Diagnostic Classification Of Lung Nodules Using 3D Neural Networks
Paper and Code
Mar 19, 2018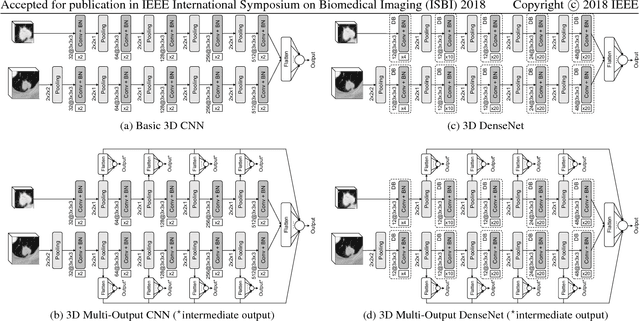
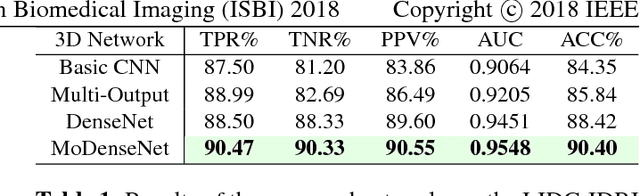
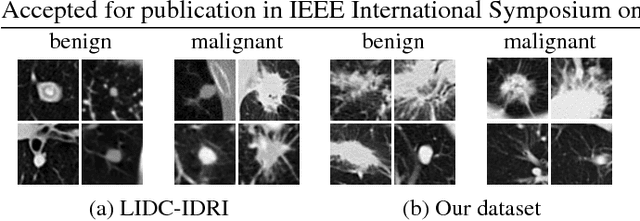
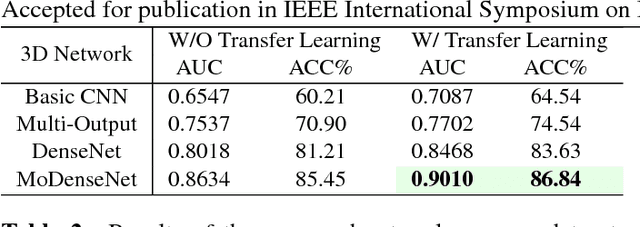
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide. Early diagnosis of pulmonary nodules in Computed Tomography (CT) chest scans provides an opportunity for designing effective treatment and making financial and care plans. In this paper, we consider the problem of diagnostic classification between benign and malignant lung nodules in CT images, which aims to learn a direct mapping from 3D images to class labels. To achieve this goal, four two-pathway Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) are proposed, including a basic 3D CNN, a novel multi-output network, a 3D DenseNet, and an augmented 3D DenseNet with multi-outputs. These four networks are evaluated on the public LIDC-IDRI dataset and outperform most existing methods. In particular, the 3D multi-output DenseNet (MoDenseNet) achieves the state-of-the-art classification accuracy on the task of end-to-end lung nodule diagnosis. In addition, the networks pretrained on the LIDC-IDRI dataset can be further extended to handle smaller datasets using transfer learning. This is demonstrated on our dataset with encouraging prediction accuracy in lung nodule classification.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge