Ziqi Zheng
Zero-shot Robotic Manipulation with Language-guided Instruction and Formal Task Planning
Jan 25, 2025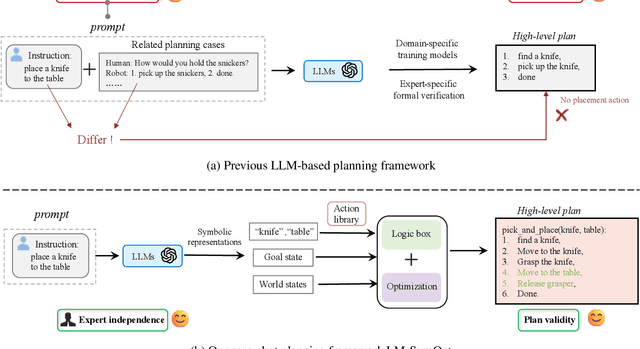
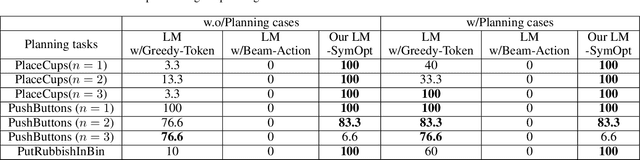
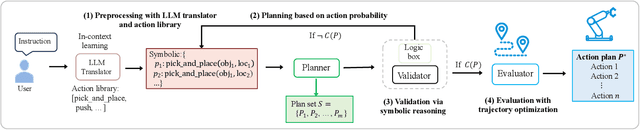
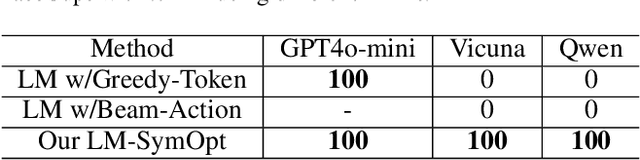
Abstract:Robotic manipulation is often challenging due to the long-horizon tasks and the complex object relationships. A common solution is to develop a task and motion planning framework that integrates planning for high-level task and low-level motion. Recently, inspired by the powerful reasoning ability of Large Language Models (LLMs), LLM-based planning approaches have achieved remarkable progress. However, these methods still heavily rely on expert-specific knowledge, often generating invalid plans for unseen and unfamiliar tasks. To address this issue, we propose an innovative language-guided symbolic task planning (LM-SymOpt) framework with optimization. It is the first expert-free planning framework since we combine the world knowledge from LLMs with formal reasoning, resulting in improved generalization capability to new tasks. Specifically, differ to most existing work, our LM-SymOpt employs LLMs to translate natural language instructions into symbolic representations, thereby representing actions as high-level symbols and reducing the search space for planning. Next, after evaluating the action probability of completing the task using LLMs, a weighted random sampling method is introduced to generate candidate plans. Their feasibility is assessed through symbolic reasoning and their cost efficiency is then evaluated using trajectory optimization for selecting the optimal planning. Our experimental results show that LM-SymOpt outperforms existing LLM-based planning approaches.
Learning to Augment Expressions for Few-shot Fine-grained Facial Expression Recognition
Jan 17, 2020



Abstract:Affective computing and cognitive theory are widely used in modern human-computer interaction scenarios. Human faces, as the most prominent and easily accessible features, have attracted great attention from researchers. Since humans have rich emotions and developed musculature, there exist a lot of fine-grained expressions in real-world applications. However, it is extremely time-consuming to collect and annotate a large number of facial images, of which may even require psychologists to correctly categorize them. To the best of our knowledge, the existing expression datasets are only limited to several basic facial expressions, which are not sufficient to support our ambitions in developing successful human-computer interaction systems. To this end, a novel Fine-grained Facial Expression Database - F2ED is contributed in this paper, and it includes more than 200k images with 54 facial expressions from 119 persons. Considering the phenomenon of uneven data distribution and lack of samples is common in real-world scenarios, we further evaluate several tasks of few-shot expression learning by virtue of our F2ED, which are to recognize the facial expressions given only few training instances. These tasks mimic human performance to learn robust and general representation from few examples. To address such few-shot tasks, we propose a unified task-driven framework - Compositional Generative Adversarial Network (Comp-GAN) learning to synthesize facial images and thus augmenting the instances of few-shot expression classes. Extensive experiments are conducted on F2ED and existing facial expression datasets, i.e., JAFFE and FER2013, to validate the efficacy of our F2ED in pre-training facial expression recognition network and the effectiveness of our proposed approach Comp-GAN to improve the performance of few-shot recognition tasks.
A Fine-Grained Facial Expression Database for End-to-End Multi-Pose Facial Expression Recognition
Jul 25, 2019



Abstract:The recent research of facial expression recognition has made a lot of progress due to the development of deep learning technologies, but some typical challenging problems such as the variety of rich facial expressions and poses are still not resolved. To solve these problems, we develop a new Facial Expression Recognition (FER) framework by involving the facial poses into our image synthesizing and classification process. There are two major novelties in this work. First, we create a new facial expression dataset of more than 200k images with 119 persons, 4 poses and 54 expressions. To our knowledge this is the first dataset to label faces with subtle emotion changes for expression recognition purpose. It is also the first dataset that is large enough to validate the FER task on unbalanced poses, expressions, and zero-shot subject IDs. Second, we propose a facial pose generative adversarial network (FaPE-GAN) to synthesize new facial expression images to augment the data set for training purpose, and then learn a LightCNN based Fa-Net model for expression classification. Finally, we advocate four novel learning tasks on this dataset. The experimental results well validate the effectiveness of the proposed approach.
Multimodal Emotion Recognition for One-Minute-Gradual Emotion Challenge
May 03, 2018



Abstract:The continuous dimensional emotion modelled by arousal and valence can depict complex changes of emotions. In this paper, we present our works on arousal and valence predictions for One-Minute-Gradual (OMG) Emotion Challenge. Multimodal representations are first extracted from videos using a variety of acoustic, video and textual models and support vector machine (SVM) is then used for fusion of multimodal signals to make final predictions. Our solution achieves Concordant Correlation Coefficient (CCC) scores of 0.397 and 0.520 on arousal and valence respectively for the validation dataset, which outperforms the baseline systems with the best CCC scores of 0.15 and 0.23 on arousal and valence by a large margin.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge