Zhongjie Lu
Comprehensive and Clinically Accurate Head and Neck Organs at Risk Delineation via Stratified Deep Learning: A Large-scale Multi-Institutional Study
Nov 01, 2021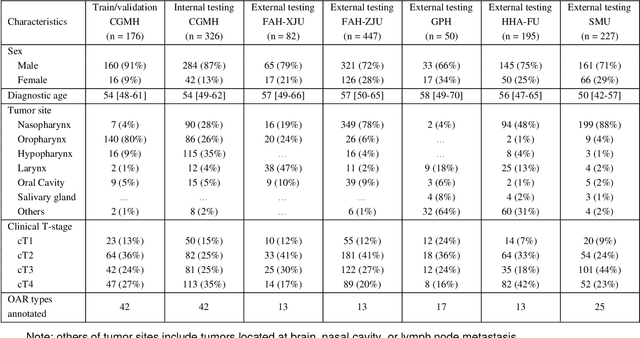
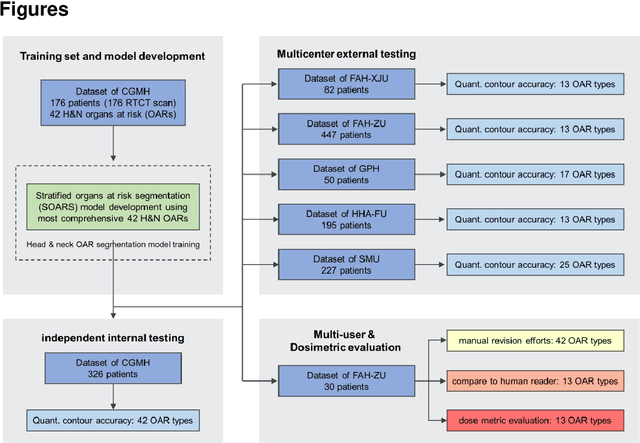
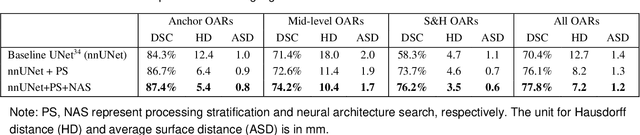
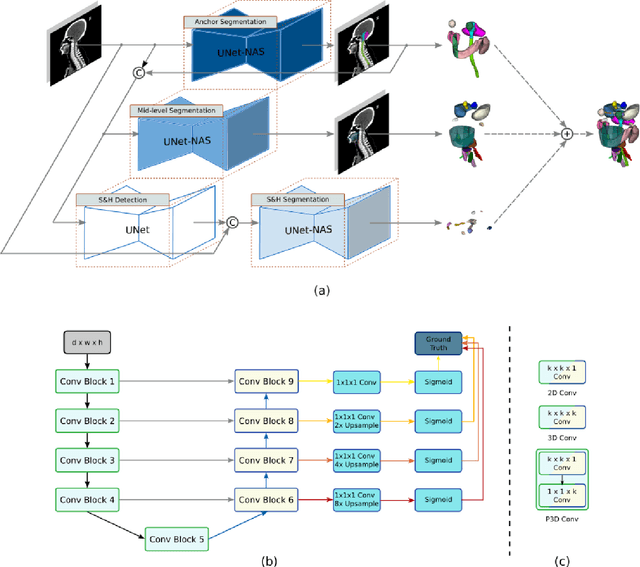
Abstract:Accurate organ at risk (OAR) segmentation is critical to reduce the radiotherapy post-treatment complications. Consensus guidelines recommend a set of more than 40 OARs in the head and neck (H&N) region, however, due to the predictable prohibitive labor-cost of this task, most institutions choose a substantially simplified protocol by delineating a smaller subset of OARs and neglecting the dose distributions associated with other OARs. In this work we propose a novel, automated and highly effective stratified OAR segmentation (SOARS) system using deep learning to precisely delineate a comprehensive set of 42 H&N OARs. SOARS stratifies 42 OARs into anchor, mid-level, and small & hard subcategories, with specifically derived neural network architectures for each category by neural architecture search (NAS) principles. We built SOARS models using 176 training patients in an internal institution and independently evaluated on 1327 external patients across six different institutions. It consistently outperformed other state-of-the-art methods by at least 3-5% in Dice score for each institutional evaluation (up to 36% relative error reduction in other metrics). More importantly, extensive multi-user studies evidently demonstrated that 98% of the SOARS predictions need only very minor or no revisions for direct clinical acceptance (saving 90% radiation oncologists workload), and their segmentation and dosimetric accuracy are within or smaller than the inter-user variation. These findings confirmed the strong clinical applicability of SOARS for the OAR delineation process in H&N cancer radiotherapy workflows, with improved efficiency, comprehensiveness, and quality.
Diagnostic Classification Of Lung Nodules Using 3D Neural Networks
Mar 19, 2018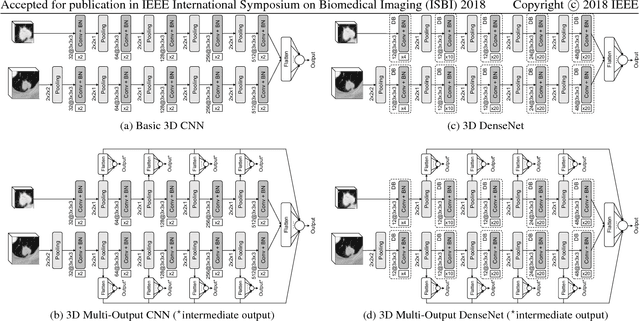
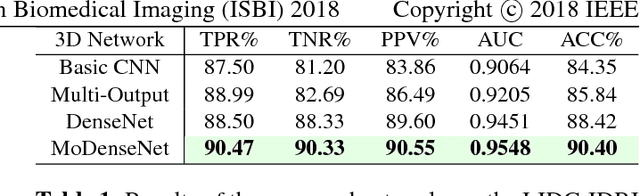
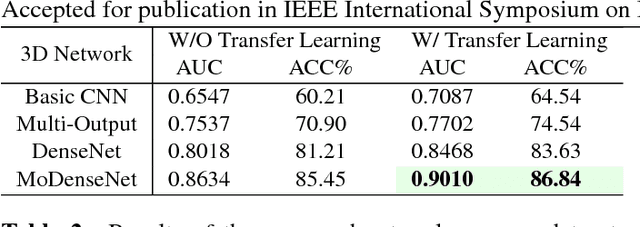
Abstract:Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide. Early diagnosis of pulmonary nodules in Computed Tomography (CT) chest scans provides an opportunity for designing effective treatment and making financial and care plans. In this paper, we consider the problem of diagnostic classification between benign and malignant lung nodules in CT images, which aims to learn a direct mapping from 3D images to class labels. To achieve this goal, four two-pathway Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) are proposed, including a basic 3D CNN, a novel multi-output network, a 3D DenseNet, and an augmented 3D DenseNet with multi-outputs. These four networks are evaluated on the public LIDC-IDRI dataset and outperform most existing methods. In particular, the 3D multi-output DenseNet (MoDenseNet) achieves the state-of-the-art classification accuracy on the task of end-to-end lung nodule diagnosis. In addition, the networks pretrained on the LIDC-IDRI dataset can be further extended to handle smaller datasets using transfer learning. This is demonstrated on our dataset with encouraging prediction accuracy in lung nodule classification.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge