Yuping Yan
IRIS: Implicit Reward-Guided Internal Sifting for Mitigating Multimodal Hallucination
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Hallucination remains a fundamental challenge for Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs). While Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) is a key alignment framework, existing approaches often rely heavily on costly external evaluators for scoring or rewriting, incurring off-policy learnability gaps and discretization loss. Due to the lack of access to internal states, such feedback overlooks the fine-grained conflicts between different modalities that lead to hallucinations during generation. To address this issue, we propose IRIS (Implicit Reward-Guided Internal Sifting), which leverages continuous implicit rewards in the native log-probability space to preserve full information density and capture internal modal competition. This on-policy paradigm eliminates learnability gaps by utilizing self-generated preference pairs. By sifting these pairs based on multimodal implicit rewards, IRIS ensures that optimization is driven by signals that directly resolve modal conflicts. Extensive experiments demonstrate that IRIS achieves highly competitive performance on key hallucination benchmarks using only 5.7k samples, without requiring any external feedback during preference alignment. These results confirm that IRIS provides an efficient and principled paradigm for mitigating MLLM hallucinations.
Adversarial Robustness in Zero-Shot Learning:An Empirical Study on Class and Concept-Level Vulnerabilities
Dec 21, 2025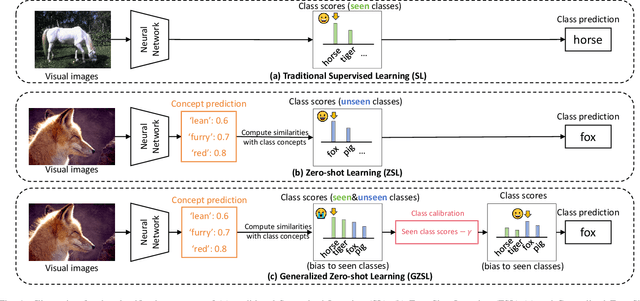

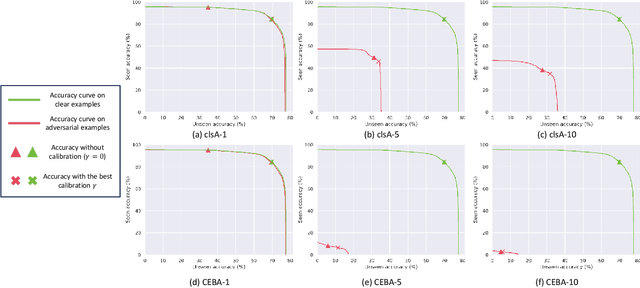
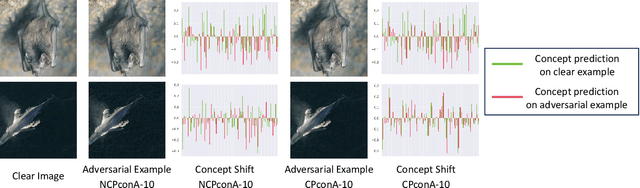
Abstract:Zero-shot Learning (ZSL) aims to enable image classifiers to recognize images from unseen classes that were not included during training. Unlike traditional supervised classification, ZSL typically relies on learning a mapping from visual features to predefined, human-understandable class concepts. While ZSL models promise to improve generalization and interpretability, their robustness under systematic input perturbations remain unclear. In this study, we present an empirical analysis about the robustness of existing ZSL methods at both classlevel and concept-level. Specifically, we successfully disrupted their class prediction by the well-known non-target class attack (clsA). However, in the Generalized Zero-shot Learning (GZSL) setting, we observe that the success of clsA is only at the original best-calibrated point. After the attack, the optimal bestcalibration point shifts, and ZSL models maintain relatively strong performance at other calibration points, indicating that clsA results in a spurious attack success in the GZSL. To address this, we propose the Class-Bias Enhanced Attack (CBEA), which completely eliminates GZSL accuracy across all calibrated points by enhancing the gap between seen and unseen class probabilities.Next, at concept-level attack, we introduce two novel attack modes: Class-Preserving Concept Attack (CPconA) and NonClass-Preserving Concept Attack (NCPconA). Our extensive experiments evaluate three typical ZSL models across various architectures from the past three years and reveal that ZSL models are vulnerable not only to the traditional class attack but also to concept-based attacks. These attacks allow malicious actors to easily manipulate class predictions by erasing or introducing concepts. Our findings highlight a significant performance gap between existing approaches, emphasizing the need for improved adversarial robustness in current ZSL models.
OutSafe-Bench: A Benchmark for Multimodal Offensive Content Detection in Large Language Models
Nov 13, 2025



Abstract:Since Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) are increasingly being integrated into everyday tools and intelligent agents, growing concerns have arisen regarding their possible output of unsafe contents, ranging from toxic language and biased imagery to privacy violations and harmful misinformation. Current safety benchmarks remain highly limited in both modality coverage and performance evaluations, often neglecting the extensive landscape of content safety. In this work, we introduce OutSafe-Bench, the first most comprehensive content safety evaluation test suite designed for the multimodal era. OutSafe-Bench includes a large-scale dataset that spans four modalities, featuring over 18,000 bilingual (Chinese and English) text prompts, 4,500 images, 450 audio clips and 450 videos, all systematically annotated across nine critical content risk categories. In addition to the dataset, we introduce a Multidimensional Cross Risk Score (MCRS), a novel metric designed to model and assess overlapping and correlated content risks across different categories. To ensure fair and robust evaluation, we propose FairScore, an explainable automated multi-reviewer weighted aggregation framework. FairScore selects top-performing models as adaptive juries, thereby mitigating biases from single-model judgments and enhancing overall evaluation reliability. Our evaluation of nine state-of-the-art MLLMs reveals persistent and substantial safety vulnerabilities, underscoring the pressing need for robust safeguards in MLLMs.
Zero-shot Robotic Manipulation with Language-guided Instruction and Formal Task Planning
Jan 25, 2025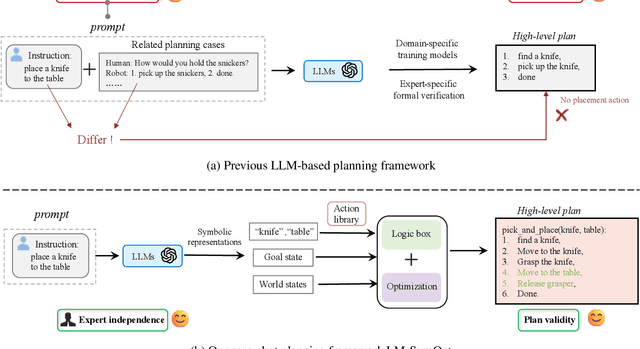
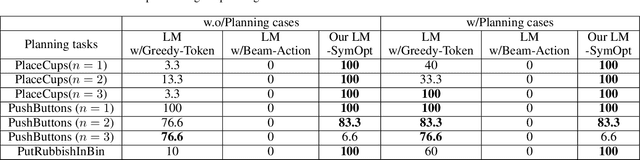
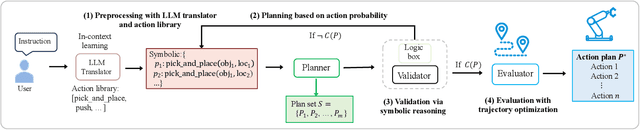
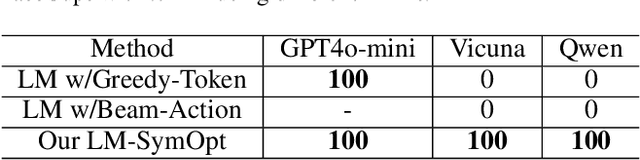
Abstract:Robotic manipulation is often challenging due to the long-horizon tasks and the complex object relationships. A common solution is to develop a task and motion planning framework that integrates planning for high-level task and low-level motion. Recently, inspired by the powerful reasoning ability of Large Language Models (LLMs), LLM-based planning approaches have achieved remarkable progress. However, these methods still heavily rely on expert-specific knowledge, often generating invalid plans for unseen and unfamiliar tasks. To address this issue, we propose an innovative language-guided symbolic task planning (LM-SymOpt) framework with optimization. It is the first expert-free planning framework since we combine the world knowledge from LLMs with formal reasoning, resulting in improved generalization capability to new tasks. Specifically, differ to most existing work, our LM-SymOpt employs LLMs to translate natural language instructions into symbolic representations, thereby representing actions as high-level symbols and reducing the search space for planning. Next, after evaluating the action probability of completing the task using LLMs, a weighted random sampling method is introduced to generate candidate plans. Their feasibility is assessed through symbolic reasoning and their cost efficiency is then evaluated using trajectory optimization for selecting the optimal planning. Our experimental results show that LM-SymOpt outperforms existing LLM-based planning approaches.
A Recurrent Spiking Network with Hierarchical Intrinsic Excitability Modulation for Schema Learning
Jan 24, 2025Abstract:Schema, a form of structured knowledge that promotes transfer learning, is attracting growing attention in both neuroscience and artificial intelligence (AI). Current schema research in neural computation is largely constrained to a single behavioral paradigm and relies heavily on recurrent neural networks (RNNs) which lack the neural plausibility and biological interpretability. To address these limitations, this work first constructs a generalized behavioral paradigm framework for schema learning and introduces three novel cognitive tasks, thus supporting a comprehensive schema exploration. Second, we propose a new model using recurrent spiking neural networks with hierarchical intrinsic excitability modulation (HM-RSNNs). The top level of the model selects excitability properties for task-specific demands, while the bottom level fine-tunes these properties for intra-task problems. Finally, extensive visualization analyses of HM-RSNNs are conducted to showcase their computational advantages, track the intrinsic excitability evolution during schema learning, and examine neural coordination differences across tasks. Biologically inspired lesion studies further uncover task-specific distributions of intrinsic excitability within schemas. Experimental results show that HM-RSNNs significantly outperform RSNN baselines across all tasks and exceed RNNs in three novel cognitive tasks. Additionally, HM-RSNNs offer deeper insights into neural dynamics underlying schema learning.
Heterogeneous Federated Learning with Convolutional and Spiking Neural Networks
Jun 14, 2024Abstract:Federated learning (FL) has emerged as a promising paradigm for training models on decentralized data while safeguarding data privacy. Most existing FL systems, however, assume that all machine learning models are of the same type, although it becomes more likely that different edge devices adopt different types of AI models, including both conventional analogue artificial neural networks (ANNs) and biologically more plausible spiking neural networks (SNNs). This diversity empowers the efficient handling of specific tasks and requirements, showcasing the adaptability and versatility of edge computing platforms. One main challenge of such heterogeneous FL system lies in effectively aggregating models from the local devices in a privacy-preserving manner. To address the above issue, this work benchmarks FL systems containing both convoluntional neural networks (CNNs) and SNNs by comparing various aggregation approaches, including federated CNNs, federated SNNs, federated CNNs for SNNs, federated SNNs for CNNs, and federated CNNs with SNN fusion. Experimental results demonstrate that the CNN-SNN fusion framework exhibits the best performance among the above settings on the MNIST dataset. Additionally, intriguing phenomena of competitive suppression are noted during the convergence process of multi-model FL.
A Secure Federated Data-Driven Evolutionary Multi-objective Optimization Algorithm
Oct 15, 2022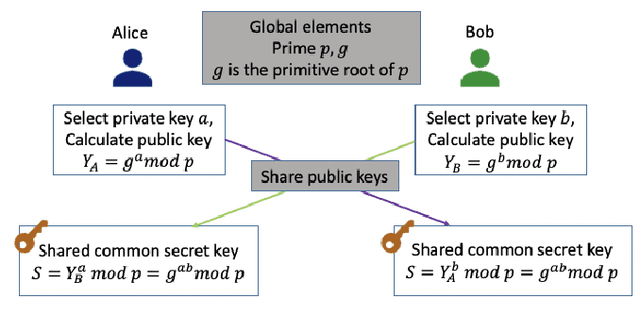
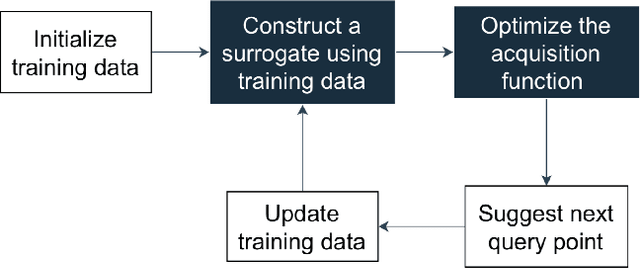
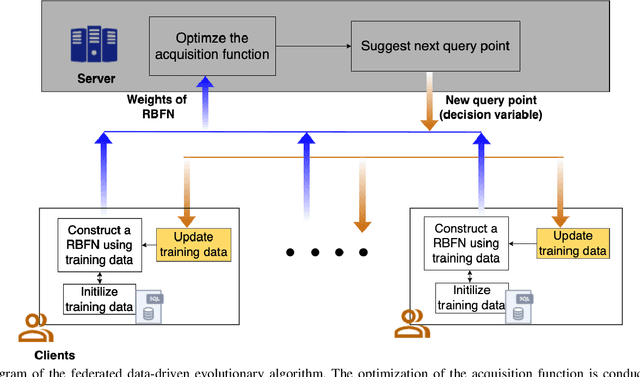
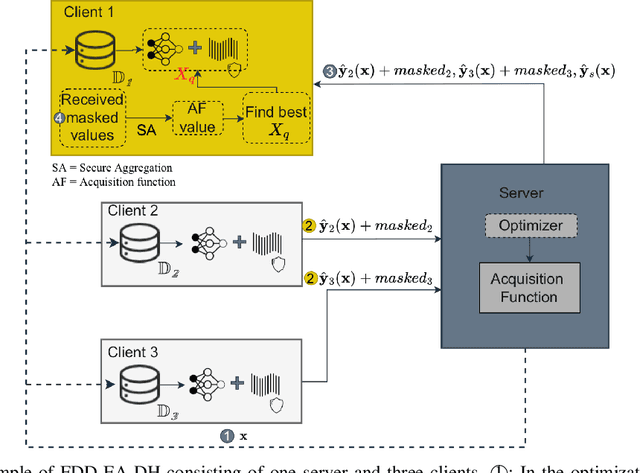
Abstract:Data-driven evolutionary algorithms usually aim to exploit the information behind a limited amount of data to perform optimization, which have proved to be successful in solving many complex real-world optimization problems. However, most data-driven evolutionary algorithms are centralized, causing privacy and security concerns. Existing federated Bayesian algorithms and data-driven evolutionary algorithms mainly protect the raw data on each client. To address this issue, this paper proposes a secure federated data-driven evolutionary multi-objective optimization algorithm to protect both the raw data and the newly infilled solutions obtained by optimizing the acquisition function conducted on the server. We select the query points on a randomly selected client at each round of surrogate update by calculating the acquisition function values of the unobserved points on this client, thereby reducing the risk of leaking the information about the solution to be sampled. In addition, since the predicted objective values of each client may contain sensitive information, we mask the objective values with Diffie-Hellmann-based noise, and then send only the masked objective values of other clients to the selected client via the server. Since the calculation of the acquisition function also requires both the predicted objective value and the uncertainty of the prediction, the predicted mean objective and uncertainty are normalized to reduce the influence of noise. Experimental results on a set of widely used multi-objective optimization benchmarks show that the proposed algorithm can protect privacy and enhance security with only negligible sacrifice in the performance of federated data-driven evolutionary optimization.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge