Zhibin Gao
Generative AI for Lyapunov Optimization Theory in UAV-based Low-Altitude Economy Networking
Jan 27, 2025



Abstract:Lyapunov optimization theory has recently emerged as a powerful mathematical framework for solving complex stochastic optimization problems by transforming long-term objectives into a sequence of real-time short-term decisions while ensuring system stability. This theory is particularly valuable in unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV)-based low-altitude economy (LAE) networking scenarios, where it could effectively address inherent challenges of dynamic network conditions, multiple optimization objectives, and stability requirements. Recently, generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) has garnered significant attention for its unprecedented capability to generate diverse digital content. Extending beyond content generation, in this paper, we propose a framework integrating generative diffusion models with reinforcement learning to address Lyapunov optimization problems in UAV-based LAE networking. We begin by introducing the fundamentals of Lyapunov optimization theory and analyzing the limitations of both conventional methods and traditional AI-enabled approaches. We then examine various GenAI models and comprehensively analyze their potential contributions to Lyapunov optimization. Subsequently, we develop a Lyapunov-guided generative diffusion model-based reinforcement learning framework and validate its effectiveness through a UAV-based LAE networking case study. Finally, we outline several directions for future research.
Joint Model Caching and Resource Allocation in Generative AI-Enabled Wireless Edge Networks
Nov 13, 2024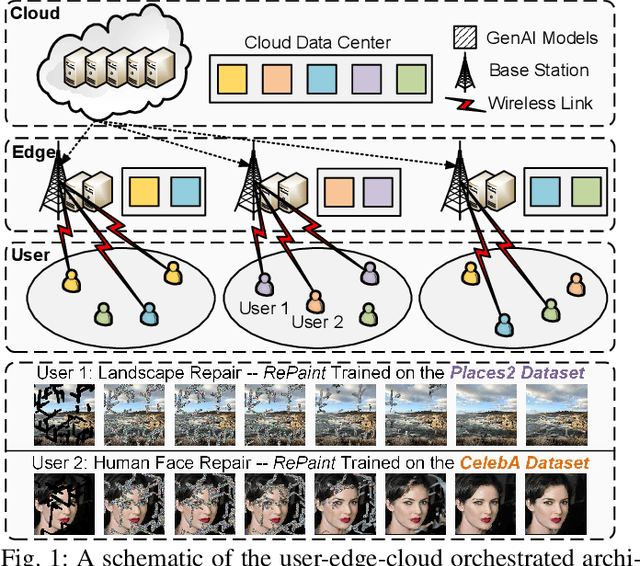
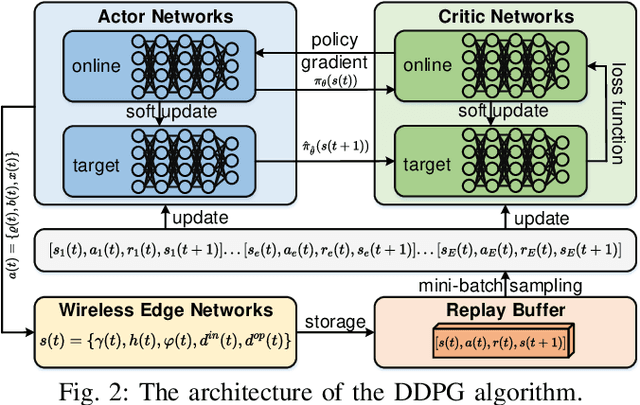
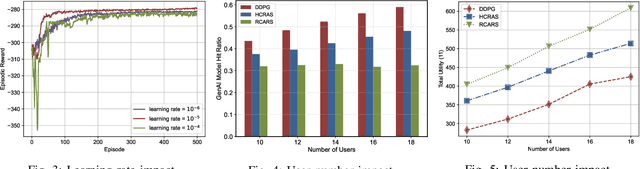
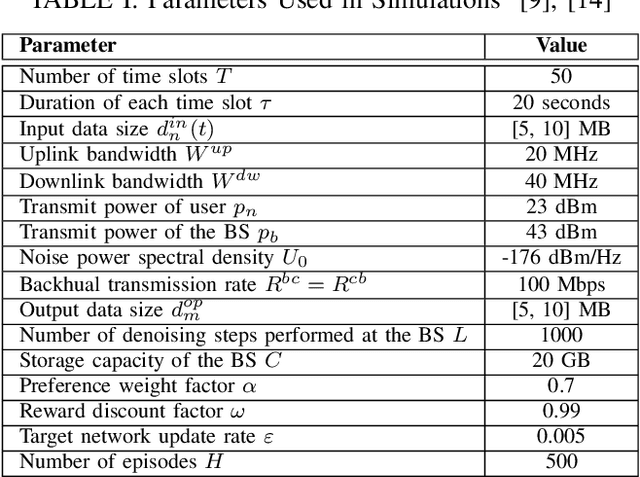
Abstract:With the rapid advancement of artificial intelligence (AI), generative AI (GenAI) has emerged as a transformative tool, enabling customized and personalized AI-generated content (AIGC) services. However, GenAI models with billions of parameters require substantial memory capacity and computational power for deployment and execution, presenting significant challenges to resource-limited edge networks. In this paper, we address the joint model caching and resource allocation problem in GenAI-enabled wireless edge networks. Our objective is to balance the trade-off between delivering high-quality AIGC and minimizing the delay in AIGC service provisioning. To tackle this problem, we employ a deep deterministic policy gradient (DDPG)-based reinforcement learning approach, capable of efficiently determining optimal model caching and resource allocation decisions for AIGC services in response to user mobility and time-varying channel conditions. Numerical results demonstrate that DDPG achieves a higher model hit ratio and provides superior-quality, lower-latency AIGC services compared to other benchmark solutions.
DNN Partitioning, Task Offloading, and Resource Allocation in Dynamic Vehicular Networks: A Lyapunov-Guided Diffusion-Based Reinforcement Learning Approach
Jun 11, 2024



Abstract:The rapid advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has introduced Deep Neural Network (DNN)-based tasks to the ecosystem of vehicular networks. These tasks are often computation-intensive, requiring substantial computation resources, which are beyond the capability of a single vehicle. To address this challenge, Vehicular Edge Computing (VEC) has emerged as a solution, offering computing services for DNN-based tasks through resource pooling via Vehicle-to-Vehicle/Infrastructure (V2V/V2I) communications. In this paper, we formulate the problem of joint DNN partitioning, task offloading, and resource allocation in VEC as a dynamic long-term optimization. Our objective is to minimize the DNN-based task completion time while guaranteeing the system stability over time. To this end, we first leverage a Lyapunov optimization technique to decouple the original long-term optimization with stability constraints into a per-slot deterministic problem. Afterwards, we propose a Multi-Agent Diffusion-based Deep Reinforcement Learning (MAD2RL) algorithm, incorporating the innovative use of diffusion models to determine the optimal DNN partitioning and task offloading decisions. Furthermore, we integrate convex optimization techniques into MAD2RL as a subroutine to allocate computation resources, enhancing the learning efficiency. Through simulations under real-world movement traces of vehicles, we demonstrate the superior performance of our proposed algorithm compared to existing benchmark solutions.
GA-DRL: Graph Neural Network-Augmented Deep Reinforcement Learning for DAG Task Scheduling over Dynamic Vehicular Clouds
Jul 03, 2023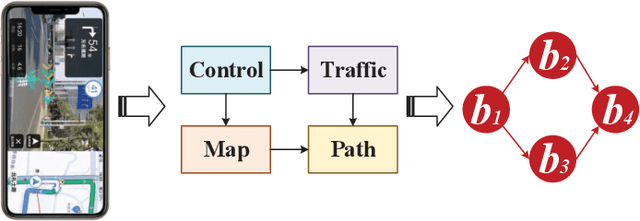
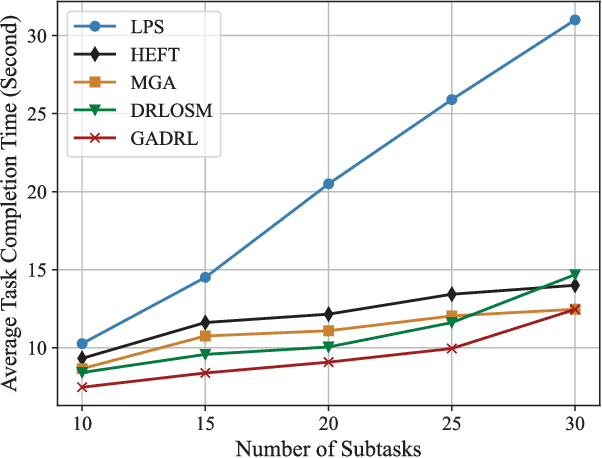
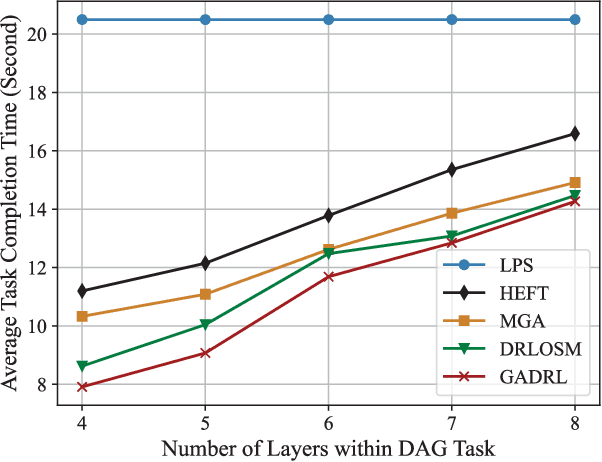
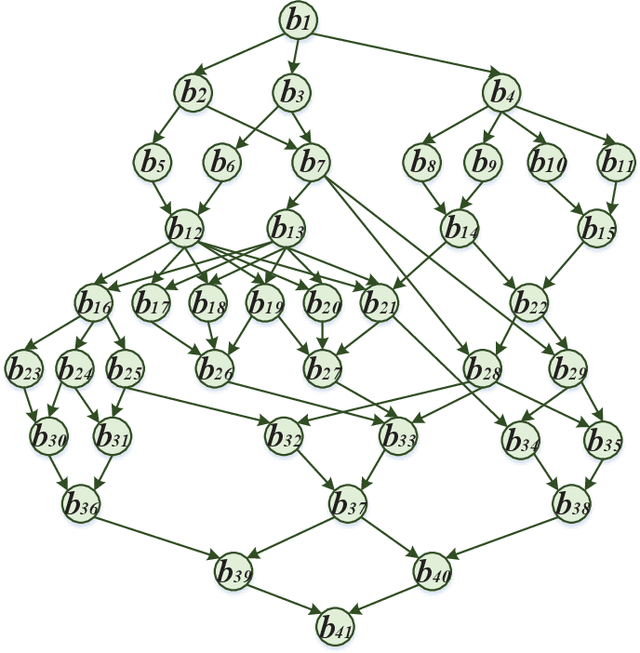
Abstract:Vehicular clouds (VCs) are modern platforms for processing of computation-intensive tasks over vehicles. Such tasks are often represented as directed acyclic graphs (DAGs) consisting of interdependent vertices/subtasks and directed edges. In this paper, we propose a graph neural network-augmented deep reinforcement learning scheme (GA-DRL) for scheduling DAG tasks over dynamic VCs. In doing so, we first model the VC-assisted DAG task scheduling as a Markov decision process. We then adopt a multi-head graph attention network (GAT) to extract the features of DAG subtasks. Our developed GAT enables a two-way aggregation of the topological information in a DAG task by simultaneously considering predecessors and successors of each subtask. We further introduce non-uniform DAG neighborhood sampling through codifying the scheduling priority of different subtasks, which makes our developed GAT generalizable to completely unseen DAG task topologies. Finally, we augment GAT into a double deep Q-network learning module to conduct subtask-to-vehicle assignment according to the extracted features of subtasks, while considering the dynamics and heterogeneity of the vehicles in VCs. Through simulating various DAG tasks under real-world movement traces of vehicles, we demonstrate that GA-DRL outperforms existing benchmarks in terms of DAG task completion time.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge