Zhiheng Yin
Meta Clustering Learning for Large-scale Unsupervised Person Re-identification
Nov 19, 2021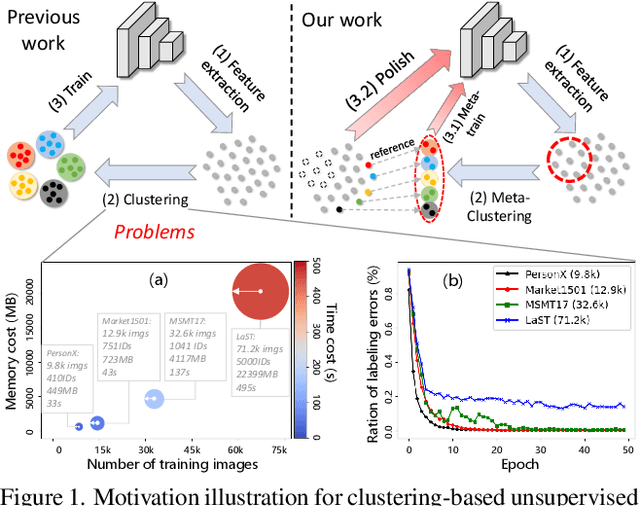


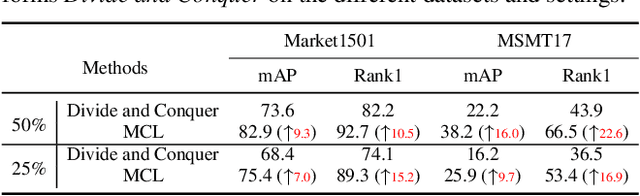
Abstract:Unsupervised Person Re-identification (U-ReID) with pseudo labeling recently reaches a competitive performance compared to fully-supervised ReID methods based on modern clustering algorithms. However, such clustering-based scheme becomes computationally prohibitive for large-scale datasets. How to efficiently leverage endless unlabeled data with limited computing resources for better U-ReID is under-explored. In this paper, we make the first attempt to the large-scale U-ReID and propose a "small data for big task" paradigm dubbed Meta Clustering Learning (MCL). MCL only pseudo-labels a subset of the entire unlabeled data via clustering to save computing for the first-phase training. After that, the learned cluster centroids, termed as meta-prototypes in our MCL, are regarded as a proxy annotator to softly annotate the rest unlabeled data for further polishing the model. To alleviate the potential noisy labeling issue in the polishment phase, we enforce two well-designed loss constraints to promise intra-identity consistency and inter-identity strong correlation. For multiple widely-used U-ReID benchmarks, our method significantly saves computational cost while achieving a comparable or even better performance compared to prior works.
Cloth-Changing Person Re-identification from A Single Image with Gait Prediction and Regularization
Apr 18, 2021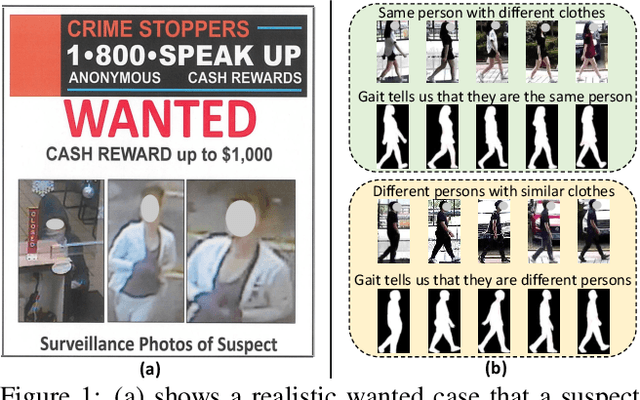


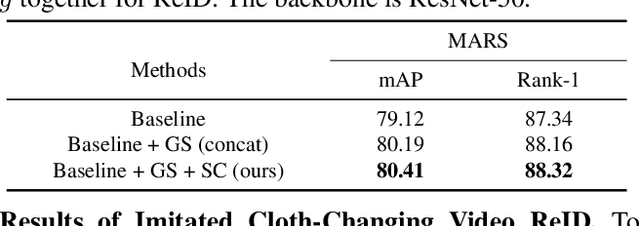
Abstract:Cloth-Changing person re-identification (CC-ReID) aims at matching the same person across different locations over a long-duration, e.g., over days, and therefore inevitably meets challenge of changing clothing. In this paper, we focus on handling well the CC-ReID problem under a more challenging setting, i.e., just from a single image, which enables high-efficiency and latency-free pedestrian identify for real-time surveillance applications. Specifically, we introduce Gait recognition as an auxiliary task to drive the Image ReID model to learn cloth-agnostic representations by leveraging personal unique and cloth-independent gait information, we name this framework as GI-ReID. GI-ReID adopts a two-stream architecture that consists of a image ReID-Stream and an auxiliary gait recognition stream (Gait-Stream). The Gait-Stream, that is discarded in the inference for high computational efficiency, acts as a regulator to encourage the ReID-Stream to capture cloth-invariant biometric motion features during the training. To get temporal continuous motion cues from a single image, we design a Gait Sequence Prediction (GSP) module for Gait-Stream to enrich gait information. Finally, a high-level semantics consistency over two streams is enforced for effective knowledge regularization. Experiments on multiple image-based Cloth-Changing ReID benchmarks, e.g., LTCC, PRCC, Real28, and VC-Clothes, demonstrate that GI-ReID performs favorably against the state-of-the-arts. Codes are available at https://github.com/jinx-USTC/GI-ReID.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge