-Constrained Neural Implicit Surfaces for Indoor Scene Reconstruction
Oct 13, 2022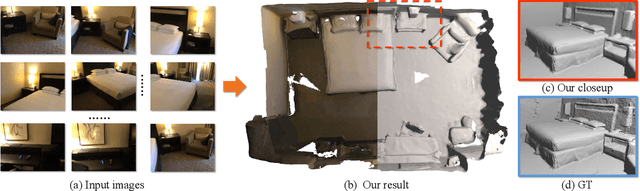
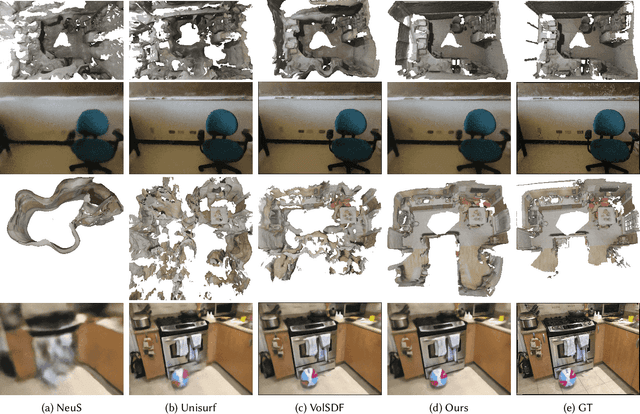

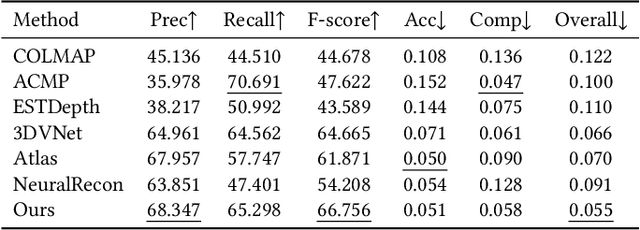
Abstract:We present a novel neural surface reconstruction method called NeuralRoom for reconstructing room-sized indoor scenes directly from a set of 2D images. Recently, implicit neural representations have become a promising way to reconstruct surfaces from multiview images due to their high-quality results and simplicity. However, implicit neural representations usually cannot reconstruct indoor scenes well because they suffer severe shape-radiance ambiguity. We assume that the indoor scene consists of texture-rich and flat texture-less regions. In texture-rich regions, the multiview stereo can obtain accurate results. In the flat area, normal estimation networks usually obtain a good normal estimation. Based on the above observations, we reduce the possible spatial variation range of implicit neural surfaces by reliable geometric priors to alleviate shape-radiance ambiguity. Specifically, we use multiview stereo results to limit the NeuralRoom optimization space and then use reliable geometric priors to guide NeuralRoom training. Then the NeuralRoom would produce a neural scene representation that can render an image consistent with the input training images. In addition, we propose a smoothing method called perturbation-residual restrictions to improve the accuracy and completeness of the flat region, which assumes that the sampling points in a local surface should have the same normal and similar distance to the observation center. Experiments on the ScanNet dataset show that our method can reconstruct the texture-less area of indoor scenes while maintaining the accuracy of detail. We also apply NeuralRoom to more advanced multiview reconstruction algorithms and significantly improve their reconstruction quality.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge