Zhijun Hu
CTP: A hybrid CNN-Transformer-PINN model for ocean front forecasting
May 16, 2025Abstract:This paper proposes CTP, a novel deep learning framework that integrates convolutional neural network(CNN), Transformer architectures, and physics-informed neural network(PINN) for ocean front prediction. Ocean fronts, as dynamic interfaces between distinct water masses, play critical roles in marine biogeochemical and physical processes. Existing methods such as LSTM, ConvLSTM, and AttentionConv often struggle to maintain spatial continuity and physical consistency over multi-step forecasts. CTP addresses these challenges by combining localized spatial encoding, long-range temporal attention, and physical constraint enforcement. Experimental results across south China sea(SCS) and Kuroshio(KUR) regions from 1993 to 2020 demonstrate that CTP achieves state-of-the-art(SOTA) performance in both single-step and multi-step predictions, significantly outperforming baseline models in accuracy, $F_1$ score, and temporal stability.
Digital Avatars: Framework Development and Their Evaluation
Aug 07, 2024


Abstract:We present a novel prompting strategy for artificial intelligence driven digital avatars. To better quantify how our prompting strategy affects anthropomorphic features like humor, authenticity, and favorability we present Crowd Vote - an adaptation of Crowd Score that allows for judges to elect a large language model (LLM) candidate over competitors answering the same or similar prompts. To visualize the responses of our LLM, and the effectiveness of our prompting strategy we propose an end-to-end framework for creating high-fidelity artificial intelligence (AI) driven digital avatars. This pipeline effectively captures an individual's essence for interaction and our streaming algorithm delivers a high-quality digital avatar with real-time audio-video streaming from server to mobile device. Both our visualization tool, and our Crowd Vote metrics demonstrate our AI driven digital avatars have state-of-the-art humor, authenticity, and favorability outperforming all competitors and baselines. In the case of our Donald Trump and Joe Biden avatars, their authenticity and favorability are rated higher than even their real-world equivalents.
* This work was presented during the IJCAI 2024 conference proceedings for demonstrations
Global-Supervised Contrastive Loss and View-Aware-Based Post-Processing for Vehicle Re-Identification
Apr 17, 2022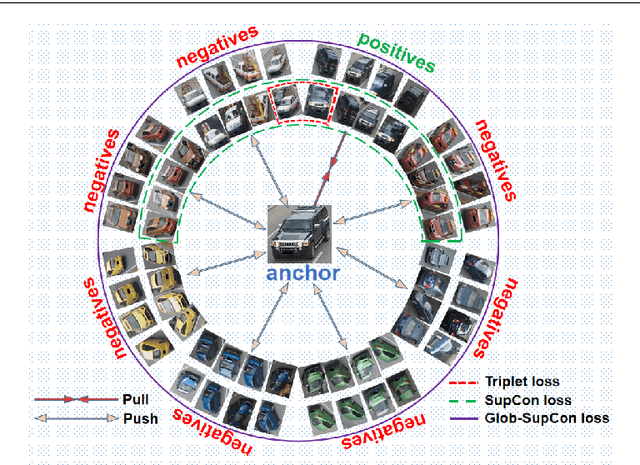
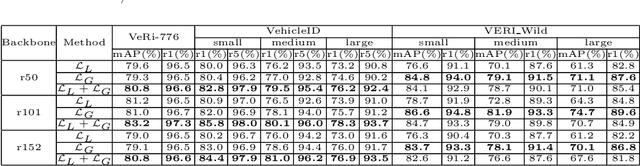
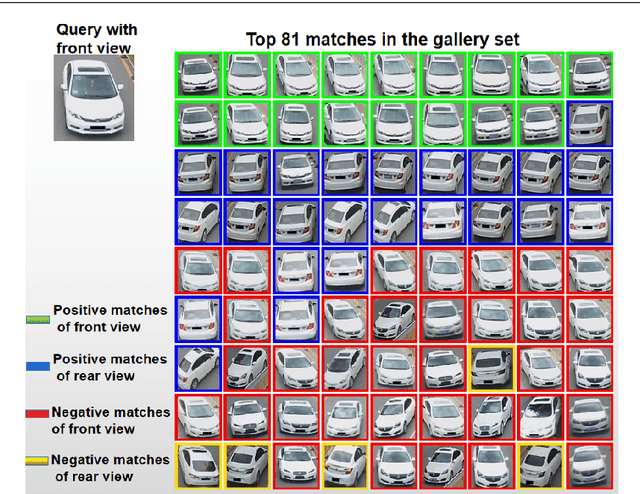
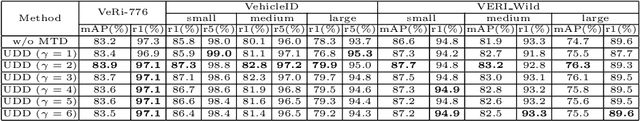
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a Global-Supervised Contrastive loss and a view-aware-based post-processing (VABPP) method for the field of vehicle re-identification. The traditional supervised contrastive loss calculates the distances of features within the batch, so it has the local attribute. While the proposed Global-Supervised Contrastive loss has new properties and has good global attributes, the positive and negative features of each anchor in the training process come from the entire training set. The proposed VABPP method is the first time that the view-aware-based method is used as a post-processing method in the field of vehicle re-identification. The advantages of VABPP are that, first, it is only used during testing and does not affect the training process. Second, as a post-processing method, it can be easily integrated into other trained re-id models. We directly apply the view-pair distance scaling coefficient matrix calculated by the model trained in this paper to another trained re-id model, and the VABPP method greatly improves its performance, which verifies the feasibility of the VABPP method.
Vehicle Re-identification Based on Dual Distance Center Loss
Dec 23, 2020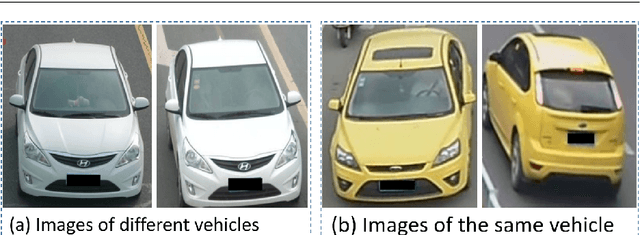
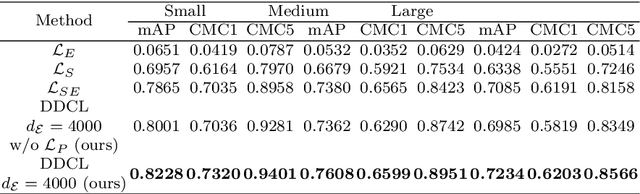
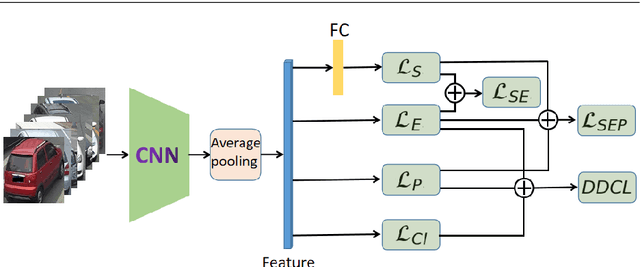
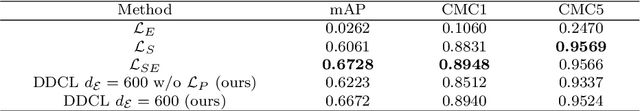
Abstract:Recently, deep learning has been widely used in the field of vehicle re-identification. When training a deep model, softmax loss is usually used as a supervision tool. However, the softmax loss performs well for closed-set tasks, but not very well for open-set tasks. In this paper, we sum up five shortcomings of center loss and solved all of them by proposing a dual distance center loss (DDCL). Especially we solve the shortcoming that center loss must combine with the softmax loss to supervise training the model, which provides us with a new perspective to examine the center loss. In addition, we verify the inconsistency between the proposed DDCL and softmax loss in the feature space, which makes the center loss no longer be limited by the softmax loss in the feature space after removing the softmax loss. To be specifically, we add the Pearson distance on the basis of the Euclidean distance to the same center, which makes all features of the same class be confined to the intersection of a hypersphere and a hypercube in the feature space. The proposed Pearson distance strengthens the intra-class compactness of the center loss and enhances the generalization ability of center loss. Moreover, by designing a Euclidean distance threshold between all center pairs, which not only strengthens the inter-class separability of center loss, but also makes the center loss (or DDCL) works well without the combination of softmax loss. We apply DDCL in the field of vehicle re-identification named VeRi-776 dataset and VehicleID dataset. And in order to verify its good generalization ability, we also verify it in two datasets commonly used in the field of person re-identification named MSMT17 dataset and Market1501 dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge