Zhiwei Zha
M2ConceptBase: A Fine-grained Aligned Multi-modal Conceptual Knowledge Base
Dec 16, 2023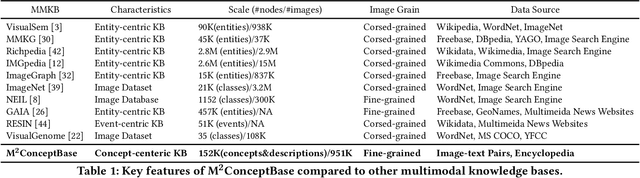
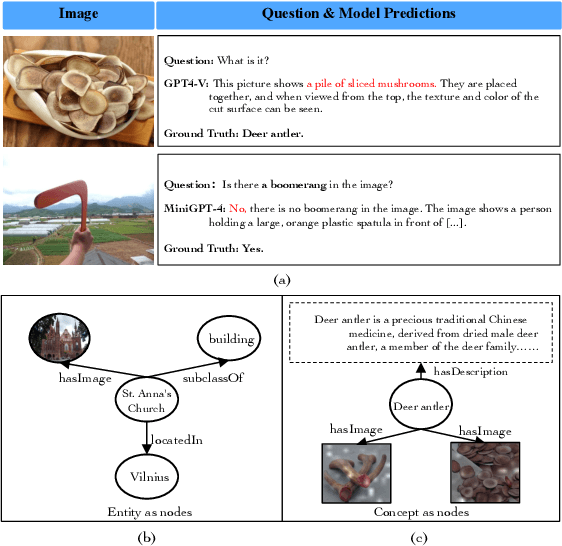
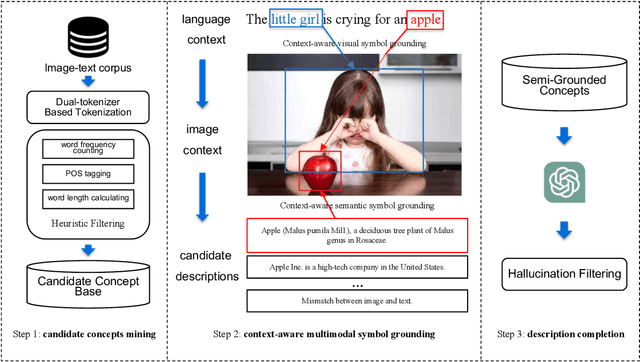
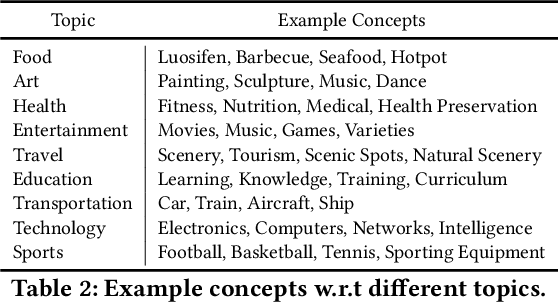
Abstract:Large multi-modal models (LMMs) have demonstrated promising intelligence owing to the rapid development of pre-training techniques. However, their fine-grained cross-modal alignment ability is constrained by the coarse alignment in image-text pairs. This limitation hinders awareness of fine-grained concepts, resulting in sub-optimal performance. In this paper, we propose a multi-modal conceptual knowledge base, named M2ConceptBase, which aims to provide fine-grained alignment between images and concepts. Specifically, M2ConceptBase models concepts as nodes, associating each with relevant images and detailed text, thereby enhancing LMMs' cross-modal alignment with rich conceptual knowledge. To collect concept-image and concept-description alignments, we propose a context-aware multi-modal symbol grounding approach that considers context information in existing large-scale image-text pairs with respect to each concept. A cutting-edge large language model supplements descriptions for concepts not grounded via our symbol grounding approach. Finally, our M2ConceptBase contains more than 951K images and 152K concepts, each associating with an average of 6.27 images and a single detailed description. We conduct experiments on the OK-VQA task, demonstrating that our M2ConceptBase facilitates the model in achieving state-of-the-art performance. Moreover, we construct a comprehensive benchmark to evaluate the concept understanding of LMMs and show that M2ConceptBase could effectively improve LMMs' concept understanding and cross-modal alignment abilities.
JIZHI: A Fast and Cost-Effective Model-As-A-Service System for Web-Scale Online Inference at Baidu
Jun 03, 2021
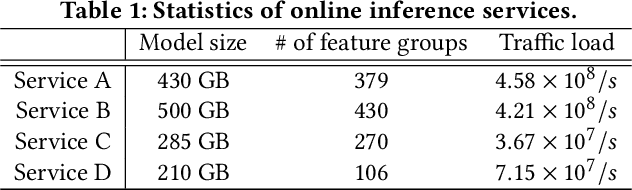
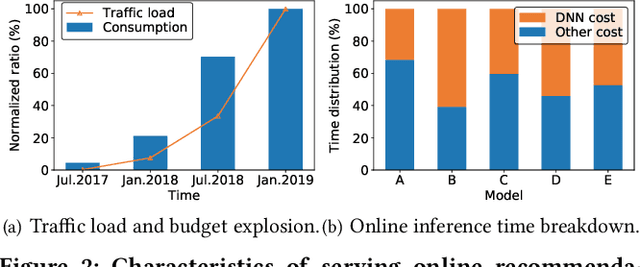
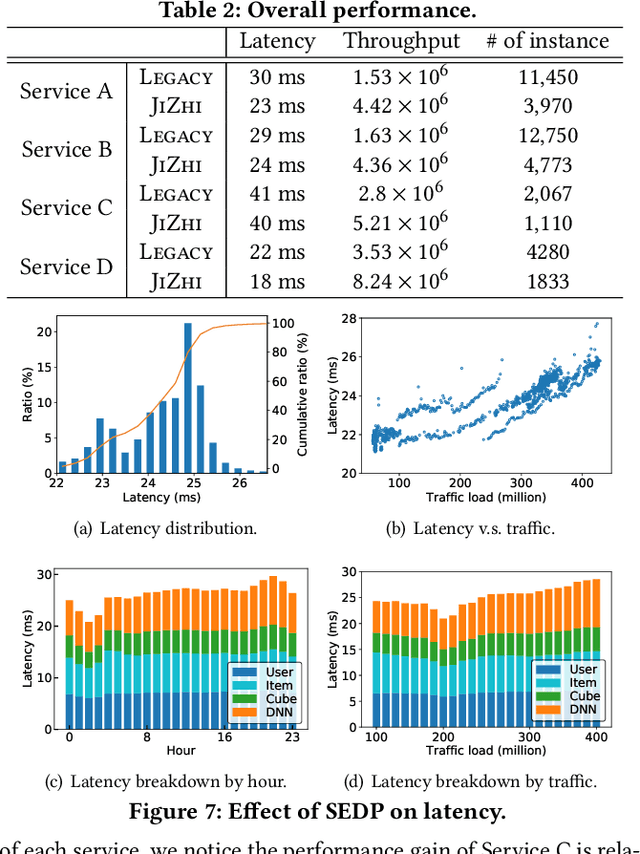
Abstract:In modern internet industries, deep learning based recommender systems have became an indispensable building block for a wide spectrum of applications, such as search engine, news feed, and short video clips. However, it remains challenging to carry the well-trained deep models for online real-time inference serving, with respect to the time-varying web-scale traffics from billions of users, in a cost-effective manner. In this work, we present JIZHI - a Model-as-a-Service system - that per second handles hundreds of millions of online inference requests to huge deep models with more than trillions of sparse parameters, for over twenty real-time recommendation services at Baidu, Inc. In JIZHI, the inference workflow of every recommendation request is transformed to a Staged Event-Driven Pipeline (SEDP), where each node in the pipeline refers to a staged computation or I/O intensive task processor. With traffics of real-time inference requests arrived, each modularized processor can be run in a fully asynchronized way and managed separately. Besides, JIZHI introduces heterogeneous and hierarchical storage to further accelerate the online inference process by reducing unnecessary computations and potential data access latency induced by ultra-sparse model parameters. Moreover, an intelligent resource manager has been deployed to maximize the throughput of JIZHI over the shared infrastructure by searching the optimal resource allocation plan from historical logs and fine-tuning the load shedding policies over intermediate system feedback. Extensive experiments have been done to demonstrate the advantages of JIZHI from the perspectives of end-to-end service latency, system-wide throughput, and resource consumption. JIZHI has helped Baidu saved more than ten million US dollars in hardware and utility costs while handling 200% more traffics without sacrificing inference efficiency.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge