Ziwei Nie
A Fully Automatic Framework for Intracranial Pressure Grading: Integrating Keyframe Identification, ONSD Measurement and Clinical Data
Sep 11, 2025Abstract:Intracranial pressure (ICP) elevation poses severe threats to cerebral function, thus necessitating monitoring for timely intervention. While lumbar puncture is the gold standard for ICP measurement, its invasiveness and associated risks drive the need for non-invasive alternatives. Optic nerve sheath diameter (ONSD) has emerged as a promising biomarker, as elevated ICP directly correlates with increased ONSD. However, current clinical practices for ONSD measurement suffer from inconsistency in manual operation, subjectivity in optimal view selection, and variability in thresholding, limiting their reliability. To address these challenges, we introduce a fully automatic two-stage framework for ICP grading, integrating keyframe identification, ONSD measurement and clinical data. Specifically, the fundus ultrasound video processing stage performs frame-level anatomical segmentation, rule-based keyframe identification guided by an international consensus statement, and precise ONSD measurement. The intracranial pressure grading stage then fuses ONSD metrics with clinical features to enable the prediction of ICP grades, thereby demonstrating an innovative blend of interpretable ultrasound analysis and multi-source data integration for objective clinical evaluation. Experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves a validation accuracy of $0.845 \pm 0.071$ (with standard deviation from five-fold cross-validation) and an independent test accuracy of 0.786, significantly outperforming conventional threshold-based method ($0.637 \pm 0.111$ validation accuracy, $0.429$ test accuracy). Through effectively reducing operator variability and integrating multi-source information, our framework establishes a reliable non-invasive approach for clinical ICP evaluation, holding promise for improving patient management in acute neurological conditions.
Automated Peripancreatic Vessel Segmentation and Labeling Based on Iterative Trunk Growth and Weakly Supervised Mechanism
Mar 06, 2023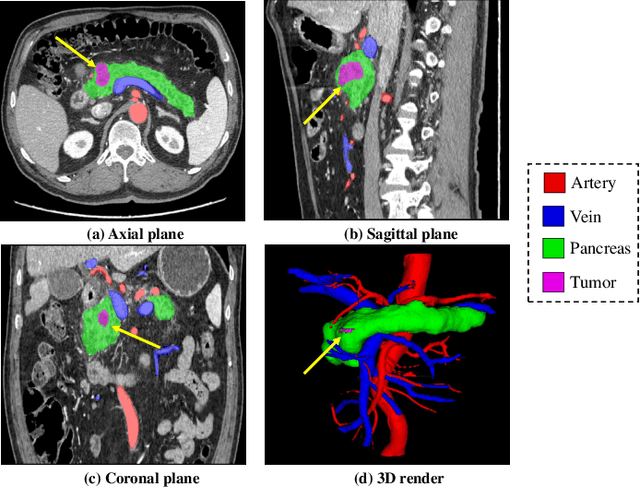
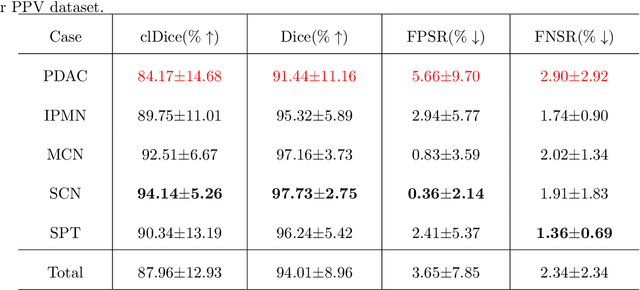
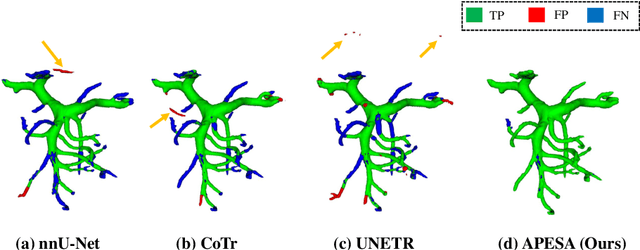
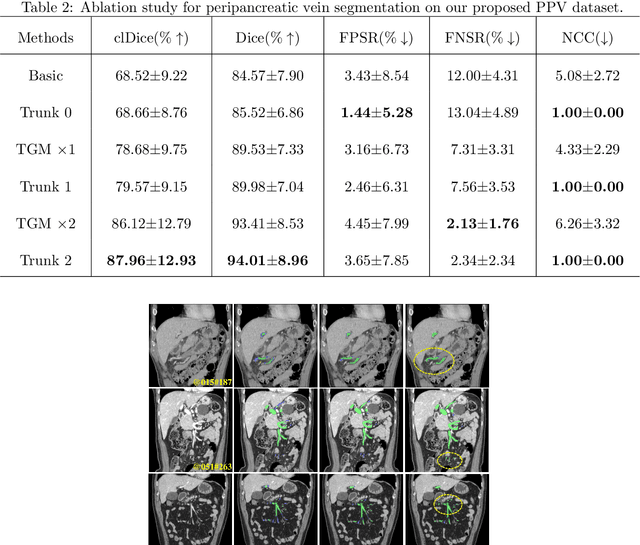
Abstract:Peripancreatic vessel segmentation and anatomical labeling play extremely important roles to assist the early diagnosis, surgery planning and prognosis for patients with pancreatic tumors. However, most current techniques cannot achieve satisfactory segmentation performance for peripancreatic veins and usually make predictions with poor integrity and connectivity. Besides, unsupervised labeling algorithms cannot deal with complex anatomical variation while fully supervised methods require a large number of voxel-wise annotations for training, which is very labor-intensive and time-consuming. To address these problems, we propose our Automated Peripancreatic vEssel Segmentation and lAbeling (APESA) framework, to not only highly improve the segmentation performance for peripancreatic veins, but also efficiently identify the peripancreatic artery branches. There are two core modules in our proposed APESA framework: iterative trunk growth module (ITGM) for vein segmentation and weakly supervised labeling mechanism (WSLM) for artery branch identification. Our proposed ITGM is composed of a series of trunk growth modules, each of which chooses the most reliable trunk of a basic vessel prediction by the largest connected constraint, and seeks for the possible growth branches by branch proposal network. Our designed iterative process guides the raw trunk to be more complete and fully connected. Our proposed WSLM consists of an unsupervised rule-based preprocessing for generating pseudo branch annotations, and an anatomical labeling network to learn the branch distribution voxel by voxel. We achieve Dice of 94.01% for vein segmentation on our collected dataset, which boosts the accuracy by nearly 10% compared with the state-of-the-art methods. Additionally, we also achieve Dice of 97.01% on segmentation and competitive performance on anatomical labeling for peripancreatic arteries.
Exploring Large Context for Cerebral Aneurysm Segmentation
Dec 30, 2020
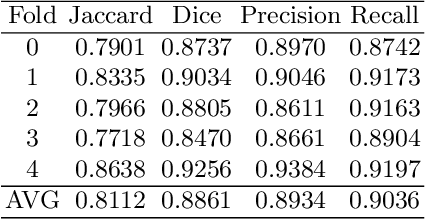
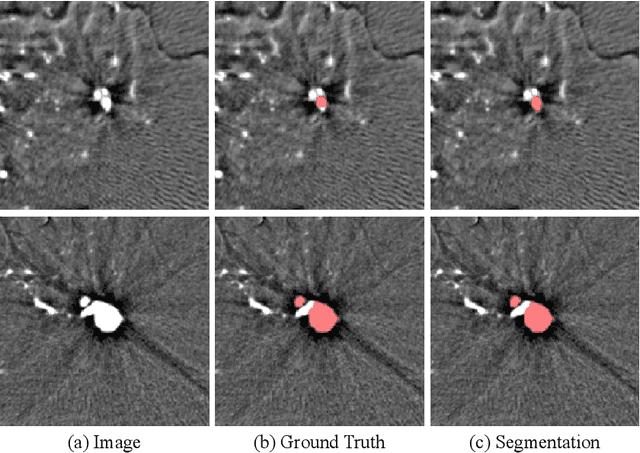
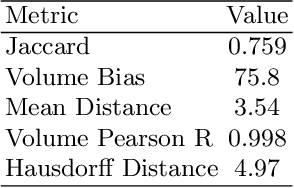
Abstract:Automated segmentation of aneurysms from 3D CT is important for the diagnosis, monitoring, and treatment planning of the cerebral aneurysm disease. This short paper briefly presents the main technique details of the aneurysm segmentation method in the MICCAI 2020 CADA challenge. The main contribution is that we configure the 3D U-Net with a large patch size, which can obtain the large context. Our method ranked second on the MICCAI 2020 CADA testing dataset with an average Jaccard of 0.7593. Our code and trained models are publicly available at \url{https://github.com/JunMa11/CADA2020}.
Towards Efficient COVID-19 CT Annotation: A Benchmark for Lung and Infection Segmentation
Apr 27, 2020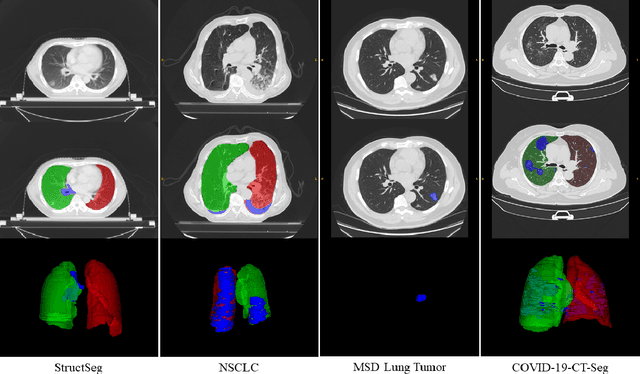
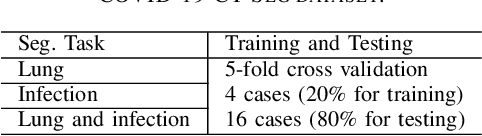
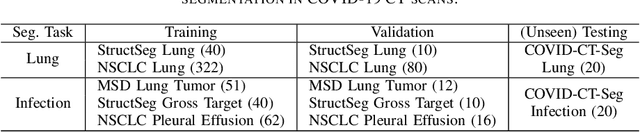
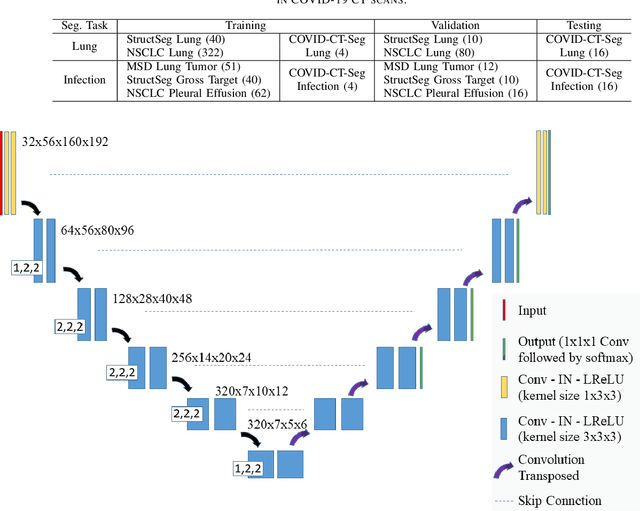
Abstract:Accurate segmentation of lung and infection in COVID-19 CT scans plays an important role in the quantitative management of patients. Most of the existing studies are based on large and private annotated datasets that are impractical to obtain from a single institution, especially when radiologists are busy fighting the coronavirus disease. Furthermore, it is hard to compare current COVID-19 CT segmentation methods as they are developed on different datasets, trained in different settings, and evaluated with different metrics. In this paper, we created a COVID-19 3D CT dataset with 20 cases that contains 1800+ annotated slices and made it publicly available. To promote the development of annotation-efficient deep learning methods, we built three benchmarks for lung and infection segmentation that contain current main research interests, e.g., few-shot learning, domain generalization, and knowledge transfer. For a fair comparison among different segmentation methods, we also provide unified training, validation and testing dataset splits, and evaluation metrics and corresponding code. In addition, we provided more than 40 pre-trained baseline models for the benchmarks, which not only serve as out-of-the-box segmentation tools but also save computational time for researchers who are interested in COVID-19 lung and infection segmentation. To the best of our knowledge, this work presents the largest public annotated COVID-19 CT volume dataset, the first segmentation benchmark, and the most pre-trained models up to now. We hope these resources (\url{https://gitee.com/junma11/COVID-19-CT-Seg-Benchmark}) could advance the development of deep learning methods for COVID-19 CT segmentation with limited data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge